Abstract
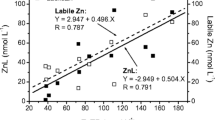
Samples from the Scheldt estuary have been assayed for dissolved Cd, Cu and Zn using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry, either as total (after UV irradiation) or labile concentrations. Under these experimental conditions, labile concentrations ranged between 51–65% of total Cu, 16–66% of total Zn and 53–91% of total Cd. The metal-organic interactions were assessed by evaluating (a) the distribution coefficient Kd for the distribution of the metals between the liquid phase (complexation) and their binding to particulate matter, and (b) the competitive effect exerted by inorganic complexing ligands using a multi-element interaction model. The proportion of organically bound metals (strong and labile) was estimated, in this speciation scheme, to range from 86 to 99% for Cu, from 90 to 96% for Zn, and from 10 to 35% for Cd. From the dissolved organic carbon distribution in the Scheldt (≤ 10 mg C 1−1) and taking into account competition from major cations Ca and Mg, free ligand concentrations available for heavy metal complexation were estimated to be ≤ 0.15 mg C 1−1. With these values, conditional stability constants for the chelation of Cu, Zn and Cd were calculated assuming either a single-step or a two-step complexation in the dissolved phase. Given the assumptions made in these models, stability constants in the range of 107.8–1010.6 for Cu, 107.0–109.1 for Zn and 106.9–108.9 for Cd were obtained. The relevance of these data to previous in vitro and in situ studies is discussed taking into consideration current concepts of metal binding affinity for organic ligands.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeyens, W., M. Bogaert, G. Decadt, H. Dedeurwaerder, F. Dehairs, M. Dejonghe, G. Gillain, L. Goeyens and S. Wartel, 1982. Distribution, transport and fate of Bi, Cd, Cu, Hg, Pb, Sb, and Zn in the Belgian coastal marine environment. In A. Distèche and I. Elskens (eds), Distribution, transport and fate of heavy metals in the Belgian coastal marine environment, Projet Mer, Rapport final, 2. Services du Premier Ministre. Programmation de la Politique Scientifique: 7–138.
Baeyens, W., G. Gillain, G. Decadt and I. Elskens, 1987. Trace metals in the eastern part of the North Sea. I: Analyses and short-term distributions. Oceanol. Acta. 10: 169–179.
Baeyens, W., M. Elskens, G. Gillain and L. Goeyens, 1998. Biogeochemical behaviour of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the Scheldt estuary during the period 1981–1983. Hydrobiologia 366: 15–44.
Balls, P. W., 1989. The partition of trace metals between dissolved and particulate phases in European coastal waters: a compilation of field data and comparison with laboratory studies. Neth. J. Sea Res. 23: 7–14.
Batley, G. E. and T. M. Florence, 1976. Determination of the chemical forms of dissolved cadmium, lead and copper in seawater. Mar. Chem. 4: 347–353.
Duinker, J. C. and C. J. Kramer, 1977. An experimental study on the speciation of dissolved zinc cadmium, lead and copper in river Rhine and North Sea water, by differential pulsed anodic stripping voltarometry. Mar. Chem. 5: 207–228.
Elskens, M., M. Leermakers, S. Panutrakul, F. Monteny & W. Baeyens, 1991. Microbial activity in sandy and muddy estuarine sediments. Gen-Marine Lett. 11: 194–198.
Florence, T. M., 1989. Electrochemical techniques for trace element speciation in waters. In G. E. Batley (ed.), Trace element speciation: Analytical Methods and Problems. CRC Press, Inc. Boca Raton, Florida: 77–116.
Frankignoulle, M., I. Bourge and R. Wollast, 1996. Atmospheric Co2 fluxes in a highly polluted estuary (The Scheldt). Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 365–369.
Houghton, R. P., 1979. Metal complexes in organic chemistry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 308 pp.
Leermakers, M., M. Elskens, S. Panutrakul, F. Monteny & W. Baeyens, 1993. Geochemistry of mercury in an intertidal flat of the Scheldt estuary. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 27: 267–277.
Lippard, S. J. and J. M. Berg, 1994. Principles of bioinorganic chemistry. University Science Books, Mill Valley, California, 409 pp.
Mantoura, R. F. C., A. Dickson and J. P. Riley, 1978. The complexation of metals with humic materials in natural waters. Estuar. coast. mar. Sci. 6: 387–408.
Monteny, F., M. Elskens and W. Baeyens, 1993. The behaviour of copper and zinc in the Scheldt estuary. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 27: 279–286.
Morel, F. and J. Morgan, 1972. A numerical method for computing equilibria in aqueous chemical systems. Envir. Sci. Technol. 6: 58–67.
Panutrakul, S. and W. Baeyens, 1991. Behaviour of heavy metals in a mud flat sediment of the Scheldt estuary, Belgium. Mar. Poll. Bull. 22: 128–134.
Piotrowicz, S. R., G. R. Harvey, M. Springer-Young, R. A. Courant & D. A. Boran, 1983. Studies of cadmium, copper, and zinc interactions with marine fulvic and humic materials in seawater using anoding stripping voltammetry. In C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Burton and E. D. Goldberg (eds), Trace Metals in Sea Water, Plenum Press, New York and London: 699–718.
Ramette, R. W., 1981. Chemical equilibrium and analysis. Addison-Wesley Publishing Compagny, Massachusetts, 765 pp.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., P. M. Gschwend and D. M. Imboden, 1993. Environmental Organic Chemistry. John Wiley and Sons, INC. New York/Chichester/Brisbane/Toronto/Singapore, 681 pp.
Stumm, W. and J. J. Morgan, 1981. Aquatic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons, INC. New York/Chichester/Brisbane/Toronto/Singapore, 780 pp.
Sugawara, M., P. Valenta, H. W. Nurnberg and T. Kambara, 1984. Voltammetric study of the speciation of cadmium (II) with Laspartic acid in sea water. J. Electroanal. chem. 180: 343–354.
Valenta, P., E. K. Duursma, A. G. A. Merks, H. Rutzel & H. W. Nurnberg, 1986. Distribution of Cd, Pb, and Cu between the dissolved and particulate phases in the Eastern and Western Scheldt estuary. Sci. Total Envir. 53: 41–76.
Valenta, P., M. L. S. Simoes-Goncalves and M. Sugawara, 1984. Voltammetric studies on the speciation of cadmium and zinc by amino acids in sea water. In C. J. M. Krammer & J. C. Duinker (eds), Complexation of Trace Metals in Natural Waters, Martinus Nijhoff/W. Junk Publ., The Hague, Boston, Lancaster: 357–366.
van den Berg, C. M. G. and S. Dharmvanij, 1984. Organic complexation of zinc in estuarine interstitial and surface water samples. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 1025–1036.
van den Berg, C. M. G., A. G. A. Merks and E. K. Duursma, 1987. Organic complexation and its control of the dissolved concentrations of copper and zinc in the Scheldt estuary. Estuar. coast. mar. Sci. 24: 785–797.
Wollast, R., 1976. Transport and accumulation de polluants dans l’estuaire de l’Escaut. In J. C. J. Nihon] and R. Wollast (ed.), L’estuaire de l’Escaut, Projet Mer, rapport final, 10. Services du Premier Ministre, Programmation de la Politique Scientifique: 191–128.
Woods, T. L. and R. M. Garrels, 1987. Thermodynamic values at low temperature for natural inorganic materials. An Uncritical Summary. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York, 242 pp.
Zuehlke, R. W. and D. R. Kester, 1983. Copper speciation in marine waters. In C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Burton & E. D. Goldberg (eds). Trace Metals in Sea Water. Plenum Press, New York and London: 773–788.
Zwolsman, J. J. G. and G. T. M. van Eck, 1991. The behaviour of dissolved Cd, Cu and Zn in the Scheldt estuary. Estuarine Water Quality Management, Springer-Verlag, Berlin: 413–420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Baeyens, W., Goeyens, L., Monteny, F., Elskens, M. (1998). Effect of organic complexation on the behaviour of dissolved Cd, Cu and Zn in the Scheldt estuary. In: Baeyens, W.F.J. (eds) Trace Metals in the Westerschelde Estuary: A Case-Study of a Polluted, Partially Anoxic Estuary. Developments in Hydrobiology, vol 128. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3573-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3573-5_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-5062-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-3573-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive