Synopsis
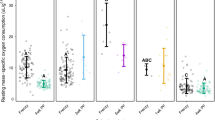
Energy expended in migration and reproduction was determined from measurements of caloric concentration and body and gonodal weight for nontrophic sea lampreys collected from different sites along the St. John River, New Brunswick. The estimated cost of locomotion in swimming the 140 km which separates the estuary from the spawning redds was 300 and 260 kcal for males and females respectively. Acutal distance which lampreys swam as well as mean swimming speed were estimated from a linear regression equation relating energy expenditure for locomotion and body weight. Energy expenditure for breeding was considerably greater than that catabolized throughout the upstream migration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Beamish, F.W.H. 1964. Seasonal changes in the standard rate of oxygen consumption of fishes. Can. J. Zool. 42: 189–194.
Beamish, F.W.H. 1973. Oxygen consumption of adult Petromyzon marinus in relation to body weight and temperature. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 30: 1367–1370.
Beamish, F.W.H. 1974. Swimming performance of adult sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus, in relation to weight and temperature. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 103: 355–358.
Beamish, F.W.H. 1978. Swimming capacity. In: W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall (ed.) Academic Press inc., New York and London.
Beamish, F.W.H. & L.M. Dickie. 1967. Metabolism and biological production in fish. pp. 215–242. In: S.D. Gerking (ed.) The Biological Basis of Freshwater Fish Production. Blackwell, Oxford and Edinburgh.
Beamish, F.W.H. & I.C. Potter. 1975. The biology of the anadromous sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) in New Brunswick. J. Zool. Lond. 177: 57–72.
Beamish, F.W.H., I.C. Potter & E.J. Thomas. 1979. Proximate composition of the adult anadromous sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus L., in relation to feeding, migration and reproduction. J. Anim. Ecol. 00: 00–00.
Bigelow, H. B.& W. C. Schroeder. 1948. Fishes of the western North Atlantic. 2. Cyclostomes. Mem. Sears Fdn. Mar. Res. No. 1, pt. 1: 29–58.
Bigelow, H.B. & W.C. Schroeder. 1953. Fishes of the Gulf of Mainee. U.S. Fish. Bull. 53: 1–577.
Brett, J.R. 1964. The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 21: 1183–1226.
Claridge, P.N. & I.C. Potter. 1975. Oxygen consumption, ventilatory frequency and heart rate of lampreys (Lampetra fluviatilis) during their spawning run. J. Exp. Biol. 63: 192–206.
Dodson, J.J., W.C. Leggett & R.A. Jones. 1972. The behaviour of adult American shad (Alosa sapidissima) during migration from salt to fresh water as observed by ultrasonic tracking techniques. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 29: 1445–1449.
Hasler, A.D. E.S. Gardella, R.M. Horrall & H.F. Henderson. 1969. Open water orientation of white bass, Roccus chrysops, as determined by ultrasonic tracking methods. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 26: 2173–2192.
Hardisty, M.W. & I.C. Potter. 1971. The general biology of adult lampreys. pp. 27–206. In: M.W. Hardisty & I.C. Potter (ed.) The Biology of Lampreys. Academic Press Inc., New York.
Johnson, J. 1960. Sonic tracking of adult salmon at Bonneville Dam, 1957. U.S. Fish. Bull. 176: 471–485.
Lanzing, W. J. R. 1959. Studies on the river lamprey, Lampetra fluviatilis, during its anadromous migration. Uitgeversmaatschappij, Neerlandia-Utrecht: 11–82.
Madison, D.M., R.M. Horrall, A.B. Stasko & A.D. Hasler. 1972. Migrating movements of adult sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) in coastal British Columbia as revealed by ultrasonic tracking. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 29: 1025–1033.
Malinin, L. K. 1973. Speed of fish migration. Rybnoye Choz. (In Russian). Transl. Ser. Vol. 3146 (8): 16–17. Fisheries and Marine Service, Canada. 1974.
McCleave, J.D. & R.M. Horrall. 1970. Ultrasonic tracking of homing cutthroat trout (Salmo clarki) in Yellowstone Lake. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 27: 715–730.
Moore, J.W. & I.C. Potter. 1976. Aspects of feeding and lipid deposition and utilization in the lampreys, Lampetra fluviatilis (L.) and Lampetra planeri (Bloch). J. Anim. Ecol. 45: 699–712.
Nikol'skii, G. W. 1961. Special Ichthyology. Second ed. Gosudarstvennoye izdatel'stvo, Moscow. Translated from Russian by the Israel Program for Scientific Translations. Jerusalem. Originally published 1954.
Nikol'skii, G. W. 1963. The Ecology of Fishes. Translated from Russian by L. Birkett. Academic Press, London. 352 pp.
Poddubny, A. G. 1967. Sonic tags and floats as a means of studying fish response to natural environmental changes and to fishing gear. FAO Conference on Fish Behaviour in Relation to Fishing Techniques and Tactics. Bergen, Norway, Exper. Pap. 46: 1–8.
Potter, I.C. & F.W.H. Beamish. 1977. The freshwater biology of adult anadromous sea lampreys, Petromyzon marinus. J. Zool. Lond. 181: 113–130.
Schmidt-Nielsen, K. 1972. Locomotion: Energy cost of swimming, flying and running. Science 177: 222–228.
Skidmore, J. F. 1959. Biology of spawning-run sea lamprey (Petromyzon Marinus) in the Pancake River, Ontario. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Western Ontario. 87 pp.
Tesch, F.W. 1974. Speed and direction of silver and yellow eels, Anguflla angufa, released and tracked in the open North Sea. Ber. dt. Wiss. Komm. Meeresforsch. 23: 181–197.
Thorson, T.B. 1971. Movement of bull sharks, Carcharhinus leucas between Caribbean Sea and Lake Nicaragua demonstrated by tagging. Copeia 2: 336–338.
Wigley, R.L. 1959. Life history of the sea lamprey of Cayuga Lake, New York. U.S. Fish. Bull. 59: 559–617.
Winberg, G. G. 1956. Rate of metabolism and food requirements of fishes. Belorussian State University, Minsk. Fish. Res. Board Can. Transl. Ser. 194.
Yuen, H.S.H. 1970. Behaviour of skipjack tuna, Katsuwonus pelamis, as determined by tracking with ultrasonic devices. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 27: 2071–2079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
William, F., Beamish, H. Migration and spawning energetics of the anadromous sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus . Environ Biol Fish 4, 3–7 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005922
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005922