Abstract
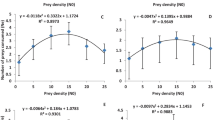
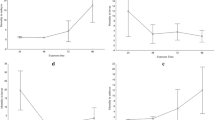
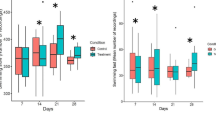
The cladoceran Daphnia ambigua was exposed to both the insecticide carbaryl and the kairomone released from the predator Chaoborus simultaneously, and its morphological changes were analyzed. Daphnia developed helmets in response to the kairomone, but not in response to carbaryl at low (sublethal) concentrations (1–3 µg 1−1). However, the carbaryl enhanced the development of high helmets and prolonged the maintenance period of the helmets over instars in the presence of the kairomone. These results suggest that sublethal concentrations of the insecticide alter predator-prey interactions by inducing helmet formation in Daphnia, which may reduce vulnerability of the Daphnia to predation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, W. L., Jr., T. Eisner & R. H. Whittaker, 1970. Allomones and kairomones: transspecific chemical messengers. BioScience 20: 21–22.
Dodson, S. I., 1988. Cyclomorphosis in Daphnia galeata mendotae Birge and D. retrocurva Forbes as a predator-induced response. Freshwat. Biol. 19: 109–114.
Dodson, S. I., 1989. Predator-induced reaction norms. BioScience 39: 447–452.
Dodson, S. I., T. Hanazato & P. Gorski, 1994. Behavioral responses of Daphnia pulex exposed to carbaryl and Chaoborus kairomone. Envir. Toxicol. Chem., in press.
Hanazato, T., l990. Induction of helmet development by a Chaoborus factor in Daphnia ambigua during juvenile stages. J. Plankton Res. 12: 1287–1294.
Hanazato, T., 1991a. Pesticides as chemical agents inducing helmet formation in Daphnia ambigua. Freshwat. Biol. 26: 419–424.
Hanazato, T., 1991b. Induction of development of high helmets by a Chaoborus-released chemical in Daphnia galeata. Arch. Hydrobiol. 122: 167–175.
Hanazato, T., 1991c. Effects of a Chaoborus-released chemical on Daphnia ambigua: Reduction in the tolerance of the Daphnia to summer water temperature. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36: 165–171.
Hanazato, T., 1991d. Influence of food density on the effects of Chaoborus-released chemical on Daphnia ambigua. Freshwat. Biol. 25: 477–483.
Hanazato, T., 1991e. Effects of long- and short-term exposure to carbaryl on survival, growth and reproduction of Daphnia ambigua. Envir. Pollut. 74: 139–148.
Hanazato, T., 1992a. Insecticide inducing helmet development in Daphnia ambigua. Arch. Hydrobiol. 123: 451–457.
Hanazato, T., 1992b. Direct and indirect effects of low-oxygen layers on lake zooplankton communities. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 35: 87–98.
Hanazato, T. & S. I. Dodson, 1992. Complex effects of a kairomone of Chaoborus and an insecticide on Daphnia pulex. J. Plankton Res. 14: 1743–1755.
Hanazato, T. & S. I. Dodson, 1993. Morphological responses of four species of cyclomorphic Daphnia to a short-term exposure to the insecticide carbaryl. J. Plankton Res. 15: 1087–1095.
Hanazato, T. & T. Ooi, 1992. Morphological responses of Daphnia ambigua to different concentrations of a chemical extract from Chaoborus flavicans. Freshwat. Biol. 27: 379–385.
Havel, J. E., 1987. Predator-induced defenses: A review. In W. C. Kerfoot & A. Sih (eds), Predation: Direct and indirect impacts on aquatic communities. New England Press, Hanover: 263–278.
Havel, J. E. & S. I. Dodson, 1984. Chaoborus predation on typical and spined morphs of Daphnia pulex: behavioral observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 487–494.
Hebert, P. D. N. & D. W. Grewe, 1985. Chaoborus-induced shifts in the morphology of Daphnia ambigua. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 1291–1297.
Krueger, D. A. & S. I. Dodson, 1981. Embryological induction and predation ecology in Daphnia pulex. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26: 219–223.
Mort, M. A., 1986. Chaoborus predation and the function of phenotypic variation in Daphnia. Hydrobiologia 133: 39–44.
Parejko, K., 1990. Mochlonyx predation on typical and spined juvenile Daphnia. Freshwat. Biol. 25: 211–217.
Threlkeld, S. T., 1979. Estimating cladoceran birth rates: the importance of egg mortality and the egg age distribution. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 601–612.
Tollrian, R., 1990. Predator-induced helmet formation in Daphnia cucullata (SARS). Arch. Hydrobiol. 119: 191–196.
Vuorinen, I., M. Ketola & M. Walls, 1989. Defensive spine formation in Daphnia pulex Leydig and induction by Chaoborus crystallinus De Geer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 245–248.
Watanabe, A., 1960. List of algal strains in collection at the Institute of Applied Microbiology, University of Tokyo. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 6: 238–292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanazato, T. Combined effect of the insecticide carbaryl and the Chaoborus kairomone on helmet development in Daphnia ambigua . Hydrobiologia 310, 95–100 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015527
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015527