Abstract
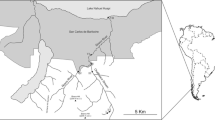
Larval abundance of Chironomus circumdatus in sewage canal and pond systems was studied during 1988–1990. Monthly changes in the morphometric features of the pond revealed that both total and littoral areas progressively decreased from 1063 and 107 m2 in December 1988 to 151 and 43 m2 in May '89; the decrease during the year 1989–1990 was from 1116 and 92 m2 in October to 109 and 31 m2 in May. A significant negative correlation (r= − 0.52) was obtained for the relation between littoral area and larval density in the pond. Larval density and biomass depended generally on the nature of the substrate and quantity of organic matter. Larval density of Ch. circumdatus was positively correlated with O2, bacterial count and organic matter content, but negatively correlated with CO2 level. Daily removal of organic matter by the larvae ranged from 20 to 31 % of the available organic matter in the sewage canal and from 3 to 11 % in the pond.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brundin, L., 1951. The relation of O2 microstratification of the mud surface to the ecology of the profundal bottom fauna. Rep. Inst. Freshwat. Res. Drottningholm 32: 32–44.
Cowell, B. C. & P. L. Hudson, 1968. Some environmental factors influencing benthic invertebrates in two Missouri River Reservoirs. In: Reversoir fishery Resources Symposium, pp. 541–555, University of Georgia Press, Athens, Southern division, American Fisheries Society special publication.
Cowell, B. C. & D. S. Vodopich, 1981. Distribution and seasonal abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates in a subtropical Florida Lake. Hydrobiologia 78: 97–105.
Cummins, K. W. & M. J. Klug, 1979. Feeding ecology of stream invertebrates. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 10: 147–172.
Davies, B. R., 1976. Wind distribution of the egg masses of Chironomus anthracinus (Zett.) (Diptera:Chironomidae) in a shallow, wind exposed lake (Loch Leven, Kinross). Freshwat. Biol. 6: 421–424.
Dermott, R., 1981. Ingestion rate of the burrowing may fly Hexagenia limbata as determined with 14C. Hydrobiologia 83: 499–503.
De Smet, W. H. O., 1982. Observations on the immature Chironomidae of a polluted lowland brook-pond system (Antwerp, Belgium), aerated by the Phallus process. Hydrobiologia 87: 171–189.
Fillion, D. B., 1967. The abundance and distribution of benthic fauna of three mountain reservoir on the Kananaskis River in Alberta. J. appl. Ecol. 4: 1–11.
Fredeen, F. J. H., 1964. Bacteria as food for blackfly larvae (Diptera:Simuliidae) in laboratory cultures and in natural streams. Can. J. Zool. 42: 527–548.
Grzybkowska, M., 1989. Production estimates of the dominant taxa of Chironomidae (Diptera) in the modified, River Widawka and the natural, River Grabia, Central Poland. Hydrobiologia 179: 245–249.
Johannsson, O. E., 1980. Energy dynamics of the eutrophic chironomid Chironomus plumosus f semireductus from the Bay of Quinte, Lake Ontario. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 1254–1265.
Johnson, R. K., 1987. Seasonal variation in diet of Chironomus plumosus (L) and C. anthracinus (Zett.) (Diptera:Chironomidae) in mesotrophic Lake Erken. Freshwat. Biol. 17: 525–532.
Johnson, R. K., B. Bostrom & W. Van de Bund, 1989. Interactions between Chironomus plumosus (L) and the microbial community in surfacial sediments of a shallow, eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 992–1003.
Jonasson, P. M., 1972. Ecology and production of the profundal benthos in relation to phytoplankton in Lake Esrom. Oikos (Suppl). 14: 1–148.
Lindegaard-Petersen, C., 1972. An ecological investigation of the Chironomidae from a Danish lowland stream (Linding Å). Arch. Hydrobiol. 69: 465–507.
Malmqvist, B. & C. Bronmark, 1982. Filter feeding in larval Lamptera planeri: effects of size, temperature and particle concentration. Oikos 38: 40–46.
Moore, J. W., 1979. Some factors influencing the distribution, seasonal abundance and feeding of subarctic Chironomidae. Arch. Hydrobiol. 85: 302–325.
Mundie, J. H., 1957. The ecology of Chironomidae in storage reservoirs. Trans. r. Ent. Soc. Lond. 109: 149–233.
Muthukrishnan, J., 1987. Role of aquatic insects in water treatment and as fish prey organisms. Sci. Dev. Environ. 181–190.
Palavesam, A., 1990. Ecophysiological studies on chironomid larvae, Ph.D., thesis, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai.
Pandian, T. J., 1987. Sustainable clean water and aquaculture. Arch. Hydrobiol. 28: 333–343.
Pinder, L. C. V., 1986. Biology of freshwater Chironomidae, Ann. Rev. Ent. 31: 1–23.
Thorp, J. H. & M. R. Diggins, 1982. Factors affecting depth distribution of dragonflies and other benthic insects in a thermally destabilized reservoir. Hydrobiologia 87: 33–44.
Walkley, A. & I. A. Black, 1934. An examination of the Detjareff Method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 63: 251–264.
Wallace, J. B. & W. R. Merritt, 1980. Filter-feeding ecology of aquatic insects. Ann. Rev. Ent. 25: 103–132.
Wallace, J. B., J. R. Webster & W. R. Woodall, 1977. The role of filter feeders in flowing waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 79: 506–532.
Welch, P. S., 1948. Limnological methods, McGraw Hill Book Co., New York: 381–384.
Wool, D. & J. Kugler, 1968. Laboratory culture of chironomid species from the Hula Nature Preserve, Israel. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 5: 153–154.
Wrubleski, D. A. & D. M. Rosenberg, 1990. The Chironomidae of Bone Pile pond, Delta Marsh, Manitoba, Canada Wetlands. 10: 243–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sankarperumal, G., Pandian, T.J. Larval abundance of Chironomus circumdatus in relation to biotic and abiotic factors. Hydrobiologia 246, 205–212 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005698
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005698