Abstract
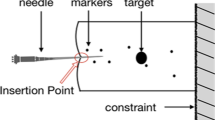
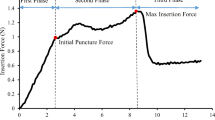
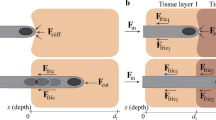
The unstable needle insertion, contributing to imprecise insertion, can be reflected from insertion force stability. To improve the accuracy of needle-based intervention procedures and guide the investigation on needle steering technologies, a series of needle insertion experiments were performed on different soft tissues including single-layer PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) phantoms, multi-layer PVA phantoms and porcine livers. The effects of insertion velocities, tissue properties and tissue structures on insertion force stability were investigated. For mechanical noises in force data vary with interventional equipment, they were filtered before quantitative analysis of insertion force stability. The unit amplitude of insertion force was directly used to reflect the insertion stability. The results from both the single-layer PVA phantoms and porcine livers show that there is a critical velocity, under which the unit amplitude sharply decreases with the increase of velocity and above which it almost does not vary with velocity. In the actual application, insertion velocity above this critical value can be adopted to improve the insertion stability. The multi-layer PVA phantom tests show that the unit amplitude increases firstly and then decreases with the increase of PVA composition. By changing the direction of insertion into the same multi-layer PVA phantom, results indicate that both friction and cutting force can lead to unstable insertion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolhassani N, Patel R (2006) Deflection of a flexible needle during insertion into soft tissue. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE EMBS annual international conference, pp 3858–3861. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2006.259519
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Ayazi F (2007a) Effects of different insertion methods on reducing needle deflection. In: Proceedings of the 29th annual international conference of the IEEE EMBS, pp 491–494. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2007.4352330
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Ayazi F (2007b) Needle control along desired tracks in robotic prostate brachytherapy. In: 2007 IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, pp 3361–3366. doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2007.4413819
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2007c) Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med Eng Phys 29(4):413–431. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2006.07.003
Abolhassani N, Patel RV, Ayazi F (2007d) Minimization of needle deflection in robot-assisted percutaneous therapy. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 3(2):140–148. doi:10.1002/rcs.136
Alja’afreh T (2010) Investigating the needle dynamic response during insertion into soft tissue. J Eng Med 224(4):531–540. doi:10.1243/09544119JEIM698
Alterovitz R, Goldberg K, Okamura A (2005) Planning for steerable bevel-tip needle insertion through 2d soft tissue with obstacles. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1640–1645. doi:10.1109/ROBOT.2005.1570348
Alterovitz R, Branicky M, Goldberg K (2008) Motion planning under uncertainty for image-guided medical needle steering. Int J Robot Res 27(11–12):1361–1374. doi:10.1177/0278364908097661
Asadian A, Patel RV, Kermani MR (2014) Dynamics of translational friction in needle-tissue interaction during needle insertion. Ann Biomed Eng 42(1):73–85. doi:10.1007/s10439-013-0892-5
Chena JG, Zhang SW (2011) Liver cancer epidemic in china: past, present and future. Semin Cancer Biol 21(1):59–69. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.11.002
DiMaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005a) Interactive simulation of needle insertion models. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(7):1167–1179. doi:10.1109/TBME.2005.847548
DiMaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005b) Needle steering and motion planning in soft tissues. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(6):965–974. doi:10.1109/TBME.2005.846734
Duindam V, Xu JJ, Alterovitz R, Sastry S, Goldberg K (2010) Three-dimensional motion planning algorithms for steerable needles using inverse kinematics. Int J Robot Res 29(7):789–800. doi:10.1177/0278364909352202
Fukushima Y, Naemura K (2014) Estimation of the friction force during the needle insertion using the disturbance observer and the recursive least square. ROBOMECH J 1(1):1–8. doi:10.1186/s40648-014-0014-7
Fukushimaa Y, Saitoa K, Naemuraa K (2013) Estimation of the cutting force using the dynamic friction coefficient obtained by reaction force during the needle insertion. Procedia CIRP 5:265–269. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2013.01.052
Glozman D, Shoham M (2007) Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Rob 23(3):459–467. doi:10.1109/TRO.2007.898972
Jiang S, Li P, Yu Y, Liu J, Yang ZY (2014) Experimental study of needle-tissue interaction forces: effect of needle geometries, insertion methods and tissue characteristics. J Biomech 47(13):3344–3353. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.08.007
Lee H, Kim J (2014) Estimation of flexible needle deflection in layered soft tissues with different elastic moduli. Med Biol Eng Compu 52(9):729–740. doi:10.1007/s11517-014-1173-7
Lorenzo DD, Koseki Y, Momi ED, Chinzei K, Okamura AM (2011) Experimental evaluation of a coaxial needle insertion assistant with enhanced force feedback. In: 33rd annual international conference of the IEEE EMBS, pp 3447–3450. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6090932
Mallapragada VG, Sarkar N, Podder TK (2009) Robot-assisted real-time tumor manipulation for breast biopsy. IEEE Trans Rob 25(2):316–324. doi:10.1109/TRO.2008.2011418
Misra S, Reed KB, Douglas AS, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2008) Needle-tissue interaction forces for bevel-tip steerable needles. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Biennial IEEE/RAS-EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, pp 224–231. doi:10.1109/BIOROB.2008.4762872
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2010a) Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int J Robot Res 29(13):1640–1660. doi:10.1177/0278364910369714
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2010b) Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int J Robot Res 29(13):1640–1660. doi:10.1177/0278364910369714
O’Leary MD, Sirnone C, Washio T, Yoshinaka K, Okamura AM (2003) Robotic needle insertion: effects of friction and needle geometry. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE international conference on robotics & automation, pp 1774–1780. doi:10.1109/ROBOT.2003.1241851
Okamura AM, Simone C, O’Leary MO (2004) Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(10):1707–1716. doi:10.1109/TBME.2004.831542
Park W, Wang YF, Chirikjian GS (2010) The path-of-probability algorithm for steering and feedback control of flexible needles. Int J Robot Res 29(7):813–830. doi:10.1177/0278364909357228
Webster RJIII, Kim JS, Cowan NJ, Chirikjian GS, Okamura AM (2006) Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int J Robot Res 25(5–6):509–525. doi:10.1177/0278364906065388
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51165040) and the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province (No. 2015-ZJ-906).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Zhejiang University Press and Springer Science+Business Media Singapore
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, Q., Gao, Dd. (2017). Research on the Stability of Needle Insertion Force. In: Yang, C., Virk, G., Yang, H. (eds) Wearable Sensors and Robots. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 399. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2404-7_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2404-7_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-2403-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-2404-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)