Abstract
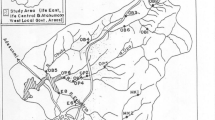
The bottom fauna of 5 tributaries of the planned Dobczyce reservoir and the River Raba below the dam was investigated in the preimpoundment period (1983–84). The abundance of macrofauna varied between 46 taxa (Wolnica stream) and 66 taxa (Brzezówka stream). Each station showed individual taxa composition except for the RABA-u and RABA-d (84% similarity). On the basis of 7 different biological indices the stations were divided into 3 categories: unpolluted (Brzezówka), slightly polluted (Bulinka, Trzemésnia and both Raba stations), and moderately polluted (Wolnica). Most sensitive to chemical pollution was the BIOTIC-index. The combination of environmental variables was used to predict biological indices. The most significant relationship (P < 0.01, R 2 = 0.71) was found between the BIOTIC-index and physico-chemical factors. Some problems in the application of indices (sampling, indicator organisms and interpretation of the results) are discussed and local adaptations of methods used are recommended.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirowicz, A., 1988. Environmental characteristics of affluents of the Dobczyce Reservoir (Southern Poland) in the preimpoundment period (1983–1985). 2. Periphyton. Acta Hydrobiol. 30: 297–304.
Armitage, P. D., D. Moss, J. F. Wright & M. T. Furse, 1983. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Wat. Res. 17: 333–347.
Balloch, D., C. E. Davies & F. H. Jones, 1976. Biological assessment of water quality in the three British rivers: the North Esk (Scotland), the Ivel (England) and the Taf (Wales). Wat. Pollut. Contr. 75: 92–110.
Bloesch, J., 1977. Bodenfaunistische Untersuchungen in Aare und Rhein. I. Teil, Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 39: 45–68.
Bloesch, J., 1980. Bodenfaunistische Untersuchungen in Aare und Rhein. II. Teil, Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 42: 285–308.
Braukmann, U., 1987. Zoozönologische und saprobiologis- the Beiträge zu einer allgemeinen regionalen Bachtypologie. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih., Ergebn. Limnol. 26: 1–355.
Chandler, J. R., 1970. A biological approach to water quality management. Wat. Pollut. Contr. Fed. 42: 415–422.
De Pauw, N. & G. Vanhooren, 1983. Method for biological quality assessment of watercourses in Belgium. Hydrobiologia 100: 153–168.
Draper, N. R. & H. Smith, 1966. Applied regression analysis. Wiley, New York.
Elliott, J. M., 1977. Some methods for the statistical analysis of samples of benthic invertebrates. Fresh. Biol. Assoc. Sci. Publ. No. 25 (2nd edn), Ambleside, 156 pp.
Frutiger, A., 1985. The production quotient PQ: A new approach for quality determination of slightly to moderately polluted running waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 104: 513–526.
Furse, M. T., D. Moss, J. F. Wright & P. D. Armitage, 1984. The influence of seasonal and taxonomic factors on the ordination and classification of running-water sites in Great Britain and on the prediction of their macroinvertebrate communities. Fresh. Biol. 14: 257–280.
Ghetti, P. F. & G. Bonazzi, 1977. A comparison between various criteria for the interpretation of biological data in the analysis of the quality of running waters. War. Res. 11: 819–831.
Ghetti, P. F. & G. Bonazzi, 1980. 3rd Technical Seminar. Biological Water Assessment Methods. Parma, October 1978. Final Report. 2. Published for the Commission of the European Communities: 1–39.
Girton, C., 1980. Ecological studies on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in relation to their use in river water quality surveillance. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis. University of Aston in Birmingham.
Gore, J. A. & R. D. Judy Jr., 1981. Predictive models of benthic macroinvertebrate density for use in instream flow studies and regulated flow management. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 38: 1363–1370.
Hellawell, J. M., 1977. Change in natural and managed ecosystems: detection, measurement and assessment. Proc. r. Soc. Lond. B. 197: 21–57.
Hildrew, A. B., C. R. Townsend & J. Henderson, 1980. Interactions between larval size, microdistribution and substrate in the stoneflies of an iron rich stream. Oikos 35: 387–396.
Jaccard, P., 1902. Lois de distribution florale dans zone alpine. Bull. Soc. Vaudoise sci. Nat. 38: 69–130.
Jelonek, M. & J. Starmach, 1988. Environmental characteristics of affluents of the Dobczyce Reservoir (Southern Poland) in the preimpoundment period (1983–1985). 3. Ichthyofauna. Acta Hydrobiol. 30: 305–316.
Klecka, W. R., 1975. ‘Discriminant analysis’, in Nie, N. H., Hull, C. H., Jenkins, J. G., Steinbrenner, K., Bent, D. H. (Eds), SPSS. Statistical Package for Social Sciences, McCraw-Hill, New York: 434–467.
Lang, C., G. L'Eplattenier & O. Reymond, 1989. Water quality in rivers of western Switzerland: Application of an adaptable index based on benthic invertebrates. Aquat. Sci. 51: 224–234.
Lienert, G. A., 1973. Verteilungsfreie Methoden in der Biostatistik. Band 1, Verlag Anton Hain, Meisenheim am Glan.
Lowrance, R., R. A. Leonard, 1988. Stream nutrient dynamics on coastal plain watersheds. J. envir. Qual. 17: 734–740.
Mazurkiewicz, G., 1988. Environmental characteristics of affluents of the Dobczyce Reservoir (Southern Poland) in the preimpoundment period (1983–1985). 1. Some physicochemical indices. Acta Hydrobiol. 30: 287–296.
Morin, A., 1985. Variability of density estimates and the optimization of sampling programs for stream benthos. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 42: 1530–1534.
Murphy, P. M., 1978. The temporal variability in biotic indices. Envir. Pollut. 17: 227–236.
Needham, P. R. & R. L. Usinger, 1956. Variability in the macrofauna of a single riffle in Prosser Creek. California. as indicated by the Surber sampler. Hilgardia 24: 383–409.
Pantle, R. & H. Buck, 1955. Die biologische Überwachung der Gewässer und die Darstellung der Ergebnisse. GWF 96/18: 604.
Perret, P., 1977. Zustand der schweizerischen Fliessgewasser in den Jahren 1974/75 (Projekt Mapos). Eidg. Amt für Umweltschutz and EAWAG.
Resh, V. H., 1979. Sampling variability and life history features: basic considerations in the design of aquatic insect studies. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 36: 290–311.
Resh, V. H. & D. G. Price, 1984. Sequential sampling: a costeffective approach for monitoring benthic macroinvertebrates in environmental impact assessments. Envir. Manage 8: 75–80.
Sladeček, V., 1973. System of water quality from ecological point of view. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 7: 1–218.
Stachowicz, K., 1986. Surface run-off pollution of agricultural basins in the protective zone of the Dobczyce dam reservoir (the Carpathian Plateau — Poland). Acta Hydrobiol. 28: 21–42.
Tolkamp, H. H., 1984. Biological assessment of water quality in running water using macroinvertebrates: a case study in Limburg, The Netherlands. War. Sci. Tech. 17: 867–878.
Turoboyski, L., 1973. The indicator organisms and their ecological variability. Acta Hydrobiol. 15: 259–274.
Turoboyski, L., 1979. Technical hydrobiology. PWN, Warszawa: 444 pp.
Verneaux, J. & G. Tuffery, 1967. Une methode zoologique practique de determination de la qualite biologique des eaux courantes. Ann. scient. Univ. Besancon 3: 79–90.
Woodiwiss, F. S., 1964. The biological system of stream classification used by Trent River Board. Chemistry and Industry: 443–447.
Woodiwiss, F. S., 1980. Biological monitoring of surface water quality. Summary report. Commission of the European Communities. Environment and consumer protection service: 45 pp.
Wright, J. F., P. D. Armitage & M. T. Fursez, 1984. A preliminary classification of running-water sites in Great Britain based on macroinvertebrate species and the prediction of community type using environmental data. Fresh. Biol. 14: 221–256.
Wright, J. F., P. D. Armitage, M. T. Furse & D. Moss, 1988. A new approach to the biological surveyllance of river quality using macroinvertebrates. Verh. Int. Ver. f. Th. and Angew. Limnol. 23: 1548–1552.
Wright, J. F., P. D. Armitage, M. T. Furse & D. Moss, 1989. Prediction of invertebrates using stream measurements. Regulated rivers: Res. and Manag. 4: 147–155.
Wróbel, S., 1980. The Dobczyce dam water reservoir and its protection. Zesz. Probl. Post. Nauk Roln. 235: 205–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fleituch, T.M. Evaluation of the water quality of future tributaries to the planned Dobczyce reservoir (Poland) using macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 237, 103–116 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016035
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016035