Abstract
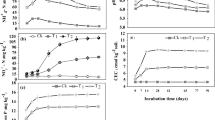
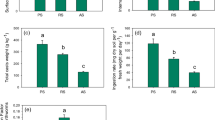
Soil solution and solid phase analyses were compared for stubble standing and stubble burnt systems on an acid, acidified and limed Alfisol in north-eastern Victoria. Exchangeable (1 M KCl) aluminium (Al), soil solution total and monomeric Al, pH (water) and soil solution pH were measured to identify any differences in soil acidification between the stubble burnt and the stubble standing treatments. All measures of Al increased with soil depth down to 10 cm in all stubble treatments and decreased in the 10–20 cm soil depth with the exception of lime treatments. Concentrations of low molecular weight organic acids in the soil solution were determined by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC). Aromatic and aliphatic acids were distributed throughout the soil depth (0–20 cm) for the stubble standing treatments but were confined to the 0–5 cm soil depth for the stubble burnt treatment. In this short term field trial (2 years for stubble management), the data suggest that the conventional practice of stubble burning was more acidifying than the soil conservation practice of stubble standing, over the 0–20 cm soil depth for the lime (6 t ha-1) treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken R L and Outhwaite R J 1987 A modified centrifuge apparatus for extracting soil solution. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 18, 1041–1047.
Carter M R and Steed G R 1992 The effects of direct-drilling and stubble retention on hydraulic properties at the surface of duplex soils in north-eastern Victoria. Aust. J. Soil Res. 30, 505–516.
Chan K Y, Roberts W P and Heenan D P 1992 Organic carbon and associated soil properties of a red earth after 10 years of rotation under different stubble and tillage practices. Aust. J. Soil Res. 30, 71–83.
Coleman N T and Thomas G W 1967 The basic chemistry of soil acidity. In Soil Acidity and Liming. Eds. R W Pearson and F Adams. pp 1–41. Agronomy Monograph No 12, Am. Soc. Agron., Wisconsin, USA.
Huang P M and Violante A 1986 Influence of organic acids on crystallization and surface properties of precipitation products of aluminum. In Interactions of soil minerals with natural organics and microbes. Eds. P M Huang and M Schnitzer. pp 159–221. SSSA Special Publication No 17, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. Madison, WI, USA.
Hue N V, Craddock G R and Adams F 1986 Effect of organic acids on aluminium toxicity in subsoils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 28–34.
Kamprath E J 1970 Exchangeable aluminum as a criterion for liming leached mineral soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 34, 252–254.
Kerven G L, Edwards D G, Asher C J, Hallman P S and Kokot S 1989 Aluminium determination in soil solution. II. Short term colorimetric procedures for the measurement of inorganic monomeric aluminium in the presence of organic acid ligands. Aust. J. Soil Res. 27, 91–102.
Kwong Ng, Kee K F and Huang P M 1979 The relative influence of low-molecular-weight complexing organic acids on the hydrolysis and precipitation of aluminium. Soil Sci. 128, 337–342.
Menzies N W, Kerven G L, Bell L C and Edwards D G 1992 Determination of total soluble aluminium in soil solution using pyrocatechol violet, lanthanum and iron to discriminate against micro-particulates and organic ligands. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 23, 2525–2545.
Slattery W J and Coventry D R 1993 Response of wheat, triticale, barley and canola to lime on four soil types in north-eastern Victoria. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 32, 609–618.
Williams C H 1980 Soil acidification under clover pasture. Aust. J. Agric. Anim. Husb. 20, 561–567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slattery, W.J., Morrison, G.R. Relationship between soil solution aluminium and low molecular weight organic acids in a conservation cropping system. Plant Soil 171, 193–197 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009587
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009587