Synopsis
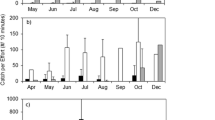
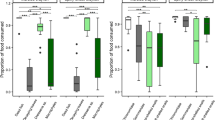
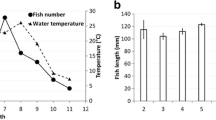
The biology of the prickly sculpin was investigated in Clear Lake, Lake County, California in order to determine how it has persisted in the face of introductions of numerous exotic species when most other native species have declined in abundance or have become extinct. Sculpins over 15 mm SL inhabited all types of benthic habitats in the lake, while post larval sculpins were pelagic when the postlarvae of exotic species were absent. The feeding ecology of sculpins was distinct from the other fishes in the lake in that they fed largely on amphipods and chironomid midge larvae regardless of the time of year, time of day, or habitat. Sculpins were uncommon in the stomachs of piscivorous fishes, except juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). It is concluded that prickly sculpins have persisted in Clear Lake in part because they are ecologically distinct from the exotic species and are not preyed upon by them to any great extent, and in part because they have managed to survive other man-related perturbations of this ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Broadway, J. E. 1978. Feeding ecology of the prickly sculpin (Cottus asper Richardson) in Clear Lake, Lake County, California. Unpubl. M.S. thesis. Univ. Calif., Davis 26 pp.
Cook, S. F., Jr. 1964. The potential of two native California fish in the biological control of chironomid midges (Diptera;Chironomidae). Mosquito News 24: 332–333.
Cook, S. F., Jr., J. D. Conners & R. L. Moore. 1964. The impact of the fishery upon the midge populations of Clear Lake, Lake County, California. Annals Entom. Soc. Amer. 57: 701–707.
Elston, R. E. & B. Bachen. 1976. Diel feeding cycle and some effects of light on feeding intensity of the Mississippi silversides,Menidia audens, in Clear Lake, California. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc. 105: 84–88.
Goldman, C. E. & R. G. Wetzel. 1963. A study of the primary productivity of Clear Lake, Lake County, California. Ecology 44: 283–294.
Hopkirk, J. D. 1973. Endemism in fishes of the Clear Lake Region. Univ. Calif. Pub. Zool. 96. 160 pp.
Hynes, H. B. N. 1950. The food of freshwater sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus andPygosteus pungitius), with a review of methods used in studies of the food of fishes. J. Anim. Ecol. 19: 36–58.
Kresja, R. J. 1967. The systematics of the prickly sculpinCottus asper Richardson, a polytypic species. Part I. Synonomy, nomenclatural history and distribution. Pac. Sci. 21: 241–251.
Moyle, P. B. 1976. Inland fishes of California. Univ. Calif. Press 405 pp.
Moyle, P. B. & N. Holzhauser. In press. Effects of the introduction of the Mississippi silverside (Menidia audens) and Florida largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides floridanus) on the feeding habits of young-of-year largemouth bass in Clear Lake, California. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc.
Paloumpis, A. A. 1958. Measurement of some factors affecting the catch in a minnow seine. Proc. Iowa Acad. Sci. 65: 580–586.
Windell, J. T. 1971. Food analysis and rate of digestion, pp. 214–216. In: W. E. Ricker (ed.), Methods for Assessment of Fish Production in Freshwaters. IBP Handbook 3. Blackwells, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broadway, J.E., Moyle, P.B. Aspects of the ecology of the prickly sculpin,Cottus asper Richardson, a persistent native species in Clear Lake, Lake County, California. Environ Biol Fish 3, 337–343 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000525
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000525