Abstract
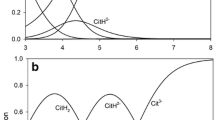
Extracellular processes, particularly the adsorption of aluminium (Al) by pectate in the cell wall, have been proposed as important in the expression of Al toxicity to plant roots. In vitro studies were conducted on the effects of Al concentration (generally ≤ 32 μM), calcium (Ca) concentration (0.05 to 10 mM) and pH (3.2 to 5.4) on Al sorption by Ca pectate. There was a rapid reaction between Al and Ca pectate, there being no difference in Al remaining in solution after reaction times of 1 to 16 min, and only a slight decrease after 24 h. Increased Al concentration in solution increased linearly the sorption of Al by Ca pectate, with 70 to 84% of the Al originally in solution sorbed with ≤32 μM Al. In contrast, Al sorption decreased with increased Ca concentration in solution, and as pH decreased from 5.4 to 3.2. Only ≤30% of the sorbed Al was desorbed after 1 h by 1 mM CaCl2, 10 mM CaCl2 or 1 mM HCl. The amount of Al desorbed increased with a desorption period of 5 h, particularly with 1 mM HCl. These studies suggest that Al sorbed by Ca pectate in root cell walls is in equilibrium with Al in solution, and that Al toxicity is associated with the strong binding between Al and Ca pectate external to the cytoplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alva A K, Asher C J and Edwards D G 1986a The role of calcium in alleviating aluminium toxicity. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 37, 375–382.
Alva A K, Edwards D G, Asher C J and Blamey F P C 1986b Relationships between root length of soybean and calculated activities of aluminum monomers in nutrient solution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 959–962.
Blamey F P C, Edmeades D C and Wheeler D M 1990 Role of root cation-exchange capacity in differential aluminum tolerance of Lotus species. J. Plant Nutr. 13, 729–744.
Clarkson D T 1967 Interactions between aluminium and phosphorus on root surfaces and cell wall material. Plant and Soil 27, 347–356.
Foy C D, Fleming A L, Burns G E and Armiger W H 1967 Characterization of differential aluminum tolerance among varieties of wheat and barley. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 31, 513–521.
Gessa C and Deiana S 1990 Fibrillar structure of Ca polygalacturonate as a model for a soil-root interface. I. A hypothesis on the arrangement of the polymeric chains inside the fibrils. Plant and Soil 129, 211–217.
Haynes R J 1980 Ion exchange properties of roots and ionic interactions within the root apoplasm: Their role in ion accumulation by plants. Bot. Rev. 46, 75–99.
Horst W J, Wagner A and Marschner H 1982 Mucilage protects root meristems from aluminium injury. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 105, 435–444.
Kerridge P C 1969 Aluminum toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum Vill. Host) Ph.D. Thesis. Oregon State University. (Diss. Abstr. B 29, 3159)
Kerven G L, Edwards D G, Asher C J, Hallman P S and Kokot S 1989 Aluminium determination in soil solution. II. Short term colorimetric procedures for the measurement of inorganic monomeric aluminium in the presence of organic acid ligands. Aust. J. Soil Res. 27, 91–102.
Kinraide T B and Parker D R 1990 Apparent phytotoxicity of mononuclear hydroxy-aluminum to four dicotyledonous species. Physiol. Plant. 79, 283–288.
Klimashevskii E L and Dedov V M 1980 Characteristics of an elastic cell wall of the root in relation to genotypic variance of plant resistance to aluminum ions. Isv. Sib. Atb. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Ser. Biol. Nauk. 1, 108–112 (Chem. Abstr. 93, 142–143).
Knight A H, Crooke W M and Inkson R H E 1961 Cation-exchange capacities of tissues of higher and lower plants and their related uronic acid contents. Nature, Lond. 192, 142–143.
Lindsay WL and Walthall PM 1989 The solubility of aluminium in soils. In The Environmental Chemistry of Aluminium. Ed. GSposito. pp 29–53. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Noble A D and Sumner M E 1988 Calcium and Al interactions and soybean growth in nutrient solutions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 19, 1119–1131.
Parker D R, Zelazny L W and Kinraide T B 1987 Improvements to the program GEOCHEM. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 488–491.
Rengel Z 1990 Competitive Al3+ inhibition of net Mg2+ uptake by intact Lolium multiflorum roots. II. Plant age effects. Plant Physiol. 93, 1261–1267.
Sposito G and Mattigod S V 1980 GEOCHEM: A computer program for the calculation of chemical equilibria in soil solution and other natural water systems. Kearney Foundation of Soil Science, University of California, Riverside, CA.
Taylor G J 1991 Current views of the aluminum stress response: The physiological basis of tolerance. Curr. Top. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 10, 57–93.
Vose P B and Randall P J 1962 Resistance to aluminium and manganese toxicities in plants related to variety and cation exchange capacity. Nature, London 196, 85–86.
Zhang G and Taylor G J 1989 Kinetics of aluminum uptake by excised roots of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Plant Physiol. 91, 1094–1099.
Zhang G and Taylor G J 1990 Kinetics of aluminum uptake in Triticum aestivum L.: Identity of the linear phase of aluminum uptake by excised roots of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive cultivars. Plant Physiol. 94, 577–584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blamey, F.P.C., Asher, C.J., Kerven, G.L. et al. Factors affecting aluminium sorption by calcium pectate. Plant Soil 149, 87–94 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010765
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010765