Abstract
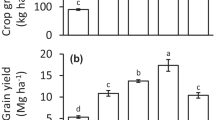
Methane flux was measured for a rice/wheat agroecosystem of Gangetic Plains, with and without application of chemical fertilizer and wheat straw (WS). Three treatments of control, fertilizer application and fertilizer + WS application, were established in a completely randomized block design and measurements were made for two consecutive years (1993 and 1994). CH4 measurements during growth of the rice crop period showed that there were significant difference in flux rates during the two years. Maximum emission occurred at the time of anthesis and minimum at the seedling stage. The flux rates were significantly higher for fertilizer or fertilizer + WS treatments. The effects of the treatments were similar across phenological stages and years. In the subsequent wheat crop and fallow period, the soils consumed CH4. There were significant differences in CH4 uptake rates between the two years. Fertilizer treatments reduced CH4 uptake in both the years. The results suggested that tropical agroecosystems may consume substantial amounts of CH4 and that the methane output can be reduced by lowering the submergence level in rice paddies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamsen A P S and King G M 1993 Methane consumption in temperate and subarctic forest soils: Rates, vertical zonation, and responses to water and nitrogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 485–490.
Adhya T K, Rath A K, Gupta P K, Rao V R, Das S N, Parida K M, Parashar D C and Sethunathan N 1994 Methane emission from flooded rice fields under irrigated conditions. Biol. Fert. Soils 18, 245–248.
Bouwman A F 1990 Soil and the Greenhouse Effect. John Wiley and Sons, New York, USA.
Castro M S, Jerry M M, Steudler P A and Chapman J W 1994 Soil moisture as a predictor of methane uptake by temperate forest soil. Can. J. For. Res. 24, 1805–1810.
Dlugokencky E J, Masaire K A, Lang P M, Tans P P, Steele L P and Nisbet E G 1994 A dramatic decrease in the growth rate of atmospheric methane in the northern hemisphere during 1992. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 45–48.
Hutsch B W, Webster C P and Powlson D S 1993 Long-term effects of nitrogen fertilization on methane oxidation in soil of the Broad-balk wheat experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 1307–1315.
Hutsch B W, Webster C P and Powlson D S 1994 Methane oxidation in soil as affected by land use, soil pH and N fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 26, 1613–1622.
Inubushi K, Hori K, Matsumoto S, Umebayashi M and Wada H 1989 Methane emission from the flooded paddy soil to the atmosphere through rice plant. Jap. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 60, 318–324 (In Japanese with English Summary).
Kimura M, Miura Y, Watanabe A, Katoh T and Haraguchi H 1991 Methane emission from paddy field (part 1). Effect of fertilization, growth stage and midsummer drainage: Pot experiment. Environ. Sci. 14, 265–271.
Lindau C W 1994 Methane emissions from Louisiana rice fields amended with nitrogen ferterlizers. Soil Biol. Biochem. 26, 353–359.
Mancinelli R L 1995 The regulation of methane oxidation in soil. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 49, 581–605.
Mariko S, Harazono Y, Owa N and Nouchi I 1991 Methane in flooded soil water and the emission through rice plants to the atmosphere. Environ. Exp. Bot. 31, 343–350.
Palmer R R and Reeve J N 1993 Methanogen genes and the moleculer biology of methane biosynthesis. In Genetics and Molecular Biology of Anaerobic Bacteria. Ed. M Sebald. pp 13–35. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Parashar D C, Gupta P K, Rai J, Sharma R C and Singh N 1993 Effect of soil temperature on methane emission from paddy field. Chemosphere 26, 247–250.
Parashar D C et al. 1994 Methane budget from paddy fields in India. Curr. Sci. 66, 938–940.
Pezeshki S R 1994 Plant response to flooding. In Plant-Environment Interaction. Ed. R E Wilkinson. pp 289–321. Marcel Dekker. Inc., New York, USA.
Schutz H, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Rennenberg H and Seiler W 1989 A-3year continuous record on the influence of day-time, season and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 16405–16416.
Seiler W, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R and Scharffe D 1984 Methane emission from rice paddies. J. Atmos. Chem. 1, 241–268.
Singh J S and SinghSmita 1995a Methane emission from rice paddies: Need for a downward revision of global estimate. Curr. Sci. 69, 293–295.
Singh J S and SinghSmita 1995b Methanogenic bacteria, methanogenesis and methane emission from rice paddies. Trop. Ecol. 36, 145–165.
Steudler P A, Bowden R D, Melillo J M and Aber J D 1989 Influence of nitrogen fertilization on methane uptake in temperate forest soils. Nature 341, 314–316.
Whitton B A and Rother J A 1988 Environmental features of deepwater rice fields in Bangladesh during the flood season. In 1987 International Deepwater Rice Workshop. pp 47–54. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines.
Yagi K and Minami K 1990 Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 36, 599–610.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J.S., Singh, S., Raghubanshi, A.S. et al. Methane flux from rice/wheat agroecosystem as affected by crop phenology, fertilization and water level. Plant Soil 183, 323–327 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011448
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011448