Summary
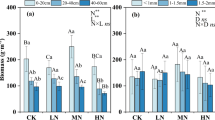
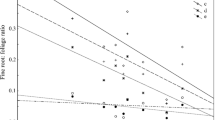
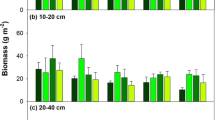
Quantitative samples of fine roots (d≤3 mm) were extracted from the soil of a 90-year-old beech-birch-maple stand that had been previously treated with lime (1120 kg/ha) or lime plus 15-10-10 NPK fertilizer (6720 kg/ha). Estimates of fine root biomass were: 1246±94 g/m2, control; 1229±194 g/m2, lime only; and 2711±423 g/m2, lime+NPK. Increased root concentration in the fertilized plot was greatest in upper soil horizons, but extended through the profile to all but the C horizon. Concentrations of N, P, Ca, and Mg in the roots were increased significantly by fertilizer treatment; K concentration was unaffected. Elements not added in the fertilizer or lime-Al, Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cu-also increased in concentration in roots from the fertilized plot. Increased root biomass, nutrient content, and rooting depth resulting from fertilization should lead to: (1) a higher organic matter and nutrient content of the deeper soil horizons, (2) availability of a larger volume of soil —with its moisture and nutrients—to the vegetation, and (3) increased wind-firmness in addition to the more direct effects of fertilization upon growth, vigor, and soil properties. re]19730806
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghilarov, M. S., Kouda, V. A., Novichkova-Ivanova, L. N., Rodin, L. E. and Sueshnikova, V. M., Methods of productivity studies in root systems and rhizosphere organisms. International Symposium. USSR Academy of Sciences. Leningrad, 1968. 239 pp. Reprinted for International Biological Program by Biddles Ltd., Guildford, U. K. (1968).
Hoyle, M. C., Variation in foliage composition and diameter growth of yellow birch with season, soil and tree size. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. SSSA Proc 29, 475–480 (1965).
Jackson, M. L., Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Inc. Englewood Cliffs, N.J. 498 pp. (1958).
Perkin Elmer Corp. Analytical methods for atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Perkin Elmer Corp., Norwalk, Conn. (1971).
Safford, L. O. and Bell, Susan, Biomass of fine roots in a white spruce plantation. Can. J. Forest Research 2, 169–172 (1972).
Steele, Robert G. D. and Torrie, James H., Principles and Procedures of Statistics. McGraw-Hill Book Co., Inc., New York. 481 pp. (1960).
Voigt, G. K., Variation in nutrient uptake by trees. In: Forest Fertilization Theory and Practice. pp. 20–27. Tenn. Valley Authority, Muscle Shoals, Alabama (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safford, L.O. Effect of fertilization on biomass and nutrient content of fine roots in a beech-birch-maple stand. Plant Soil 40, 349–363 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011517
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011517