Abstract
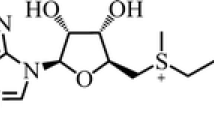
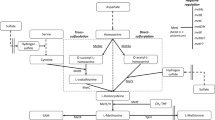
S-Adenosyl-L-methionine is an important bioactive sulfur-containing amino acid. Large scale preparation of the amino acid is of great significance. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine can be synthesized from L-methionine and adenosine triphosphate in a reaction catalyzed by methionine adenosyltransferase. In order to enhance S-adenosyl-L-methionine biosynthesis by industrial microbial strains, various strategies have been employed to optimize the process. Genetic manipulation has largely focused on enhancement of expression and activity of methionine adenosyltransferase. This has included its overexpression in Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli, molecular evolution, and fine-tuning of expression by promoter engineering. Furthermore, knocking in of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin and knocking out of cystathionine-β-synthase have also been effective strategies. Besides genetic modification, novel bioprocess strategies have also been conducted to improve S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthesis and inhibit its conversion. This has involved the optimization of feeding modes of methanol, glycerol and L-methionine substrates. Taken together considerable improvements have been achieved in S-adenosyl-L-methionine accumulation at both flask and fermenter scales. This review provides a contemporary account of these developments and identifies potential methods for further improvements in the efficiency of S-adenosyl-L-methionine biosynthesis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CBS:
-
Cystathionine-β-synthase
- C-source:
-
Carbon source
- L-Met:
-
L-methionine
- MAT:
-
Methionine adenosyltransferase
- PAOX :
-
Promoter of alcohol oxidase 1 gene
- PGAP :
-
Promoter of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene
- SAH:
-
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
- SAM:
-
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
- VHb:
-
Vitreoscilla hemoglobin
References
Alper H, Fischer C, Nevoigt E, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Tuning genetic control through promoter engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12678–12683
Andersen HW, Pedersen MB, Hammer K, Jensen PR (2001) Lactate dehydrogenase has no control on lactate production but has a strong negative control on formate production in Lactococcus lactis. Eur J Biochem 268:6379–6389
Bakke I, Berg L, Aune TE, Brautaset T, Sletta H, Tondervik A, Valla S (2009) Random mutagenesis of the PM promoter as a powerful strategy for improvement of recombinant-gene expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2002–2011
Barcelo HA, Wiemeyer JC, Sagasta CL, Macias M, Barreira JC (1990) Experimental osteoarthritis and its course when treated with S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Rev Clin Esp 187:74–78
Bhave SL, Chattoo BB (2003) Expression of vitreoscilla hemoglobin improves growth and levels of extracellular enzyme in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:658–666
Catoni GL (1952) The nature of the active methyl donor formed enzymatically from L-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J Am Chem Soc 74:2942–2943
Catoni GL (1953) S-Adenosylmethionine; a new intermediate formed enzymatically from L-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J Biol Chem 204:403–416
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2000) Heterologous protein expression in the methalotropic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24(1):45–66
Chan SY, Appling DR (2003) Regulation of S-adenosylmethionine levels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 278:43051–43059
Chen H, Chu J, Zhang S, Zhuang Y, Qian J, Wang Y, Hu X (2007) Intracellular expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin improves S-adenosylmethionine production in a recombinant Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1205–1212
Cregg JM, Madden KR, Barringer KJ, Thill GP, Stillman CA (1989) Functional characterization of the two alcohol oxidase genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris. Mol Cell Biol 9:1316–1323
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol (NY) 11:905–910
De Mey M, Maertens J, Lequeux GJ, Soetaert WK, Vandamme EJ (2007) Construction and model-based analysis of a promoter library for E. coli: an indispensable tool for metabolic engineering. BMC Biotechnol 7:34. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-7-34
Dikshit KL, Webster DA (1988) Cloning, characterization and expression of the bacterial globin gene from Vitreoscilla in Escherichia coli. Gene 70:377–386
Friedel HA, Goa KL, Benfield P (1989) S-adenosyl-L-methionine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in liver dysfunction and affective disorders in relation to its physiological role in cell metabolism. Drugs 38:389–416
Gleeson MA, Sudbery PE (1988) The methylotrophic yeasts. Yeast 4:1–15
Gross A, Geresh S, Whitesides GM (1983) Enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-methionine from L-methionine and ATP. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 8:415–422
Hartner FS, Ruth C, Langenegger D, Johnson SN, Hyka P, Lin-Cereghino GP, Lin-Cereghino J, Kovar K, Cregg JM, Glieder A (2008) Promoter library designed for fine-tuned gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e76
He J, Deng J, Zheng Y, Gu J (2006) A synergistic effect on the production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine in Pichia pastoris by knocking in of S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthase and knocking out of cystathionine-beta synthase. J Biotechnol 126:519–527
Hu X, Chu J, Zhang S, Zhuang Y, Wang Y, Zhu S, Zhu Z, Yuan Z (2007) A novel feeding strategy during the production phase for enhancing the enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by methylotrophic Pichia pastoris. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:669–674
Hu X, Chu J, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Zhuang Y, Wang Y, Guo M, Chen H, Yuan Z (2008) Effects of different glycerol feeding strategies on S-adenosyl-L-methionine biosynthesis by PGAP-driven Pichia pastoris overexpressing methionine adenosyltransferase. J Biotechnol 137:44–49
Hu H, Qian J, Chu J, Wang Y, Zhuang Y, Zhang S (2009a) DNA shuffling of methionine adenosyltransferase gene leads to improved S-adenosyl-L-methionine production in Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 141:97–103
Hu H, Qian J, Chu J, Wang Y, Zhuang Y, Zhang S (2009b) Optimization of L-methionine feeding strategy for improving S-adenosyl-L-methionine production by methionine adenosyltransferase overexpressed Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:1105–1114
Huang Y, Gou X, Hu H, Xu Q, Lu Y, Cheng J (2011) Enhanced S-adenosyl-L-methionine production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by spaceflight culture, overexpressing methionine adenosyltransferase and optimizing cultivation. J Appl Microbiol 112:683–694
Lee SW, Park BS, Choi ES, Oh MK (2010) Overexpression of ethionine resistance gene for maximized production of S-adenosylmethionine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae sake kyokai No 6. Korean J Chem Eng 27(2):587–589
Li DY, Yu J, Tian L, Ji XS, Yuan ZY (2002) Production of SAM by recombinant Pichia pastoris. Chin J Biotechnol 3:295–299
Lieber CS (1999) Role of S-adenosyl-L-methionine in the treatment of liver diseases. J Hepatol 30:1155–1159
Lin JP, Tian J, You JF, Jin ZH, Xu ZN, Cen PL (2004) An effective strategy for the co-production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine and glutathione by fed-batch fermentation. Biochem Eng J 21:19–25
Luo Y, Yuan Z, Luo G, Zhao F (2008) Expression of secreted His-tagged S-adenosylmethionine synthetase in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and its characterization, one-step purification, and immobilization. Biotechnol Prog 24:214–220
Mato JM, Pajares MA, Mingorance J, and Avarez L (1995) Production of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) by fermentation of transformed bacteria. European Patent, vol 0647712A1, edited by E. P. Office.
Mato JM, Alvarez L, Ortiz P, Pajares MA (1997) S-adenosylmethionine synthesis: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 73:265–280
Matos JR, Raushel FM, Wong CH (1987) S-Adenosylmethionine: study on chemical and enzymatic synthesis. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 9:39–52
Minas W, Brunker P, Kallio PT, Bailey JE (1998) Improved erythromycin production in a genetically engineered industrial strain of Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Biotechnol Prog 14:561–566
Mincheva K, Kamburova V, Balutzov V (2002) Production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by a mutant strain of Kluyveromyces lactis. Biotechnol Lett 24:985–988
Nevoigt E, Kohnke J, Fischer CR, Alper H, Stahl U, Stephanopoulos G (2006) Engineering of promoter replacement cassettes for fine-tuning of gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5266–5273
Nevoigt E, Fischer C, Mucha O, Matthaus F, Stahl U, Stephanopoulos G (2007) Engineering promoter regulation. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:550–558
Park J, Tai JZ, Roessner CA, Scott AI (1996) Enzymic synthesis of s-adenosyl-L-methionine on the preparative scale. Bioorg Med Chem 4:2179–2185
Qin X, Qian J, Yao G, Zhuang Y, Zhang S, Chu J (2011) GAP promoter library for fine-tuning of gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3600–3608
Schlenk F, Depalma RE (1957) The preparation of S-adenosylmethionine. J Biol Chem 229:1051–1057
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene expression. Biotechnol (N Y) 12:181–184
Shiomi N, Fukuda H, Fukuda Y, Murata K, Kimura A (1990) Production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells carrying a gene for ethionine resistance. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:1120–1124
Shiomi N, Fukuda H, Fukuda Y, Murata K, Kimura A (1991) Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a gene conferring resistance to ethionine in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 71:211–215
Shiozaki S, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1984) Unusual intracellular accumulation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 48:2293–2300
Shiozaki S, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1986) Production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by Saccharomyces sake. J Biotechnol 4:345–354
Shiozaki S, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1989) S-Adenosyl-L-methionine production by Saccharomyces sake: optimization of the culture conditions for the production of cells with a high S-adenosyl-L-methionine content. Agric Biol Chem 53:3269–3274
Shobayashi M, Mukai N, Iwashita K, Hiraga Y, Iefuji H (2006) A new method for isolation of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-accumulating yeast. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:704–710
Shobayashi M, Fujii T, Iefuji H (2007) Effects of accumulated S-adenosylmethionine on growth of yeast cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1595–1597
Stipanuk MH (1986) Metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids. Annu Rev Nutr 6:179–209
Torta R, Cicolin A, Keller R (1998) Transmethylation and affective disorders. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl 6:499–506
Waterham HR, Digan ME, Koutz PJ, Lair SV, Cregg JM (1997) Isolation of the Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and regulation and use of its promoter. Gene 186:37–44
Yu ZL, Wu XJ, Li DY, Yang S, Zhou Z, Cai J, Yuan ZY (2003) Enhancement of the production of SAM by overexpression of SAM synthetase in Pichia pastoris. Acta Biochem Biophys Sin 35:127–132
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by grants from National key Basic Research Program of China (2012CB725202), the Public Topic of Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education (KLIB-KF201003) and State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University (SKLF-TS-201124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hu, X., Quinn, P.J., Wang, Z., Han, G., Wang, X. (2012). Genetic Modification and Bioprocess Optimization for S-Adenosyl-L-methionine Biosynthesis. In: Wang, X., Chen, J., Quinn, P. (eds) Reprogramming Microbial Metabolic Pathways. Subcellular Biochemistry, vol 64. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5055-5_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5055-5_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-007-5054-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-5055-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)