Abstract
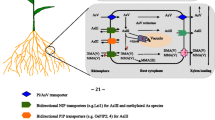
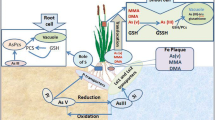
Arsenic (As) in food is a threat for human health, and among all cereal rice is the most important source of the metalloid through diet. The dynamic of the element and the natural ability of rice to uptake, transport, and accumulate the metalloid at grains have motivated important research to be carried out in this regard. Thus, the aim of this chapter is to draw a synthesis on the main factors which ultimately determines As content in rice, from its uptake from the soil solution to its transport, metabolism, and final accumulation in grain. The element is of natural occurrence, varying in concentration, and its chemical species are modified due to a range of factors, such as the soil redox state. Among all As species, arsenite [As (III)] is the most common in anoxic conditions, such as the ones found in flooded paddy rice fields, which form is preferred for rice root uptake. Rice is naturally efficient in As(III) uptake, compared to most crops already studied, which is mainly due to its improved ability to uptake and transport silicon, especially with the aid of aquaporins, as silicic acid and arsenite are chemically analogous. Similarly, the second most important As form, arsenate [As(V)], is mainly uptaken and transported through the phosphate way. After being uptaken, As is transported either via xylem or phloem and is loaded to the grain. Within rice tissues, the element can be metabolized, being reduced, biomethylated, complexed to other elements, or even sequestered into vacuoles. The knowledge regarding the mechanisms of As uptake, transport, and metabolization in rice allows one to draw strategies in order to mitigate the content of this element in the grains, either via management practices or also via breeding and biotechnological approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas G, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Khan MI, Amjad M, Hussain M, Natasha (2018) Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:59
Abedin MJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2002) Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiol 128:1120–1128
Awasthi S, Chauhan R, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD (2017) The journey of arsenic from soil to grain in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:1007
Bakhat HF, Zia Z, Fahad S, Abbas S, Hammad HM, Shahzad AN, Abbas F, Alharby H, Shahid M (2017) Arsenic uptake, accumulation and toxicity in rice plants: possible remedies for its detoxification: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:9142–9158
Bastías JM, Beldarrain T (2016) Arsenic translocation in rice cultivation and its implication for human health. Chil J Agric Res 76:114–122
Batista BL, Nigar M, Mestrot A, Rocha BA, Barbosa Júnior F, Price AH, Raab A, Feldmann J (2014) Identification and quantification of phytochelatins in roots of rice to long-term exposure: evidence of individual role on arsenic accumulation and translocation. J Exp Bot 65:1467–1479
Bauer P, Hell R (2006) Translocation of Iron in plant tissues. In: Barton LL, Abadia J (eds) Iron nutrition in plants and Rhizospheric microorganisms, 1st edn. Springer, Switzerland, pp 279–288
Briat J (2010) Arsenic tolerance in plants: “Pas de deux” between phytochelatin synthesis and ABCC vacuolar transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:20853–20854
Cao Y, Sun D, Ai H, Mei H, Liu X, Sun S, Xu G, Liu Y, Chen Y, Ma LQ (2017) Knocking out OsPht1;4 gene decreases arsenic uptake by rice plants and inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grains. Environ Sci Technol 51:12131–12138
Carey AM, Scheckel KG, Lombi E, Newville M, Choi Y, Norton GJ, Charnock JM, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2010) Grain unloading of arsenic species in rice. Plant Physiol 152:309–319
Carey AM, Norton GJ, Deacon C, Scheckel KG, Lombi E, Punshon T, Guerinot ML, Lanzirotti A, Newville M, Choi Y, Price AH, Meharg AA (2011a) Phloem transport of arsenic species from flag leaf to grain during grain filling. New Phytol 192:87–98
Carey AM, Lombi E, Donner E, de Jonge MD, Punshon T, Jackson BP, Guerinot ML, Price AH, Meharg AA (2011b) A review of recent developments in the speciation and location of arsenic and selenium in rice grain. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:3275–3286
Chen Y, Moore KL, Miller AJ, McGrath SP, Ma JF, Zhao FJ (2015) The role of nodes in arsenic storage and distribution in rice. J Exp Bot 66:3717–3724
Chen Y, Han Y-H, Cao Y, Zhu Y-G, Rathinasabapathi B, Ma LQ (2017) Arsenic transport in rice and biological solutions to reduce arsenic risk from rice. Front Plant Sci 8:268
Deng F, Yamaji N, Ma JF, Lee S, Jeon J, Martinoia E, Lee Y, Song W (2018) Engineering rice with lower grain arsenic. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1691–1699
Dhankher OP, Li Y, Rosen BP, Shi J, Salt D, Senecoff JF, Sashti NA, Meagher RB (2002) Engineering tolerance and hyperaccumulation of arsenic in plants by combining arsenate reductase and γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase expression. Nat Biotechnol 20:1140–1145
Dixit G, Singh AP, Kumar A, Singh PK, Kumar S, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Pandely V, Norton GJ, Dhankher OP, Tripathi RD (2015) Sulfur mediated reduction of arsenic toxicity involves efficient thiol metabolism and the antioxidant defense system in rice. J Hazard Mater 298:241–251
Duan G, Zhou Y, Tong Y, Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen BP, Zhu Y (2007) A CDC25 homologue from rice functions as an arsenate reductase. New Phytol 174:311–321
Duan G-L, Hu Y, Schneider S, McDermott J, Chen J, Sauer N, Rosen BP, Daus B, Liu Z, Zhu YG (2016) Inositol transporters AtINT2 and AtINT4 regulate arsenic accumulation in Arabidopsis seeds. Nat Plants 2:15202
Fleck AT, Mattusch J, Schenk MK (2013) Silicon decreases the arsenic level in rice grain by limiting arsenite transport. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 176:785–794
Guillod-Magnin R, Brüschweiler BJ, Aubert R, Haldimann M (2018) Arsenic species in rice and rice-based products consumed by toddlers in Switzerland. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 35:1164–1178
Hashimoto Y, Kanke Y (2018) Redox changes in speciation and solubility of arsenic in paddy soils as affected by sulfur concentrations. Environ Pollut 238:617–623
Hayashi S, Kuramata M, Abe T, Takagi H, Ozawa K, Ishikawa S (2017) Phytochelatin synthase OsPCS1 plays a crucial role in reducing arsenic levels in rice grains. Plant J 91:840–848
Hell R, Bergmann L (1990) γ-Glutamylcysteine synthetase in higher plants: catalytic properties and subcellular localization. Planta 180:603–612
Hu M, Li F, Liu C, Wu W (2015) The diversity and abundance of As(III) oxidizers on root iron plaque is critical for arsenic bioavailability to rice. Sci Rep 5:13611
Islam S, Rahman MM, Rahman MA, Naidu R (2017) Inorganic arsenic in rice and rice-based diets: health risk assessment. Food Control 82:196e202
Jia Y, Huang H, Zhong M, Wang F, Zhang L, Zhu Y (2013) Microbial arsenic methylation in soil and rice rhizosphere. Environ Sci Technol 47:3141–3148
Kamiya T, Islam MR, Duan G, Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2013) Phosphate deficiency signaling pathway is a target of arsenate and phosphate transporter OsPT1 is involved in As accumulation in shoots of rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59:580–590
Kumar S, Dubey RS, Tripathi RD, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK (2015) Omics and biotechnology of arsenic stress and detoxification in plants: current updates and prospective. Environ Int 74:221–230
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Meharg A, Bundschuh J (2018a) Arsenic speciation dynamics in paddy rice soil-water environment: sources, physico-chemical, and biological factors-a review. Water Res 140:403–414
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Meharg A, Bundschuh J (2018b) Arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is influenced by environment and genetic factors. Sci Total Environ 642:485–496
Lai PY, Cottingham KL, Steinmaus C, Karagas MR, Miller MD (2015) Arsenic and rice: translating research to address health care providers’ needs. J Pediatr 167:797–803
Li RY, Ago Y, Liu WJ, Mitani N, Feldmann J, McGrath SP, Ma JF, Zhao FJ (2009) The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species. Plant Physiol 150:2071–2080
Lindsay ER, Maathuis FJ (2017) New molecular mechanisms to reduce arsenic in crops. Trends Plant Sci 22:1016–1026
Liu WJ, Wood BA, Raab A, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Feldmann J (2010) Complexation of arsenite with phytochelatins reduces arsenite efflux and translocation from roots to shoots in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152:2211–2221
Lomax C, Liu WJ, Wu L, Xue K, Xiong J, Zhou J, McGrath SP, Meharg AA, Miller AJ, Zhao FJ (2012) Methylated arsenic species in plants originate from soil microorganisms. New Phytol 193(3):665–672
Luan M, Liu J, Liu Y, Han X, Sun G, Lan W, Luan S (2018) Vacuolar phosphate transporter 1 (VPT1) affects arsenate tolerance by regulating phosphate homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1345–1352
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu XY, Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9931–9935
Ma L, Wang L, Jia Y, Yang Z (2017) Accumulation, translocation and conversion of six arsenic species in rice plants grown near a mine impacted city. Chemosphere 183:44e52
Majzlan J, Drahota P, Filippi M (2014) Parageneses and crystal chemistry of arsenic minerals. Rev Mineral Geochem 79:17–184
Marin AR, Masscheleyn PH, Patrick WH (1992) The influence of chemical form and concentration of arsenic on rice growth and tissue arsenic concentration. Plant Soil 139:175–183
Meharg C, Meharg AA (2015) Silicon, the silver bullet for mitigating biotic and abiotic stress, and improving grain quality, in rice? Environ Exp Bot 120:8–17
Meng XY, Qin J, Wang LH, Duan GL, Sun GX, Wu HL, Chu CC, Ling HQ, Rosen BP, Zhu YG (2011) Arsenic biotransformation and volatilization in transgenic rice. New Phytol 191:49–56
Mishra S, Wellenreuther G, Mattusch J, Stärk HJ, Küpper H (2013) Speciation and distribution of arsenic in the non-hyperaccumulator macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum. Plant Physiol 163:1396–1408
Mishra S, Mattush J, Wennrich R (2017) Accumulation and transformation of inorganic and organic arsenic in rice and role of thiol-complexation to restrict their translocation to shoot. Sci Rep 7:40522
Mitra A, Chatterjee S, Moogouei R, Gupta DK (2017) Arsenic accumulation in rice and probable mitigation approaches: a review. Agronomy 7:67
Norton GJ, Lou-Hing DE, Meharg AA, Price AH (2008) Rice-arsenate interactions in hydroponics: whole genome transcriptional analysis. J Exp Bot 59:2267–2276
Pal R, Rai JPN (2010) Phytochelatins: peptides involved in heavy metal detoxification. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:945–963
Punshon T, Jackson BP, Meharg AA, Warczack T, Scheckel K, Guerinot ML (2017) Understanding arsenic dynamics in agronomic systems to predict and prevent uptake by crop plants. Sci Total Environ 581–582:209–220
Rahman MA, Hassler C (2014) Is arsenic biotransformation a detoxification mechanism for microorganisms? Aquat Toxicol 146:212–219
Rai A, Tripathi P, Dwivedi S, Dubey S, Shri M, Kumar S, Tripathi PK, Dave R, Kumar A, Singh R, Adhikari B, Bag M, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK, Chakrabarty D, Tuli R (2011) Arsenic tolerances in rice (Oryza sativa) have a predominant role in transcriptional regulation of a set of genes including sulphur assimilation pathway and antioxidant system. Chemosphere 82:986–995
Seyfferth AL (2015) Abiotic effects of dissolved oxyanions on iron plaque quantity and mineral composition in a simulated rhizosphere. Plant Soil 397:43–61
Sharma I (2012) Arsenic induced oxidative stress in plants. Biologia 67:447–453
Shen J, Yuan L, Zhang J, Li H, Bai Z, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang F (2011) Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiol 156:997–1005
Shi S, Wang T, Chen Z, Tang Z, Wu Z, Salt DE, Chao D, Zhao F (2016) OsHAC1;1 and OsHAC1;2 function as arsenate reductases and regulate arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol 172:1708–1719
Song WY, Park J, Mendoza-Cozatl DG, Suter-Grotemeyer M, Shim D, Hortensteiner S, Geisler M, Weder B, Rea PA, Rentsch D, Schroeder JI, Lee Y, Martinoia E (2010) Arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis is mediated by two ABCC-type phytochelatin transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:21187–21192
Song WY, Yamaki T, Yamaji N, Ko D, Jung KH, Fujii-Kashino M, An G, Martinoia E, Lee Y, Ma JF (2014) A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:15699–15704
Souri Z, Karimi N, Sandalio LM (2017) Arsenic Hyperaccumulation strategies: An overview. Front Cell Dev Biol 5:67
Stroud JL, Khan MA, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Dasgupta T, Zhu YG, Price AH, Meharg AA, McGrat SP, Zhao FJ (2011) Assessing the labile arsenic pool in contaminated paddy soils by isotopic dilution techniques and simple extractions. Environ Sci Technol 45:4262–4269
Suriyagoda LDB, Dittert K, Lambers H (2018) Mechanism of arsenic uptake, translocation and plant resistance to accumulate arsenic in rice grains. Agric Ecosyst Environ 253:23–37
Tang Z, Chen Y, Chen F, Ji Y, Zhao FJ (2017) OsPTR7 (OsNPF8. 1), a putative peptide transporter in rice, is involved in dimethylarsenate accumulation in rice grain. Plant Cell Physiol 58:904–913
Thomas D, Bron P, Ranchy G, Duchesne L, Cavalier A, Rolland J-P, Raguénès-Nicol C, Hubert J-F, Haase W (2002) Aquaglyceroporins, one channel for two molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta 1555:181–186
Tiwari M, Sharma D, Dwivedi S, Singh M, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK (2014) Expression in Arabidopsis and cellular localization reveal involvement of rice NRAMP, OsNRAMP1, in arsenic transport and tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 37:140–152
Tuli R, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Tripathi RD (2010) Recent advances in arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice. Mol Breed 26:307–323
Uraguchi S, Tanaka N, Hofmann C, Abiko K, Ohkama-Ohtsu N, Weber M, Kamiya T, Sone Y, Nakamura R, Takanezawa Y, Kiyono M, Fujiwara T, Clemens S (2017) Phytochelatin synthase has contrasting effects on cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice grains. Plant Cell Physiol 58:1730–1742
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Mechanisms to cope with arsenic or cadmium excess in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:364–372
Verma PK, Verma S, Meher AK, Pande V, Mallick S, Bansiwal AK, Tripathi RD, Dhankher OP, Chakrabarty D (2016) Overexpression of rice glutaredoxins (OsGrxs) significantly reduces arsenite accumulation by maintaining glutathione pool and modulating aquaporins in yeast. Plant Physiol Biochem 106:208–217
Wang P, Zhang W, Mao C, Xu G, Zhao F-J (2016) The role of OsPT8 in arsenate uptake and varietal difference in arsenate tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 67:6051–6059
Wu Z, Ren H, McGrath SP, Wu P, Zhao F-J (2011) Investigating the contribution of the phosphate transport pathway to arsenic accumulation in Rice. Plant Physiol 157:498–508
Xu XY, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2007) Rapid reduction of arsenate in the medium mediated by plant roots. New Phytol 176:590–599
Yamaguchi N, Nakamura T, Dong D, Takahashi Y, Amachi S, Makino T (2011) Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution. Chemosphere 83:925–932
Yamamoto T, Nakamura A, Iwai H, Ishii T, Ma JF (2012) Effect of silicon deficiency on secondary cell wall synthesis in rice leaf. J Plant Res 125:771–779
Yang J, Gao MX, Hu H, Ding XM, Lin HW, Wang L, Xu JM, Mao CZ, Zhao FJ, Wu ZC (2016) OsCLT1, a CRT-like transporter 1, is required for glutathione homeostasis and arsenic tolerance in rice. New Phytol 211:658–670
Ye Y, Li P, Xu T, Zeng L, Cheng D, Yang M, Luo J, Lian X (2017) OsPT4 contributes to arsenate uptake and transport in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:2197
Zhang J, Zhao QZ, Duan GL, Huang YC (2011) Influence of sulphur on arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 72:34–40
Zhang J, Martinoia E, Lee Y (2018) Vacuolar transporters for cadmium and arsenic in plants and their applications in phytoremediation and crop development. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1317–1325
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg AA, McGrath SP (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181:777–794
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010) Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:535–559
Zhao F-J, Stroud JL, Khan MA, McGrath SP (2012) Arsenic translocation in rice investigated using radioactive 73As tracer. Plant Soil 350:413–420
Zhao F-J, Zhu YG, Meharg AA (2013) Methylated arsenic species in rice: geographical variation, origin, and uptake mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 47:3957–3966
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Costa de Oliveira, A., Batista, B.L., Pegoraro, C., Venske, E., Viana, V.E. (2020). Mechanisms of Arsenic Uptake, Transport, and in planta Metabolism in Rice. In: Srivastava, S. (eds) Arsenic in Drinking Water and Food. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8587-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8587-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8586-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8587-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)