Abstract
-
(i)
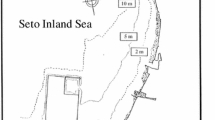
A study was made of Rivularia atra at a sheltered bay in S-E. Scotland, where it is frequent in summer in pools of the upper eulittoral. Monthly measurements of water chemistry and phosphate activities were made at the same stage in the tidal cycle during April 1992–October 1993, together with other short intensive studies.
-
(ii)
Drift seaweed deposited at high tide levels (>4.9 m) released high concentrations of inorganic nutrients to adjacent pools, where the water sometimes exceeded 6000 µg l−1 PO4−P. Combined inorganic N was, however, always low and the N:P ratio fell to 0.001–0.003:1 (by weight) in August, when the temperature was relatively high: much N was lost to the atmosphere as ammonia.
-
(iii)
Total P concentrations in the Rivularia pools (mostly covered by 4.5–4.8 m tides) were much lower than in the drift seaweed pools, but similar to the sea, though with higher % organic P in the former (means of 50% v. 28%): total N concentrations were much lower in the Rivularia pools than in seawater, leading to a very low N:P for most of the time. Aqueous organic P tended to increase (in summer) during the period between tidal cover, even in pools lacking input drainage, suggesting that much of the organic P may be autochthonous.
-
(iv)
All 9 Rivularia pools showed high concentrations of P in June in one or both years. At the same time the Rivularia colonies formed abundant hormogonia, followed 4–8 weeks later by a marked increase in macroscopically obvious colonies.
-
(v)
Assays of ‘surface’ phosphomonoesterase activity by Rivularia colonies showed different results according to whether p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) or 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate (4-MUP) was used as substrate. Both substrates indicated obvious activity at intervals during the year. Using pNPP, activity was very low in June, usually followed by a very high value in July or August; use of 4-MUP showed a different response, with a high value one or two months later than with pNPP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiralty Tide Tables. 1992–1994, Vol. 1 European Waters. The Hydrographer of the Navy, Taunton, England.
Andrews, J. W., 1991. The Ecology of the Manx Strand Line. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Liverpool, 160 pp.
Chróst, R. J. & Krambeck, H. J., 1986. Fluorescence correction for measurements of enzyme activity in natural waters using methylumbelliferyl-substrates. Arch. Hydrobiol. 106: 79–90.
East Lothian District Council, 1976. John Muir Country Park: descriptive management plan. East Lothian District Council, Scotland, 78 pp.
Eisenreich, S. J., R. T. Bannerman & D. E. Armstrong, 1975. A simplified phosphorus analysis technique. Envir. Lett. 9: 43–53.
Elliott, R. J. & A. G. Porter, 1971. A rapid cadmium reduction method for the determination of nitrate in bacon and curing brines. Analyst. Lond. 96: 522–527.
Fedde, K. N. & M. P. Whyte, 1990. Alkaline phosphatase (tissue-nonspecific isoenzyme) is a phosphoenthanolamine and pyridoxal 5′ phosphate ectophosphatase: normal and hypophosphatasia fibroblast study. Am. J. Genet. 47: 767–775.
Frémy, P., 1929–33. Cyanophycées des Côtes d'Europe. Mem. Soc. natn. Sci. nat. mat. Cherbourg 41: 234 pp. + 66 pl.
Fries, L., 1963. On the cultivation of axenic red algae. Physiol. Pl. 16: 695–708.
Grainger, S. L. J., A. Peat, D. N. Tiwari & B. A. Whitton, 1989. Phosphomonoesterase activity of the cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Calothrix parietina. Microbios 59: 7–17.14.
Hanisak, M. D., 1993. Nitrogen release from decomposing seaweeds: species and temperature effects. J. appl. Phycol. 5: 175–181.
Hernández, I., F. X. Neill & J. A. Fernández, 1992. Alkaline phosphatase activity in Porphyra umbilicalis (L.) Kützing. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 159: 1–13.
Joint Nature Conservation Committee, 1993. An Inventory of UK Estuaries 4. North and East Scotland. Joint Nature Conservation Committee, Peterborough, U.K.
Khoja, T. M., D. Livingstone & B. A. Whitton, 1984. Ecology of a marine Rivularia population. Hydrobiologia 108: 65–73.
Livingstone, D. & B. A. Whitton, 1984. Water chemistry and phosphatase activity of the blue-green alga Rivularia in Upper Teesdale streams. J. Ecol. 72: 405–421.
Marker, A. F. H., C. A. Crowther & R. M. Gunn, 1980. Methanol and acetone as solvents for estimating chlorophyll a and phaeopigments by spectrophotometry. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 14: 52–69.
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 799–801.
Stainton, M. P., M. H. Capel & F. A. J. Armstrong, 1977. The Chemical Analysis of Freshwater (2nd edn). Fish. Mar. Serv. Misc. Spec. Publ. 25.
Whitton, B. A., 1987. The biology of Rivulariaceae. In P. Fay & C. Van Baalen (eds), The Cyanobacteria — A Comprehensive Review. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 543 pp., 513–534.
Whitton, B. A., 1991. Use of phosphatase assays with algae to assess phosphorus status of aquatic environments. In D. W. Jeffrey & B. Madden (eds), Bioindicators and Environmental Management. Proc. 6th International Bioindicators Symposium Academic Press, London. 458 pp., 295–310.
Whitton, B. A., S. L. J. Grainger, G. R. W. Hawley & J. W. Simon, 1991. Cell-bound and extracellular phosphatase activities of cyanobacterial isolates. Microb. Ecol. 21: 85–98.
Whitton, B. A., J. M. Yelloly, M. Christmas & I, Hernández, in press. Surface phosphatase activity of benthic algae in a stream with highly variable ambient phosphate concentrations. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 26:
Williams, S. L., 1984. Decomposition of the tropical macroalga Caulerpa cupressoides (West) C. Agardh. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 80: 109–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yelloly, J.M., Whitton, B.A. Seasonal changes in ambient phosphate and phosphatase activities of the cyanobacterium Rivularia atra in intertidal pools at Tyne Sands, Scotland. Hydrobiologia 325, 201–212 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014985
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014985