Abstract
M-learning is a potential method for teaching and learning, but its effects on students’ learning performance are varied compared with traditional instruction. This meta-analysis is a statistical review of 34 experimental studies during the period 2010–2016, in which 4052 participants and 49 effect sizes were analyzed. The combined effect size is 0.828, which shows that (a) M-learning is more effective than traditional learning with a significant difference. Furthermore, moderating variable analyses manifest that (b) mobile learning has a positive impact on those selected moderators, and (c) there is no significant difference in different levels of manipulated variables. Theory and practice of the findings are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
References
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J., & Rothstein, H. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Chu, H. C. (2014). Potential negative effects of mobile learning on students’ learning achievement and cognitive load – a format assessment perspective. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 17(1), 332–344.
Crescente, M. L., & Lee, D. (2011). Critical issues of m-learning: Design models, adoption processes, and future trends. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Industrial Engineers., 28(2), 111–123.
Crompton, H. (2013). A historical overview of mobile learning: Toward learner-centered education. In Z. L. Berge & L. Y. Muilenburg (Eds.), Handbook of mobile learning (pp. 3–14). Florence, KY: Routledge.
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. London: Routledge.
Huang, C. S., Yang, S. J., Chiang, T. H., & Su, A. Y. (2016). Effects of situated mobile learning approach on learning motivation and performance of EFL students. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 19(1), 263.
Kim, H., Lee, M., & Kim, M. (2014). Effects of mobile instant messaging on collaborative learning processes and outcomes: The case of South Korea. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 17(2), 31.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2000). Practical meta-analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sandberg, J., Maris, M., & de Geus, K. (2011). Mobile English learning: An evidence-based study with fifth graders. Computers & Education, 57(1), 1334–1347.
Sung, Y. T., Chang, K. E., & Liu, T. C. (2016). The effects of integrating mobile devices with teaching and learning on students’ learning performance: A meta-analysis and research synthesis. Computers & Education, 94, 252–275.
Zacharia, Z. C., Lazaridou, C., & Avraamidou, L. (2016). The use of mobile devices as means of data collection in supporting elementary school students’ conceptual understanding about plants. International Journal of Science Education, 38(4), 596–620.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendices
Appendices
-
Appendix 1: Forest plot of the effect sizes and 95% CI of the 34 experiments
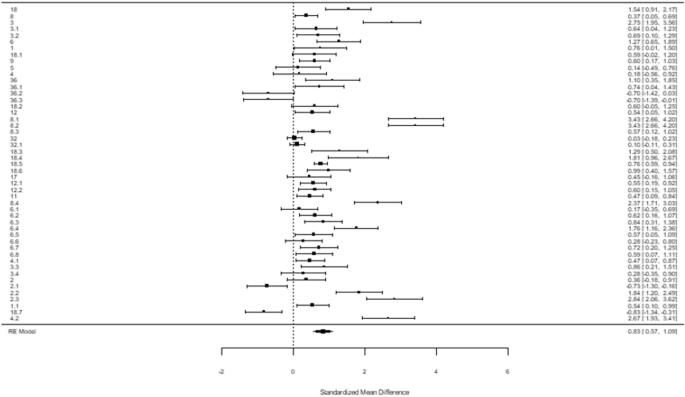
-
Appendix 2: Funnel plot of the effect sizes of 34 experiments
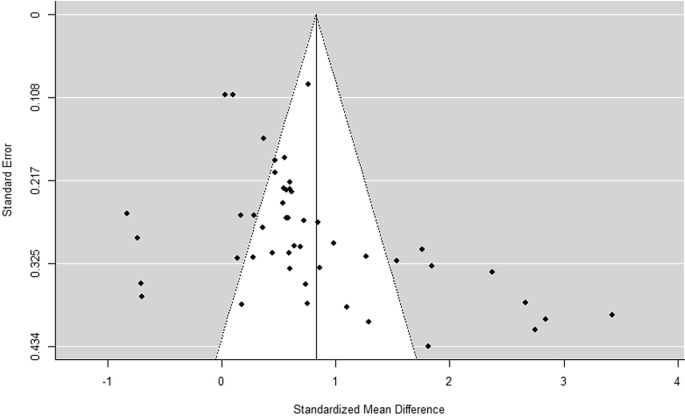
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Feng, Y., Liao, Y., Ren, Y. (2018). Effects of M-Learning on Students’ Learning Outcome: A Meta-analysis. In: Deng, L., Ma, W., Fong, C. (eds) New Media for Educational Change. Educational Communications and Technology Yearbook. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8896-4_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8896-4_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-8895-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-8896-4
eBook Packages: EducationEducation (R0)



