Abstract
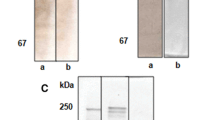
The egg yolk precursor, vitellogenin (VTG), was purified from blood plasma of striped bass by chromatography on hydroxylapatite or DEAE-agarose. The fish were first implanted with estradiol-17β (E2), which induced vitellogenesis. A rabbit antiserum (a-FSPP) raised against plasma from mature female striped bass, and then adsorbed with mature male plasma, was used to detect female-specific plasma protein (FSPP) in the chromatography fractions. Striped bass VTG (s-VTG) was collected from the peak fraction that was induced by E2, reacted with a-FSPP, and contained all detectable phosphoprotein. It appeared as a single band (Mr ≂ 170,000) in SDS-PAGE or Western blots using a-FSPP, and as a pair of closely-spaced phospholipoprotein bands in native gradient-PAGE, suggesting that there is more than one circulating form of s-VTG. The relationship of s-VTG to the yolk proteins was verified using a-FSPP. The antiserum reacted with the main peak from gel filtration of saline ovary extracts, and it specifically immunostained the two main bands in Western blots of the extracts and the yolk granules of mature oocytes. The amino acid composition of s-VTG was similar to that of VTG from other fish and Xenopus. A radial immunodiffusion assay for s-VTG was developed using a-FSPP and purified s-VTG as standard. The s-VTG was not detected in blood plasma of males, immature females, or regressed adult females, but plasma s-VTG levels were highly correlated with plasma E2 and testosterone levels, and oocyte growth, in maturing females. The results indicate that the maturational status of female striped bass can be identified by s-VTG immunoassay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergink, E.K. and Wallace, R.A. 1974. Precursor-product relationship between amphibian vitellogenin and the yolk proteins, lipovitellin and phosvitin. J. Biol. Chem. 249: 2897–2903.
Berlinsky, D.L. and Specker, J.L. 1991. Changes in gonadal hormones during oocyte development of striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 9: 51–62.
Bjornsson, B.T. and Haux, C. 1985. Distribution of calcium, magnesium and inorganic phosphate in plasma of estradiol-17β treated rainbow trout. J. Comp. Physiol. B. 155: 347–352.
Blythe, W.G. 1992. Induced maturation and spawning of striped bass, Morone saxatilis, exposed to 6-, 9-, and 12-month photothermal regimes. M.Sc. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Bradley, J.T., and Grizzle, J.M. 1989. Vitellogenin induction by estradiol in channel catfish, Ictaluris punctatus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 73: 28–39.
Byrne, B.M., Gruber, M. and Ab, G. 1989. The evolution of egg yolk proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 53: 33–69.
Campbell, C.M. and Idler, D.R. 1980. Characterization of an estradiol-induced protein from rainbow trout serum as vitellogenin by the composition and radioimmunological cross reactivity to ovarian yolk fractions. Biol. Reprod. 22: 605–617.
Chen, T.T. 1983. Identification and characterization of estrogen-responsive gene products in the liver of rainbow trout. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 61: 802–810.
Copeland, P.A. and Thomas, P. 1988. The measurement of plasma vitellogenin levels in a marine teleost, the spotted seatrout (Cynoscion nebulosus) by homologous radioimmunoassay. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 91B: 17–23.
Craik, J.C.A. and Harvey, S.M. 1984. The magnitudes of three phosphorus-containing fractions in the blood plasma and mature eggs of fishes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. 78: 539–543.
Deeley, R.G., Mullinix, K.P., Wetekam, W., Kronenberg, H.M., Meyers, M., Eldridge, J.D. and Goldberger, R.F. 1975. Vitellogenin synthesis in the avian liver. J. Biol. Chem. 25: 9060–9066.
de Vlaming, V.L., Wiley, H.S., Delahuntry, G. and Wallace, R.A. 1980. Goldfish (Carassius auratus) vitellogenin: Induction, isolation, properties and relationship to yolk proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 67B: 613–623.
Ding, J.L., Hee, P.L. and Lam, T.J. 1989. Two forms of vitellogenin in the plasma and gonads of male tilapia (Oreochromis aureus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 93B: 363–370.
Fostier, A., Jalabert, B., Billiard, R., Breton, B. and Zohar, Y. 1983. The gonadal steroids. In Fish Physiology, Vol. 9A, pp. 277–372. Edited by W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall and E.M. Donaldson, Academic Press, New York.
Gamst, O. and Try, K. 1980. Determination of serum phosphate without deproteinization by ultraviolet spectrophotometry of the phosphomolybdic acid complex. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 40: 483–486.
Hara, A. 1987. Studies on female-specific serum proteins (vitellogenin) and egg yolk proteins in teleosts: immunochemical, physiochemical and structural studies. Mem. Fac. Fish, Hokkaido Univ. 34: 1–59.
Hara, A. and Hirai, H. 1978. Comparative studies on immunochemical properties of female-specific serum protein and egg yolk proteins in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 59B: 339–343.
Hara, A., Yamauchi, K. and Hirai, H. 1980. Studies on female-specific serum protein (vitellogenin) and egg yolk protein in Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65B: 315–320.
Harlow, E. and Lane, D. 1988. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York.
Hodson, R.G., Smith, T., McVey, J., Harrell, R. and Davis, N. 1987. Hybrid striped bass culture: status and perspective. University of North Carolina Sea Grant College Program North Carolina.
Hodson, R.G. and Sullivan, C.V. 1993. Induced maturation and spawning of domestic and wild striped bass (Morone saxatilis) broodstock with implanted GnRH analogue and injected hCG. J. Aquacult. Fish. Managem. 24: 271–280.
Hori, S.H., Kodama, T. and Tanahashi, K. 1979. Induction of vitellogenin synthesis in goldfish by massive doses of androgens. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 37: 306–320.
John, A.C. and Thomas, F.R. 1973. Staining of phospho-proteins on acrylamide gel electrophoregrams. Anal. Biochem. 54: 386–394.
Kishida, M., Anderson, T.R. and Specker, J.L. 1992. Induction by β-estradiol of vitellogenin in striped bass (Morone saxatilis): characterization and quantification in plasma and mucus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 88: 29–39.
Mancini, G., Carbonara, A.O. and Heremans, J.F. 1965. Immunological quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 2: 235–254.
Mannos, E., Zanuy, S., Carillo, M., Nunez Rodriguez, J. and Le Menn, F. 1991. Quantification by ELISA of vitellogenin levels in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) maintained under different photoperiods. In Proc. IV Int. Symp. Reproductive Physiology of Fish. p. 325. Edited by A.P. Scott, J.P. Sumpter, D.E. Kime and M.S. Rolfe. FishSymp 91, Sheffield.
Mayer, I., Shackley, S.E. and Ryland, J.S. 1988. Aspects of the reproductive biology of the bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. I. An histological and histochemical study of oocyte development. J. Fish Biol. 33: 609–622.
Mommsen, T.P. and Walsh, P.J. 1988. Vitellogenesis and oocyte assemby. In Fish Physiology. Vol. 9A, pp. 347–406. Edited by W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall and E.M. Donaldson. Academic Press, New York.
Ng, T.B. and Idler, D.R. 1983. Yolk formation and differentiation in teleost fishes. In Fish Physiology. Vol. 9A, pp. 373–404. Edited by W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall and E.M. Donaldson. Academic Press. New York.
Norberg, B. and Haux, C. 1985. Induction, isolation and characterization of the lipid content of plasma vitellogenin from two Salmo species: rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) and sea trout (Salmo trutta). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 81B: 869–876.
Nozaki, M., Miyata, K., Oota, Y., Gorbman, A. and Plisetskaya, E.P. 1988. Different cellular distributions of two somatostatins in brain and pancreas of salmonids, and their separate associations with insulin and glucagon secreting cells. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 69: 267–280.
Nunez-Rodriguez, J.N., Kah, O., Geffard, M. and Le Menn, F. 1989. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for sole (Solea vulgaris) vitellogenin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 92B: 741–746.
Ouchi, K., Hara, A., Adachi, S., Arimoto, M., Mizuta, Y. and Nagahama, Y. 1989. Changes in serum concentrations of steroid hormones and vitellogenin during the period of vitellogenesis in the yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. Bull. Nansei Regional Fish. Res. Laboratory 22: 1–11.
Prat, J.P., Lamy, J.N. and Weill, J.D. 1969. Coloration des lipoproteins apres electrophoreses en gel de ployacrylamid. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. 51: 1367.
Redshaw, M.R. and Follet 1971. The crystaline yolk-platelet proteins and their soluble plasma precursor in an amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Biochem. J. 124: 759–766.
Rees, R.A. and Harrell, R.M. 1990. Artificial spawning and fry production of striped bass and hybrids. In Culture and Propagation of Striped Bass. pp. 43–72. Edited by R.M. Harrell, J.H. Kerby and R.V. Minton. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda.
Selman, K. and Wallace, R.A. 1989. Cellular aspects of oocyte growth in teleosts. Zool. Sci. 6: 211–231.
Silversand, C. and Haux, C. 1989. Isolation of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) vitellogenin by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. J. Chrom. 478: 387–397.
Specker, J.L., Berlinsky, D.L., Bibb, H.D. and O'Brien, J.F. 1987. Oocyte development in striped bass: factors influencing estimates of age at maturity. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 1: 162–174.
Sullivan, C.V., Tao, Y., Hodson, R.G., Hara, A., Bennett, R.O. and Woods, L.C. III. 1991. In Proc. IV Int. Symp. Reproductive Physiology of Fish. pp. 315–317. Edited by A.P. Scott, J.P. Sumpter, D.E. Kime and M.S. Rolfe. Fish-Symp 91, Sheffield.
Sumpter, J.P. 1991. The purification, radioimmunoassay and plasma levels of vitellogenin from the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. In Current Trends in Comparative Endocrinology. Edited by B. Lofts and W.N. Holmes. Vol. 1, pp. 355–357. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.
Tyler, C. 1991. Vitellogenesis in Salmonids. In Proc. IV Int. Symp. Reproductive Physiology of Fish. pp. 295–299. Edited by A.P. Scott, J.P. Sumpter, D.E. Kime and M.S. Rolfe. FishSymp 91, Sheffield.
Tyler, C.R. and Sumpter, J.P. 1990. The development of a radioimmunoassay for carp, Cyprinus carpio, vitellogenin. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 8: 129–140.
Valotaire, Y., Tenniswood, M., Le Guellec, C. and Tata, J.R. 1984. The preparation and characterization of vitellogenin messenger RNA from rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Biochem. J. 217: 73–77.
Wang, S.-Y. and Williams, D.L. 1982. Biosynthesis of vitellogenin. Identification and characterization of nonphosphorylated precursors to avian vitellogenin I and vitellogenin II. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 3837–3846.
Wahli, W., Dawid, I.B., Ryffel, G.U. and Weber, R. 1981. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science 212: 298–304.
Wallace, R.A. 1985. Vitellogenesis and oocyte growth in non-mammalian vertebrates. In Developmental Biology. Vol. 1, pp. 127–177. Edited by L.W. Browder. Plenum Press, New York.
Wallace, R.A. and Selman, K., 1982. A new procedure for the isolation of intact vitellogenin from teleosts. In Reproductive Physiology of Fish. pp. 161. Edited by C.J.J. Richter and H.J.Th. Goos. Pudoc, Wageningen.
Wiegand, M.D. 1982. Vitellogenesis in fishes. In Reproductive Physiology of Fish. pp. 136–146. Edited by C.J.J. Richter and H.J.Th. Goos. Pudoc, Wageningen.
Woods, J.C. III, Bennett, R.O. and Sullivan C.V. 1992. Reproduction of a domestic striped bass broodstock. Prog. Fish Cult. 54: 184–188.
Woods, J.C. III and Sullivan, C.V. 1993. Reproduction of striped bass (Morone saxatilis) broodstock: monitoring maturation and hormonal induction of spawning. J. Aquacult. Fish. Managem. 24: 213–224.
Woods, L.C. III, Woiwode, J.G., McCarthy, M.A., Theisen, D.D. and Bennett, R.O. 1989. Noninduced spawning of captive striped bass in tanks. Prog. Fish Cult. 52: 201–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Y., Hara, A., Hodson, R.G. et al. Purification, characterization and immunoassay of striped bass (Morone saxatilis) vitellogenin. Fish Physiol Biochem 12, 31–46 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004320
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004320