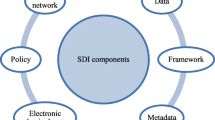
Abstract
From several years, public health is one of the major problems faced by several countries including India. This requires proper Public Health Information System (PHIS) that is safe, reliable, and efficient. At present, most of the public-health-based information and management system are lacking the support of real-time data uploading, data visualization, data analysis, and decision-making. To overcome these issues, Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) became the promising approach through which the improvements can be made. SDI provides an environment in which users can share and access the geospatial data with the common set of policies, standards, and network protocols. The main objective of the present work is to conceptualize an SDI framework for public health using open-source resources so that users can access the health information easily from the developed system. Moreover, the concept presented in the paper can be applied onto the larger scale.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathys T, Boulos MNK (2011) Geospatial resources for supporting data standards, guidance and best practice in health informatics. BMC Res Notes 4:19
Buzzelli M, Jerrett M, Burnett R, Finklestein N (2003) Spatiotemporal perspectives on air pollution and environmental justice in Hamilton, Canada, 1985–1996. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 93:557–573
Martin C, Curtis B, Fraser C, Sharp B (2002) The use of a GIS-based malaria information system for malaria research and control in South Africa. Health Place 8:227–236
Mitchell R, Dorling D, Shaw M (2002) Population production and modelling mortality—an application of geographic information systems in health inequalities research. Health Place 8:15–24
Croner CM (2004) Public health GIS and the internet. J Map Geogr Libr 1:105–135. Adv Geosp Inf Collect Arch
Gao S, Mioc D, Yi X, Anton F, Oldfield E, Coleman DJ (2009) Towards web-based representation and processing of health information. Int J Health Geogr 8:3
Nebert DD (2004) Developing spatial data infrastructures: the SDI cookbook
Warnest M, Feeney MEF, Rajabifard A, Williamson IP (2002) Fundamental partnerships driving spatial data infrastructure development within Australia. Cartography 31:11–20
Rajabifard A, Williamson IP (2001) Spatial data infarstructures: concept, SDI hierarchies and future directions. In: Proceedings of GEOMATICS’80 conference, p 10
Granell C, Fernández ÓB, Díaz L (2014) Geospatial information infrastructures to address spatial needs in health: collaboration, challenges and opportunities. Futur Gener Comput Syst 31:213–222
Rajabifard A, Williamson IP, Holland P, Johnstone G (2000) From local to global SDI initiatives: a pyramid of building blocks. In: 4th global spatial data infrastructure conference, Cape Town, South Africa, pp 13–15
Rajabifard A, Feeney M-E, Williamson IP (2002) Directions for the future of SDI development. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 4:11–22
Crompvoets J, Bregt A, Rajabifard A, Williamson I (2004) Assessing the worldwide developments of national spatial data clearinghouses. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 18:665–689
Yang CP, Cao Y, Evans J, Kafatos M, Bambacus M (2006) Spatial web portal for building spatial data infrastructure. Geogr Inf Sci 12:38–43
FGDC. Homeland security and geographic information systems-how GIS and mapping technology can save lives and protect property in post-September 11th America. https://www.fgdc.gov/resources/whitepapers-reports/white-papers/homeland-security-gis
Foster RW, Ryttersgaard J (2001) The Nairobi statement on spatial information for sustainable development. In: FIG working week 2001, Nairobi
Richards T, Croner C, Rushton G, Brown C, Fowler L (1999) Geographic information systems and public health mapping the future. Public Health Rep 114:359–373
Yang DH, Goerge R, Mullner R (2006) Comparing GIS-based methods of measuring spatial accessibility to health services. J Med Syst 30:23–32
Hu R, Dong S, Zhao Y, Hu H, Li Z (2013) Assessing potential spatial accessibility of health services in rural China: a case study of Donghai county. Int J Equity Health 12:35
Thompson J, Eagleson S, Ghadirian P, Rajabifard A (2009) SDI for collaborative health services planning. In: Global spatial data infrastructures world conference, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Boulos MNK (2004) Towards evidence-based, GIS-driven national spatial health information infrastructure and surveillance services in the United Kingdom. Int J Health Geogr 3:1
Goodchild MF, Fu P, Rich P (2007) Sharing geographic information: an assessment of the geospatial one-stop. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 97:250–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tripathi, A.K., Agrawal, S., Gupta, R.D. (2020). A Conceptual Framework of Public Health SDI. In: Ghosh, J., da Silva, I. (eds) Applications of Geomatics in Civil Engineering. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering , vol 33. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7067-0_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7067-0_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-7066-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-7067-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)