Abstract
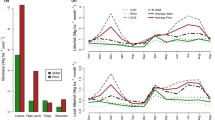
Past and current work on biological processes related to nitrogen fluxes and cycling in natural and disturbed Mediterranean forest sites are discussed. In natural conditions, the main point reviewed is mineral nitrogen availability in the soil, and particularly the process of mineralization (ammonification, nitrification) in the field as well as nitrogen uptake by Pinus pinea. Some aspects of nitrogen translocation within the trees are also considered. Perturbation of the nitrogen status, and especially nitrogen mineralization, as a result of manipulation of forest sites are discussed by comparing both a holm oak coppice with a clearcut and a Pinus halepensis woodland before and after prescribed fire.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billes G, Lossaint P and Cortez J 1971 L'activité biologique des sols dans les écosystème méditerranéens. II. Minéralisation de l'azote. Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol 8, 533–552.
Billes G, Cortez J and Lossaint P 1975 Etude comparative de l'activité biologique des sols sous peuplements arbustifs et herbacés de la garrigue Méditerranéenne. I. Minéralisation du carbone et de l'azote. Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol 12, 115–139.
Cabanettes A and Rapp M 1978 Biomasse, minéralomasse et productivité d'un écosystème à Pins pignons (Pinus pinea L.) du littoral méditerranéen. I. Biomasse. Oecol. Plant. 13, 271–286.
Cabanettes A and Rapp M 1981a Biomasse, minéralomasse et productivité d'un écosystème à Pins pignons (Pinus pinea L.) du littoral méditerranéen. III. Croissance. Acta Oecol., Oecol. Plant. 2, 121–136.
Cabanettes A and Rapp M 1981b Biomasse, minéralomasse et productivité d'un écosystème à Pins pignons (Pinus pinea L.) du littoral méditerranéenn. IV. Production. Acta Oecol., Oecol. Plant. 2, 381–394.
Chaussod R and Nicolardot B 1982 Mesure de la biomasse microbienne dans les sols cultivés. I. Approche cinétique et estimation simplifiée du carbone facilement minéralisable. Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol. 19, 501–502.
Ed Derfoufi F 1986 Gestion et dynamique des nutrients dans des taillis de chêne vert âgés et très jeunes. Thèse 3ème cycle, USTL Montpellier, 131 p.
Gillon D and Rapp M 1989 Nutrient losses during a winter low intensity prescribed fire in a Mediterranean forest. Plant and Soil 120, 69–77.
Jenkinson D S and Powlson D S 1976 The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil. I. Fumigation with chloroforme. Soil Biol. Biochem. 8, 167–177.
Lemée G 1967 Investigations sur la minéralisation de l'azote et son évolution annuelle dans les humus forestiers in situ. Oecol. Plant. 2, 285–324.
Lemée G 1978 La hêtraie naturelle de Fontainebleau. In Problèmes d'Ecologie, Ecosystèmes terrestres, Eds. M Lamotte and F Bourliere. pp 75–128. Masson, Paris.
Lossaint P and Rapp M 1969 Repartition de la matière organique, productivité et cycle des éléments minéraux dans des écosystèmes de climat méditerranéen. In Productivity of Forest Ecosystems pp 597–617. Proceedings of the Brussels Symposium, UNESCO, Paris.
Lossaint P and Rapp M 1978 La forêt méditerranéenne de chênes verts. In Problèmes d'Ecologie, Ecosystèmes terrestres. Eds. M Lamotte and F Bourliere. pp 129–185. Masson, Paris.
Merzouki A 1986 Les effets d'une coupe à blanc sur l'activité biologique d'un sol fersiallitique méditerranéen. Thèse 3ème cycle, USTL Montpellier, 122p.
Raison R J, Connel N J and Khanna P K 1987 Methodology for studying fluxes of soil mineral nitrogen in situ. Soil Biol. Biochem. 19, 521–530.
Rapp M 1984 The monthly cycling of nutrients in a stand of Pinus pinea L. In State and Change of Forest Ecosystems—Indicators in Current Research. Ed. G I Agren. Swed. Univ. Agric. Sci. Dept. Ecology and Environmental Research. Report No. 13, 261–291.
Rapp M, Leclerc M Cl and Lossaint P 1979 The nitrogen economy in a Pinus pinea L. stand. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2, 221–231.
Rapp M and Cabanettes A 1980 Biomasse, minérralomasse et productivité d'un écosystème à Pins pignons (Pinus pinea L.) du littoral méditerranéen. II. Composition chimique et minéralomasse. Acta Oecol., Oecol. Plant. 1, 151–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rapp, M. Nitrogen status and mineralization in natural and disturbed mediterranean forests and coppices. Plant Soil 128, 21–30 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009393
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009393