Abstract
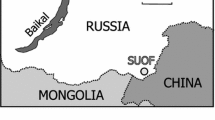
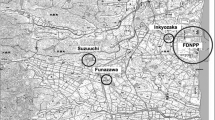
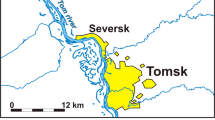
Field experiments and laboratory studies were performed to investigate migration processes of plutonium isotopes in the aquifer at the experimental site. The objectives of these experiments were to characterize the spatial distribution and possible migration mechanisms of plutonium in the aquifer, and to obtain the parameters that determine radionuclide retardation. During 2005–2006 experimental investigations were carried out and spatial distributions of plutonium isotopes (239,240Pu, 238Pu), 90Sr and main dissolved ions in aquifer along the groundwater flow were obtained. Radionuclide specific activities in groundwater depended on the location of the piezometer and varied in the range of 1 ÷ 200 mBq/L for 239,240Pu, 0.5 ÷ 100 mBq/L for 238Pu and n·100 ÷ n·104 Bq/L for 90Sr. It was found that the spatial features of the specific activities distributions of plutonium and strontium in groundwater were similar, i.e., there was a correlation between the positions of the radionuclides activity maximums. The Pu isotopes' plume in the aquifer spreads about 10 m downstream of the radionuclides source. Characterization of the initial radionuclide composition of waste showed that all plutonium in the aquifer originated from the trench. Ratio of plutonium isotopes (239,240Pu/238Pu) was the same in waste material and in groundwater samples. In-situ ultrafiltration of several groundwater samples was carried out. Obtained size fractionation data on plutonium activities in collected colloids suggest that significant part of Pu (50–80%) was associated with low molecular weight fraction (<5 kDa).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buddemeier, R.W. and Hunt, J.R. (1988) Transport of colloidal contaminants in groundwater: radionuclide migration at the Nevada Test Site, Applied Geochemistry, 3: 535–548.
Bugai, D., Kashparov, V., Dewiere, L., Khomutinin, Yu., Levchuk, S., and Yoschenko, V. (2005) Characterization of subsurface geometry and radioactivity distribution in the trench containing Chernobyl clean-up wastes, Environmental Geology, 47(6): 869–881.
Dai, M.H., Kelley, J.M., and Buesseler, K.O. (2002) Sources and migration of plutonium in groundwater at the Savannah River site, Environmental Science & Technology, 36: 3690–3699.
Dai, M.H., Buesseler, K.O., and Pike, S.M. (2002) Plutonium in groundwater at the 100K-Area of the U.S. DOE Hanford Site, Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 76: 167–189.
Dewiere, L., Bugai, D., Grenier, C., Kashparov, V., and Ahamdach, N. (2004) 90Sr migration to the geo-sphere from a waste burial in the Chernobyl exclusion zone, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 74(1–3): 139–150.
Kersting, A.B., Efurd, D.W., Finnegan, D.L., Rokop, D.J., Smith, D.K., and Thompson, J.L. (1999) Migration of Plutonium in Groundwater at the Nevada Test Site, Nature, 397: 56–59.
Kaplan, D.I., Bertsch, P.M., Adriano, D.C., and Orlandini, K.A. (1994) Actinide association with groundwater colloids in a coastal plain aquifer, Radiochim. Acta, 66/67: 181–187.
McCarthy, J.F., Williams, T.M., Liang, L., Jardine, P.M., Palumbo, A.V., Jolley, L.W., Cooper, L.W., and Taylor, D.L. (1993) Mobility of natural organic matter in a sandy aquifer, Environmental Science & Technology, 27: 667–676.
McCarthy, J.F., Gu, B., Liang, L., Mas-Pla, J., Williams, T.M., and Yeh, T.-C.J. (1996) Field tracers tests on the mobility of natural organic matter in a sandy aquifer, Water Resources Research, 32 (5): 1223–1228.
Novikov, A.P., Kalmykov, S.N., Utsunomiya, S., Ewing, R.C., Horréard, F., Merkulov, A., Clark, S.B., Tkachev, V.V., and Myasoedov, B.F. (2006) Colloid transport of Plutonium in the farfield of the Mayak production association, Russia, Science, 314: 638–641.
Penrose, W.R., Polzer, W.L., Essington, E.H., Nelson, D.M., and Orlandini, K.A. (1990) Mobility of plutonium and americium through a shallow aquifer in a semiarid region, Environmental Science & Technology,24: 228–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science + Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Levchuk, S., Yoschenko, V., Kashparov, V., Van Meir, N., Ardois, C., Bugaï, D. (2009). Phenomenon of a Fast Migration of Plutonium Radioisotops in Ground Water: Colloids or Soluble Form?. In: Oughton, D.H., Kashparov, V. (eds) Radioactive Particles in the Environment. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2949-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2949-2_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-2947-8
Online ISBN: 978-90-481-2949-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)