Synopsis
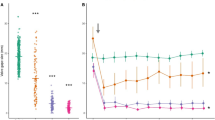
Foraging behaviour of lake charr, Salvelinus namaycush, exposed to 0.5 and 5.0 μg l−1 cadmium concentrations for 106–112 d, was examined in a flow-through stream channel using fathead minnows, Pimephales promelas, as prey. Five modes of foraging behaviour were observed and quantified (ending at fixate-orient; ending at approach and/or chase; ending at failed attack; ending at capture and loss; successful consumption). Each mode represented an increasingly progressive end-point from initial sighting of the prey to final consumption. Compared to controls., 0.5 μg l−1 Cd-exposed predators captured significantly fewer prey, while 5 μg l−1 Cd-exposed predators made fewer attacks. Both Cd-exposed groups consumed fewer prey than controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Atchison, G.J., M.G. Henry & M.B. Sandheinrich. 1987. Effects of metals on fish behaviour: a review. Env. Biol. Fish. 18: 11–25.
Benoit, D.A., E.N. Leonard, G.M. Christensen & J.T. Franat. 1976. Toxic effects of cadmium of three generations of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 105: 550–560.
Bull, J.C. & J.E. McInerney. 1974. Behaviour of juvenile coho salmon (Onchorhynchus kisutch) exposed to sumithion (Fenitrothion), an organophosphate insecticide. J. Fish. Res. Board. Can. 31: 1867–1872.
Cleveland, L., E.E. Little, S.J. Hamilton, D.R. Buckler & J.B. Hunn. 1986. Interactive toxicity of aluminium and acidity to early life stages of brook trout. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 115: 610–620.
Fletcher, D.J. 1984. The physiological control of appetite in fish. Comp. Biochem Physiol. 78A: 617–628.
Giles, M.A. 1988. Accumulation of cadmium by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri, during extended exposure. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 45: 1045–1053.
Giles, M.A. 1984. Electrolyte and water balance in plasma and urine of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri)) during chronic exposure to cadmium. Bull. Env. Cont. Toxicol. 36: 199–203.
Hara, T.J. 1982. Chemoreception in fishes. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam. 433 pp.
Harrison, S.E., J.F. Klaverkamp & R.H. Hesslein. 1990. Fates of metal radiotracers added to a whole-lake accumulation in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) and lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Water Air and Soil Pollution 52: 277–293.
Henry, M.G. & G.J. Atchison. 1979. Behavioral changes in bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) as indicators of sublethal effects of metals. Env. Biol. Fish. 4: 37–42.
Henry, M.G. & G.J. Atchison. 1986. Behavioral changes in social groups of bluegills exposed to copper. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 115: 590–595.
Hollander, M. & D.A. Wolfe. 1973. Nonparametric statistical methods. Wiley, New York.
Kislalioglu, M. & R.N. Gibson. 1976. Some factors governing prey selection by the 15-spines stickleback, Spinachia spinachia (L.). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 25: 150–169.
Little, E.E., R.D. Archeski, B.A. Flerow & V.I. Kozlovskaya. 1990. Behavioral indicators of sublethal toxicity in rainbow trout. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19: 380–385.
Mance, G. 1987. Pollution threat of heavy metals in aquatic environments. Pollution Monitoring Series, London. 372 pp.
Mathers, R.A., J.A. Brown & P.H. Johansen. 1985. The growth and feeding behaviour responses of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) exposed to PCP. Aquatic Toxicol 6: 157–164.
McCarty, L.S., J.A.C. Henry & A.H. Houston. 1978. Toxicity of cadmium to goldfish, Carassius auratus, in hard and soft water. J. Fish. Res. Board. Can. 35: 35–42.
McNicol, R.E. & E. Scherer. 1993. Influence of cadmium pre-exposure on the preference-avoidance responses of lake whitefish, Coregonus clupeaformis to cadmium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25: 36–40.
McNicol, R.E. & E. Scherer. 1991. Behavioral responses of large whitefish, Coregonus clupeaformis, to cadmium during preference-avoidance testing. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10: 225–234.
Morgan, M.J. & J.W. Kiceniuk. 1990. Effect of fenitrothion on the foraging behaviour of juvenile Atlantic salmon. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 9: 489–495.
Olla, B.L., W.H. Pearson & A.L. Studholme. 1980. Applicability of behavioral measures in environmental stress assessment. Rapp. P.V. Reun. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer. 179: 162–173.
Rand, G.M. 1984. Behaviour. pp. 221–263. In: G.M. Rand & S.P. Petrocelli (ed.) Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation. Washington, D.C.
Ravera, O. 1984. Cadmium in freshwater ecosystems. Experientia 40: 3–14.
Rombough, P.J. & E.T. Garside. 1984. Disturbed ion balance in allevins of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Can. J. Zool. 60: 2006–2014.
Sandheinrich, M.B. & G.J. Atchison. 1990. Sublethal toxicant effects on fish foraging behaviour: empirical vs. mechanistic approaches. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9: 107–119.
Sandheinrich, M.B. & G.J. Atchison. 1989. Sublethal copper effects on Bluegill, Leponmis macrochirus, foraging behaviour. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 46: 1977–1985.
Scherer, E. 1992. Behavioral responses as indicators of environmental alterations: approaches, results, developments. J Appl. Ichthyol. 8: 122–131.
Schuytema, G.S., P.O. Nelson, K.W. Malueg, A.V. Nebeker, D.F. Krawczyk, A.K. Ratcliff & J.H. Gakstatler. 1984. Toxicity of cadmium in water and sediment slurries to Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 3: 293–308.
Sprague, J.B. 1987. Effects of cadmium on freshwater fish. pp. 139–169. In: J.O. Nriagu & J.B. Sprague (ed.) Cadmium in the Aquatic Environment, John Wiley & Sons, Toronto.
Sprague, J.B. 1971. Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish, 3. Sublethal effects and safe concentrations. Water Research 5: 245–266.
Sturgeon, R.E., J.A.H. Desaulniers, S.S. Berman & D.S. Russel 1982. Determination of trace metals in estuarine sediments by graphite-fumace atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 134: 283–301.
Sullivan, J.F., G.J. Atchison, D.J. Kolar & A.W. McIntosh. 1978. Changes in the predator-prey behaviour of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) and large mouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) caused by cadmium. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 35: 446–451.
Woo, P.T.K., M. Sin & K. Wong. 1993. The effects of short-term acute cadmium exposure on blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus. Env. Biol. Fish. 37: 67–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kislalioglu, M., Scherer, E. & McNicol, R.E. Effects of cadmium on foraging behaviour of lake charr, Salvelinus namaycush . Environ Biol Fish 46, 75–82 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00001700
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00001700