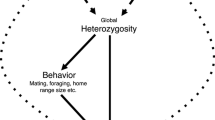
Abstract
Developmental homeostasis, measured as either fluctuating asymmetry or variance of morphological characters,increases with enzyme heterozygosity in many, but not all, natural populations. These results have been reported for Drosophila, monarch butterflies, honeybees, blue mussels, side-blotched lizards, killifish, salmonid fishes, guppies, Sonoran topminnows, herring, rufous-collared sparrows, house sparrows, brown hares, white-tailed deer, and humans. Because heterozygosity at a few loci can not predict heterozygosity of the entiry genome, these loci must be detecting localized zones that influence the developmental environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard, R. W., 1975. The mating system and microevolution. Genetics 79s: 115–126.
Baker, C. M. A. & C. Manwell, 19077. Heterozygosity of the sheep: Polymorphism of ’malic enzyme’, isocitrate dehydrogenase (Nadp), catalase and esterase. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 30: 127–140.
Bayne, B. L. & R. C. Newell, 1983. Physiological energetics in marine molluscs. In A. S. M. Saleudden and K. M. Wilburg (eds.) The Mollusca 4: 407–515. Academic Press, New York.
Beacham, T. D. & R. E. Withler, 1985. Heterozygosity and morphological variability of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) in southern British Columbia. Heredity 54: 313–322.
Beacham, T. D. & R. E. Withler, 1987. Developmental stability and heterozygosity in chum (Oncorhynchus keta) and pink (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) salmon. Can. J. Zool 65: 1823–1826.
Beacham, T. D., 1991. Developmental stability, heterozygosity, and genetic analysis of morphological variation in pink salmon ’Oncorhynchus gorbuscha’. Can. J. Zool. 69: 274–278.
Beardmore, J. A. & S. A. Shami, 1979. Heterozygosity and the optimum phenotype under stabilising selection. Aquilo. Ser. Zool. 20: 100–110.
Bijlsma-Meeles, E. & R. Bijlsma, 1988. The alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism in Drosophila melanogaster. Fitness measurements and predictions under conditions with no alcohol stress. Genetics 120: 743–753.
Booth, C. L., P. S. Woodruff & S. J. Gould, 1990. Lack of significant associations between allozyme heterozygosity and phenotypic traits in the land snail Cerion. Evolution 44: 210–213.
Bottini, E., F. Gloria-Bottini, P. Lucarelli, Al Polzonetti, F. Santoro & A. Ververi, 1979. Genetic polymorphisms and intrauterine development: Evidence of decreased heterozygosity in light for dates human newborn babies. Experientia 35: 1565–1567.
Bruckner, D., 1976. The influence of genetic variability on wing symmetry in honeybees. (Apis mellifera). Evolution 30: 100–108.
Chakraborty, R., 1981. The distribution of the number of heterozygous loci in an individual in natural populations. Genetics 98: 461–466.
Chakraborty, R., 1987. Biochemical heterozygosity and phenotypi variability of polygenic traits. Heredity 59: 19–28.
Chakraborty, R. & N. Ryman, 1983. Relationship of mean and variance of genotypic values with heterozygosity per individual in a natural population. Genetics. 103: 149–152.
Clarke, G. M., G. W. Brand & M. J. Whitten, 1986. Fluctuating asymmetry: A technique for measuring developmental stress caused by inbreeding. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 39: 145–153.
Clarke, G. M., B. P. Oldroyd & P. L. Hunt, 1992. The genetic basic of developmental stability in Apis mellifera: heterozygosity versus genic balance. Evolution 46: 753–762.
Clarke, G. M. & J. A. McKenzie, 1987. Developmental stability of insecticide resistant phenotypes in the blowfly: A result of canalizing natural selection. Nature 325: 345–346.
Coelho, J. R. & J. B. Mitton, 1988. Oxygen consumption during hovering is associated with genetic variation of enzymes in honey-bees. Functional Ecology 2: 141–146.
Cothran, E. G., R. Chesser, M. H. Smith & P. E. Johns, 1983. Influences of genetic variability and maternal factors on fetal growth in white-tailed deer. Evolution 37: 282–291.
Danzmann, R. G., M. M. Ferguson & F. W. Allendorf, 1987. Heterozygosity and oxygen-consumption rate as predictors of growth and developmental rate in rainbow trout. Physiol. Zool. 60: 211–220.
Danzmann, R. G., M. M. Ferguson & F. W. Allendorf, 1988. Heterozygosity and components of fitness in a strain of rainbow trout. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 39: 285–304.
Diehl, W. J., 1989. Genetics of carbohydrate metabolism and growth in Eisemia foetida (Oligochataea: Lumbricidae). Heredity 61: 379–387.
Diehl, W. J., P. M. Gaffney & R. K. Koehn, 1986. Physiological and genetic aspects of growth in the mussel Mytilus edulis. I. Oxygen consumption, growth, and weight loss. Physiol Zool. 59:201–211.
Diehl, W. P., P. M. Gaffney, J. H. McDonald & R. K. Koehn, 1985. Relationship between weight standardized oxygen consumption and multiple-locus heterozygosity in the marine mussel Mytilus edulis L. (Mollusca), pp. 531–536 in Proceedings of the 19th European Marine Biology Symposium,edited by P. Gibbs. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
DiMichele, L., K. Paynter & D. A. Powers, 1991. Lactate dehydrogenase-B allozymes directly affect development of Fundulus heteroclitus. Science 253: 898–900.
DiMichele, L. & D. A. Powers, 1991. Developmental heterochrony and differential mortality in the model teleost, Fun- dulus heteroclitus. Physiological Zoology 64: 1426–1443.
DiMichele, L. & D. A. Powers, 1982a. Physiological basis for swimming endurance differences between LDH-B genotypes of Fundulus heteroclitus. Science 216: 1014–1016.
DiMichele, L. & D. A. Powers, 1982b. LDH-B genotype specific hatching times of Fundulus heteroclitus embryos. Nature 296: 560–563.
DiMichele, L. & D. A. Powers, 1984. Developmental and oxygen consumption differences between LDH-B genotypes of Fundulus heteroclitus and their effect on hatching times. Physiol.. Zool. 57: 52–56.
Dobzhansky, Th. & B. Wallace, 1953. The genetics of homeostasis in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 39: 162–171.
Eanes, W. F., 1978. Morphological variance and enzyme heterozygosity in the monarch butterfly. Nature 276: 263–264.
Eanes, W. F., 1981. Enzyme heterozygosity and morphological variance. Nature 290: 609–610.
Fleischer, R. C., R. F. Johnston & W. J. Klitz, 1983. Allozymic heterozygosity and morphological variation in house sparrows.Nature 304: 628–630.
Garton, D. W., 1984. Relationship between multiple locus heterozygosity and physiological energetics of growth in the estuarine gastropod Thais haemastoma. Physiol. Zool. 57: 530–543.
Garton, D. W., R. K. Koehn & T. M. Scott, 1984. Multiple-locus heterozygosity and the physiological energetics of growth in the coot clam, Mulinia lateralis, from a natural population. Genetics: 445–455.
Gajardo, G. M. & J. A. Beardmore, 1989. Ability to switch reproductive mode in Artemia is related to maternal heterozygosity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 55: 191–195.
Govindaraju, D. R. & B. P. Dancik, 1987. Allozyme heterozygosity and homeostasis in germinating seeds of jack pine. Heredity 59: 279–283.
Hall, J. G. & R. K. Koehn, 1983. The evolution of enzyme catalytic efficiency and adaptive inference from steady-state kinetic data. Evol. Biol. 16: 53–96.
Handford, P., 1980. Heterozygosity at enzyme loci and morphological variation. Nature 286: 261–262.
Haiti, G. B., G. Lang, F. Klein & R. Willing, 1991. Relationships between allozymes, heterozygosity and morphological characters in red deer (Cervus elaphus), and the influence of selective hunting on allele frequency distributions. Heredity 66: 343–350.
Hartl, G. B., F. Suchentrunk, R. Willing & R. Petznek, 1993.Allozyme heterozygosity and fluctuating asymmetry in the brown hare (Lepus europaeus): a test of the developmental homeostasis hypothesis, (in preparation).
Hawkins, A. J. S., B. L. Bayne & A. J. Day, 1986. Protein turnover, physiological energetics and heterozygosity in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis: the basis of variable age-specific growth. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 229: 161–176.
Hawkins, A. J. S., B. L. Bayne, A. J. Day, J. Rusing & C. M. Worrall, 1989. Genotype-dependent interrelations between energy metabolism, protein metabolism and fitness, pp. 283–292 in Reproduction, Genetics and Distributions of Marine Organisms, edited by J. S. Ryland and P. A. Tyler. Olsen and Olsen, Fredensborg, Denmark.
Kasule, F. K. & L. M. Cook, 1988. Phenotypic variability and heterozygosity at an esterase locus in the mosquito Aedus aegypti. Heredity 61: 427–431.
King, D. P. F., 1985. Enzyme heterozygosity associated with anatomical character variance and growth in the herring (Clupea harengus L.). Heredity 54: 289–296.
Kobyliansky, E. & G. Livshits, 1985. Differential fertility and morphological constitution of spouses. Z. Morph. Anthrop. 76: 95–105.
Koehn, R. K., 1991. The cost of enzyme synthesis in the genetics of energy balance and physiological performance. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 44:231–247.
Koehn, R. K. & B. L. Bayne, 1988. Towards a physiological and genetical understanding of the energetics of the stress response.Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 37: 157–171.
Koehn, R. K., W. J. Diehl & T. M. Scott, 1988. The differential contribution by individual enzymes of glycolysis and protein catabolism to the relationship between heterozygosity and growth rate in the coot clam, Mulinia lateralis. Genetics 118: 121–130.
Koehn, R. K. & P. M. Gaffney, 1984. Genetic heterozygosity and growth rate in Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 82: 1–7.
Koehn, R. K. & S. E. Shumway, 1982. A genetic/physiological explanation for differential growth rate among individuals of the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin). Mar. Biol. Letters 3: 35–42.
Koehn, R. K., A. J. Zera & J. G. Hall, 1983. Enzyme polymorphism and natural selection, pp. 115–136 in Evolution of Genes and Proteins, edited by M. Nei and R. K. Koehn. Sinauer Associates Inc. Sunderland, Mass.
Leary, R. F., F. W. Allendorf & K. L. Knudsen, 1983. Developmental stability and enzyme heterozygosity in rainbow trout. Nature 301: 71–72.
Leary, R. F., F. W. Allendorf & K. L. Knudsen, 1984. Superior developmental stability of heterozygotes at enzyme loci in salmonid fishes. Amer. Natur. 124: 540–551.
Leary, R. F., F. W. Allendorf & K. L. Knudsen, 1985. Inheritance of meristic variation and the evolution of developmental stability in rainbow trout. Evolution 39: 308–314.
Lerner, I. M., 1954. Genetic homeostasis. Oliver and Boyd, Edingburgh, 154 pp.
Livshits, G. & E. Kobyliansky, 1984. Biochemical heterozygosity as a predictor of developmental homeostasis in man. Ann. Hum. Genet. 48: 173–184.
Livshits, G. & E. Kobyliansky, 1985. Lerner’s concept of developmental homeostasis and the problem of heterozygosity level in natural populations. Heredity 55: 341–353.
Makaveev, T., I. Venev & M. Baulov, 1978. Investigations on activity level and polymorphisms of some blood enzyme in farm animals with different growth energy. II. Correlations between homo- and heterozygosity of some protein and enzyme phenotypes and fattening ability and slaughter indices in various breeds of fattened pigs. Genet. Sel. 10: 229–236.
McAndrew, B. J., R. D. Ward & J. A. Beardmore, 1982. Lack of relationship between morphological variance and enzyme heterozygosity in the plaice, Pleuronectes platessa. Heredity 48: 117–125.
Messier, S. & J. B. Mitton. Heterozygosity at the malate dehydrogenase locus and fluctating asymmetry in Apis mellifera. Evolution, in review.
Mitton, J. B., 1978. Relationship between heterozygosity for enzyme loci and variation of morphological characters in natural populations. Nature 273: 661–662.
Mitton, J. B., 1993. Theory and data pertinent to the relationship between heterozygosity and fitness, in The Natural History of Inbreeding and Outbreeding, edited by W. Shields and N. Thornhill. University of Chicago Press.
Mitton, J. B., C. Carey & T. D. Kocher, 1986. The relation of enzyme heterozygosity to standard and active oxygen consumption and body size of tiger salamanders, Ambystoma tigrinum. Physiol. Zool. 59: 574–582.
Mitton, J. B. & M. C. Grant, 1984. Associations among protein heterozygosity, growth rate, and developmental homeostasis.Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 15: 479–499.
Mitton, J. B. & R. K. Koehn, 1975. Genetic organization and adaptive response of allozymes to ecological variables in Fundulus heteroclitus. Genetics 79: 97–111.
Mitton, J. B. & R. K. Koehn, 1985. Shell shape variation in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis L., and its association with enzyme heterozygosity. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 90: 73–80.
Mitton, J. B. & B. A. Pierce, 1980. The distribution of individual heterozygosity in naural populations. Genetics 95: 1043–1054.
Mukai, T., L. E. Mettler & S. Chigusa, 1971. Linkage disequilibrium in a local population of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68: 1065–1069.
Mukai, T. & O. Yamaguchi, 1974. The genetic structure of natural populations of Drosphila melanogaster. XI. Genetic variability in a local population. Genetics 76: 339–366.
Parsons, P. A., 1971. Extreme environment heterosis and genetic loads. Heredity 26: 479–483.
Parsons, P. A., 1973. Genetics of resistance to environmental stresses in Drosophila populations. Ann. Rev. Genet. 7: 239–265.
Parsons, P. A., 1987. Evolutionary rates under environmental stress. Evolutionary Biology 21: 311–347.
Paynter, K. T., I. DiMichele, S. C. Hand & D. A. Powers, 1991. Metabolic implications of LDH-B genotype during early development in Fundulus heteroclitus. J. Exp. Zool. 257: 24–33.
Pierce, B. A. & J. B. Mitton, 1982. Allozyme heterozygosity and growth in the tiger salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum. J. Hered. 73: 250–253.
Place, A. R. & D. A. Powers, 1979. Genetic variation and relative catalytic efficiencies: LDH-B allozymes of Fundulus heteroclitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76: 2354–2358.
Powers, D. A., L. DiMichele & A. R. Place, 1983. The use of enzyme kinetics to predict differences in cellular metabolism,developmental rate, and swimming performance between LDH-B genotypes of the fish, Fundulus heteroclitus,in Isozymes: Current Topics in Biological and Medical Research.Volume 10, edited by G. Whitt and G. C. Markert. Academic Press, New York.
Powers, D. A., G. S. Greaney & A. R. Place, 1979. Physiological correlation between lactate dehydrogenase genotype and haemoglobin function in killifish. Nature 277: 240–241.
Powers, D. A. & A. R. Place, 1978. Biochemical genetics of Fundulus heteroclitus (L.). I. Temporal and spatial variation in gene frequencies of Ldh-B, Mdh-A, Gpi-B, and Pgm-A. Biochem. Genet. 16: 593–607.
Prakash, S., 1974. Gene differences between the Sex Ratio and Standard gene arrangements of the X chromosome and linkage disequilibrium between the Standard gene arrangements and the X chromosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics 77: 795–804.
Prakash, S. & R. C. Lewontin, 1968. A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. III. Direct evidence of coadaptation in gene arrangements of Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 59: 398–450?
Prakash, S. & R. C. Lewontin, 1971. A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. V. Further direct evidence of coadaptations in inversions of Drosophila. Genetics 69: 405–408.
Prakash, S. & R. B. Merritt, 1972. Direct evidence of genic differentiation between Sex Ratio and Standard gene arrangements of X chromosome in Drosophila pseudoobscura.Genetics 72: 169–175.
Policansky, D. & E. Zouros, 1977. Gene differences between the sex ratio and standard gene arrangements on the X chromosome in Drosophila persimilis. Genetics 85: 507–511.
Powers, D. A., M. Smith, I. Gonzalez-Villasenor, L. DiMichele, D. Crawford, G. Bernardi & T. Lauerman, 1993. A multidisciplinary approach to the selectionist/neutralist controversy using the model teleost Fundulus heteroclitus. Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology, Oxford University Press.
Quattro, J. M. & R. C. Vrijenhoek, 1989. Fitness differences among remnant populations of the endangered sonoran topminnow. Science 245: 976–978.
Robertson, F. W. & E. C. Reeve, 1952. Heterozygosity, environmental variation and heterosis. Nature 170: 286–287.
Rodhouse, P. G. & P. M. Gaffney, 1984. Effect of heterozygosity on metabolism during starvation in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Biol. 80: 179–188.
Rodhouse, P. G., J. H. McDonald, R. I. E. Newell & R. K. Koehn, 1986. Gamete production, somatic growth and multiple locus heterozygosity in Mytilus edulis L. Mar. Biol. 90’: 209–214.
Rogers, S., R. Wells & M. Rechsteiner, 1986. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science 234: 364–368.
Scott, T. M. & R. K. Koehn, 1990. The effect of environmental stress on the relationship of heterozygosity to growth rate in the coot clam Mulinia lateralis (Say). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 135: 109–116.
Scribner, K. T., M. H. Smith & P. E. Johns, 1989. Environmental and genetic components of antler growth in whitetailed deer. J. Mamm. 70: 284–291.
Scribner, K. T. & M. H. Smith, 1990. Genetic variability and antler development, pp 460–473 in Horns, Pronghorns, and Antlers, edited by G. A. Bubenik and A. B. Bubenik. Springer, New York.
Serradilla, J. M. & F. J. Ayala, 1983. Alloprocoptic selection: A mode of natural selection promoting polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80: 2022–2025.
Singh, S. M. & E. Zouros, 1978. Genetic variation associated with growth rate in the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica).Evolution 32: 342–353.
Smith, M. H., K. T. Scribner, P. E. Johns & O. E. Rhodes, Jr., 1991. Genetics and Antler development. Proc. 18th Congr. Internat. Union Game Biol., Krakow, Poland.
Soulé, M. E., 1967. Phenetics of natural populations. II. Asymmetry and evolution in a lizard. Amer. Natur. 101: 141–160.
Soulé, M. E., 1971. The variation problem: the gene-flow-variation hypothesis. Taxon 20: 37–50.
Soulé, M. E., 1979. Heterozygosity and developmental stability: another look. Evolution 33: 396–401.
Soulé, M. E., 1982. Allomeric variation. 1. The theory and some consequences. Amer. Natur. 120: 751–764.
Soulé, M. E. & S. Y. Yang, 1974. Genetic variation sideblotched lizards on islands in the Gulf of California. Evolution 27: 593–600.
Strauss, R. E., 1989. Associations between genetic heterozygosity and morphological variability in freshwater sculpins, genus Cottus (Teleostei: Cottidae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 17: 333–340.
Strauss, R. E., 1991. Correlations between heterozygosity and phenotypic variability in Cottus (Teleostei: Cottidae): character components. Evolution 45: 1950–1956.
Teska, W. R. M. H. Smith & J. M. Novak, 1990. Food quality, heterozygosity, and fitness correlates in Peromyscus polionotus.Evolution 44: 1318–1325.
Van Valen, L., 1978. The statistics of variation. Evol. Theory 4: 33–43.
Vrijenhoek, R. C. & S. Lerman, 1982. Heterozygosity and developmental stability under sexual and asexual breeding systems.Evolution 36: 768–767.
Ward, R. D., M. Sarfarazi, C.Azimi-Garakani & J. A. Beardmore,1985. Population genetics of polymorphisms in Cardiff newborn: Relationship betwene blood group and allozyme heterozygosity and birth weight. Hum. Hered. 35: 171–177.
Watt, W. B., 1985. Bieonergetics and evolutionary genetics: opportunities for new synthesis. Amer. Natur. 125: 118–143.
Watt, W. B., 1986. Power and efficiency as indexes of fitness in matabolic organization. Amer. Natur. 127: 629–653.
Watt, W. B., 1992. Eggs, enzymes, and evolution-natural genetic variants change insect fecundity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 10608–10612.
Wooten, M. C. & M. H. Smith, 1986. Fluctuating asymmetry and genetic variability in a natural population of Mus musculus J. Mammalogy 67: 725–732.
Yezerinac, S. M., S. C. Lougheed & P. Handford, 1992. Morphological variability and enzyme heterozygosity: individual and population level correlations. Evolution 46: 1959–1964.
Zouros, E. & D. W. Foltz, 1987. The use of allelic isozyme variation for the study of heterosis, pp 2–59 in Isozymes: Current Topics in Biological and Medical research, Volume 13, edited by M. C. Rattazzi, J. G. Scandalios and G. S. Whitt. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mitton, J.B. (1994). Enzyme heterozygosity, metabolism, and developmental stability. In: Markow, T.A. (eds) Developmental Instability: Its Origins and Evolutionary Implications. Contemporary Issues in Genetics and Evolution, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0830-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0830-0_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-4357-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-0830-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive