Abstract
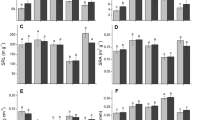
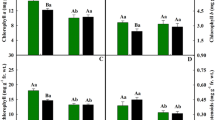
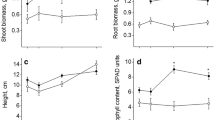
This experiment was designed to examine the effects of aluminium (Al) on the growth of Pinus radiata (D. Don) and Eucalyptus mannifera subsp. mannifera (Mudie) seedlings in culture solutions in a glasshouse to help explain the failure of radiata pine trees on some acid, low fertility soils in Australia on which the native eucalypts flourish. Aluminium (Al) in culture solution increased the growth of roots and shoots of seedlings of both species but while growth of the eucalypt continued to increase with increases in Al to 2.222 μM, growth of the pine was largest at 370 μM Al. In addition to total root length, specific root length (length per unit dry weight), a measure of fineness of the root, increased in the eucalypt seedlings as the substrate Al increased. Growth of the shoots and roots of the pine in the absence of any added Al was extremely poor suggesting that Al, in low concentrations, may be an essential element or ameliorate some other factors in solution culture at low pH.
Root and shoot concentrations of K increased with increasing Al, whilst Ca and Mg Concentrations decreased and Mn concentrations were unaffected in both species. Tissue Ca and Mg concentrations were 2 to 3 times higher in the eucalypt seedlings than the pine at all levels of added Al due to greater uptake of these elements by the eucalypt. In contrast, at the highest concentration of Al in the medium, shoot Al concentrations were lower in the cucalypt than in the pine due to a greater proportion of Al being retained in the eucalypt roots.
These differences between the seedlings in terms of root growth and tissue cation concentrations may help explain the ability of eucalypt species to maintain vigorous growth on acid soils high in Al and low in Ca and P, where growth of the pines failed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asp H, Bengtsson B and Jensen P 1988 Growth and cation uptake in spruce (Picea abies Karst.) grown in sand culture with various aluminium contents. Plant and Soil 111, 127–133.
Blamey F P C, Asher C J and Edwards D G 1987 Hydrogen and aluminium tolerance. Plant and Soil 99, 31–37.
Blamey F P C, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1983 Effects of aluminium, OH:Al and P:Al molar ratios and ionic strength on soybean root elongation in solution culture. Soil Sci. 136, 197–207.
Cumming J R, Eckert R T and Evans L S 1985 Effect of aluminium on potassium uptake by red spruce seedlings. Can. J. Bot. 63, 1099–1103.
Edmeades D C, Blamey F P C, Asher C J and Edwards D G 1991 Effects of pH and aluminium on the growth of temperate pasture species. I. Temperate grasses and legumes supplied with inorganic nitrogen. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 42, 559–569.
Flinn D W 1975 Calcium nutrition of Pinus radiata D. Don. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Melbourne. 191 p.
Foy C D, Caney R L and White M C 1978 The physiology of metal toxicity in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29, 511–566.
Gentle S W and Humphreys F R 1968 Experience with phosphatic fertilizers in man-made forests of Pinus radiata in New South Wales. 9th Commonwealth For. Conf., India. 37 p.
Grime J P and Hodgson J G 1969 An investigation of the ecological significance of lime-chlorosis by means of largescale comparative experiments. In Ecological Aspects of Mineral Nutrition of Plants. Ed. I HRorison. pp 67–99. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford and Edinburgh, UK.
Hanson J B 1984 The function of calcium in plant nutrition. Adv. Plant Nutr. 1, 149–208.
Hecht-Buchholz Ch and Foy C D 1981 Effects of aluminium toxicity on root morphology of barley. Plant and Soil 63, 93–95.
Hecht-Buchholz Ch, Jorns C A and Keil P 1987 Effect of excess aluminium and manganese on Norway spruce seedlings as related to magnesium nutrition during Al stress. J. Plant Nutr. 10, 1103–1110.
Hewitt E J 1966 Sand and Water Culture Methods Used in the Study of Plant Nutrition (2nd ed). Tech. Communication No. 22 (Revised) Commonwealth Bureau of Horticulture and Plantation Crops. East Malling, Maidstone, Kent. 101 p.
Hoagland D R and Snyder W C 1933 Nutrition of strawberry plants under controlled conditions. (a) Effects of deficiencies of boron and certain other elements. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 30, 288–293.
Huang J 1991 Comparative Responses of Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus Species to Nutritional Stresses. Ph.D. Thesis. Department of Forestry, The Australian National University, ACT, Australia. 386 p.
Huang J, Bachelard E P and Banks J C G 1991 Growth and nutrient status of Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus species on a nutrient-poor soil. In Productivity in Perspective. Ed. P J Ryan. Third Australian Forest Soils and Nutrition Conference, Melbourne, 7–11 October 1991. p. 37.
Humphreys F R and Truman R A 1978 The role of aluminium in the nutrition of Pinus spp. I. The effects of aluminium on the uptake of phosphorus by Pinus radiata from solutions containing luxury amounts of phosphate. For. Comm. N.S.W., Wood Tech. and For. Res. Div., Sydney. 20 p. (unpublished).
Keltjens W G and vanLoenen E 1989 Effects of aluminium and mineral nutrition on growth and chemical composition of hydroponically grown seedlings of five tree species. Plant and Soil 119, 39–50.
Kramer P J and Kozlowski T T 1979 Physiology of Woody Plants. Academic Press, New York. 881 p.
Lambert M J 1976a Preparation of plant material for estimating a wide range of elements. Research Note No. 29. Forestry Commission of N. S. W. 64 p.
Lambert M J 1976b Methods for chemical analysis. Forestry Commission of N. S. W. Tech. Paper No. 25.
Lance J C and Pearson R W 1969 Effect of low concentrations of aluminium on growth and water and nutrient uptake by cotton roots. Soil Sci. Amer. Proc. 33, 95–98.
Magistad O C 1925 The aluminium content of the soil solution and its relation to soil reaction and plant growth. Soil Sci. 20, 181–225.
McLean E O 1976 Chemistry of soil aluminium. Commun. Soil Sci. and Plant Anal. 7, 619–636.
Mullette K J 1975 Stimulation of growth in Eucalyptus due to aluminium. Plant and Soil 42, 495–499.
Paganelli D J, Seiler J R and Feret P P 1987 Root regeneration as an indicator of aluminium toxicity in loblolly pine. Plant and Soil 102, 115–118.
Raynal D J, Thornton F C, Schaedle M and Henderson G S 1990 Sensitivity of tree seedlings to aluminum. III. Red spruce and loblolly pine. J. Environ. Qual. 19, 180–187.
Schaedle M, Thornton F, Raynal D and Tepper H 1989 Response of tree seedlings to aluminum. Tree Physiol. 5, 337–356.
Tan K and Keltjens W G 1990 Interaction between aluminium and phosphorus in sorghum plants. Plant and Soil 124, 25–32.
Thornton F C, Schaedle M and Raynal D J 1987 Effects of aluminium on red spruce seedlings in solution culture. Environ. Exp. Bot. 27, 489–498.
Truman R and Humphreys F R 1979 The role of aluminium in the nutrition of Pinus spp. IV. The effect of a three-way substitution between aluminium, calcium and magnesium on the uptake of phosphorus, aluminium and the major cations by Pinus radiata from solutions containing an adequate level of phosphorus. Forestry Commission of NSW. Wood Tech. For. Res: Sydney. (unpublished).
Wagatsuma T 1984 Characteristics of upward translocation of aluminium in plants. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 30, 345–358.
Wheeler D M, Edmeades D C and Christie R A 1992 Effect of aluminum on relative yield and plant chemical concentrations of cereals grown in solution culture at low ionic strength. J. Plant Nutr. 15, 403–418.
Will G M 1985 Nutrient deficiencies and fertilizer use in New Zealand exotic forests. N.Z. FRI., Bulletin No. 97, 53 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Bachelard, E.P. Effects of aluminium on growth and cation uptake in seedlings of Eucalyptus mannifera and Pinus radiata . Plant Soil 149, 121–127 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010769
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010769