Summary
The effect of Zn-P-Fe interaction in the nutrition of the maize plant was first examined by a well-controlled pot culture experiment and the results subsequently evaluated by a field trial.
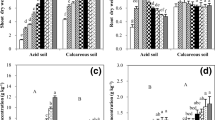
Dry matter production by root and shoot was affected significantly by the nutrient interaction. Enhanced P application reduced Zn concentration in shoot by more than half as compared to root. While Zn concentration per se in the plant increased, its relative mobility from root to shoot was vastly impeded, implying a physiological inhibition in movement from root to shoot. Root uptake of P almost doubled resultant from enhanced P application indicating a ‘concentration effect’. A ‘locking up’ process of P movement from root to shoot was observed. Relatively more Fe than Zn was root absorbed and immobilized resulting in reduced translocation to shoot. Dry matter yield increases were recorded generally at or around a P/Zn ratio of 19 and 65 respectively in root and shoot. Corresponding values for P/Fe and Fe/Zn ratios were 284 and 11 and 67 and 6 respectively. Sampling of the substrate at 15 days interval indicated decreased availability of Zn, P and Fe as a function of time consequent to plant growth. Significant differences in availability with reference to higher amounts of applied Zn were observed only later during crop growth, while in the case of P and Fe they were observed at each sampling. Available Zn and P correlated positively with plant shoot and root tissue concentration. With Fe, the correlation was negative in the case of shoot. The contrasting ‘r’ values of Zn and Fe in shoot implicates the strong possibility of P-induced Zn-Fe antagonism.
Field evaluation of the experiment indicated the depressing effect of high P application on grain yield and also its nullifying effects on the otherwise positive effect of Zn and Fe application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biddulph, O. and Woodbridge, C. G., The uptake of phosphorus by bean plants with particular reference to the effects of iron. Plant Physiol. 27, 431–444 (1952).
Brown, J. C., Holmes, R. S. and Tiffin, L. O., Hypothesis concerning iron chlorosis. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 23, 231–234 (1959).
Brown, J. C. and Tiffin, L. O., Zinc deficiency and iron chlorosis dependent on the plant species and nutrient-element balance in Tulare clays. Agron. J. 54, 356–358 (1962).
Chapman, H. D., Cation-exchange capacity. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Black, C. A. (ed.). Amer. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A. pp. 891–901 (1965).
Cottenie, A. and Gabriels, R., Trace element fractions and their availability. Trans. Comm. II & IV, Intern. Soc. Soil Sci. Aberdeen, 247–253 (1966).
Cochran, W. G. and Cox, G. M., Experimental Designs. John Wiley & Sons Inc. New York (1950).
Jackson, M. L., Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall Pvt. Ltd., India, pp. 498 (1967).
Kilmer, V. J. and Alexander, L. T., Methods of making mechanical analysis of soils. Soil Sci. 68, 15–24 (1949).
Nair, K. P. P. and Cottenie, A., A study of the plant uptake in relation to changes in extractable amounts of native trace elements from soil profiles using the Neubauer seedling method. Soil Sci. 108, 74–78 (1969).
Nair, K. P. P. and Cottenie, A., Zinc adsorption and exchange studies in some Indian soils. (in press).
Olson, R. V., Iron. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Black, C. A. (ed.). Amer. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A. pp. 963–973. (1965).
Olsen, S. R. and Dean, L. A., Phosphorus. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Black, C. A. (ed.). Amer. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A. pp. 1035–1049 (1965).
Peck, T. R., Walker, W. M. and Boone, L. V., Relationship between corn (Zea mays L.) yield and leaf levels of ten elements. Agron. J. 61, 299–301 (1969).
Pratt, P. F., Potassium. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Black, C. A. (ed.). Am. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A., pp. 1022–1034 (1965).
Sharma, K. C., Krantz, B. A. and Brown, A. L., Interaction of P and Zn on two dwarf wheats. Agron. J. 60, 329–332 (1968).
Sharma, K. C., Krantz, B. A., Brown, A. L. and Quick, J., Interaction of Zn and P in top and root of corn and tomato. Agron. J. 60, 453–456 (1968).
Stuckenholtz, D. D., Olsen, R. J., Gogan, G., and Olsen, R. A., On the mechanism of phosphorus-zinc interaction in corn nutrition. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 30, 759–763 (1966).
Viets, F. G.Jr. and Boawn, L. C., Zinc. In: Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Black, C. A. (ed.). Am. Soc. Agron. Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A. pp. 1090–1101 (1965).
Warnock, R. E., Micronutrient uptake and mobility within corn plants (Zea mays L.) in relation to phosphorus-induced zinc deficiency. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 34, 765–769 (1970).
Watanabe, F. S., Lindsay, W. L. and Olsen, S. R., Nutrient balance involving phosphorus, iron and zinc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 562–565 (1965).
Wilkinson, H. F., Loneragan, J. F. and Quirk, J. P., The movement of zinc to plant roots. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 32, 831–833 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Associate professor and graduate student
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, K.P.P., Babu, G.R. Zinc-phosphorus-iron interaction studies in maize. Plant Soil 42, 517–536 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009940
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009940