Abstract
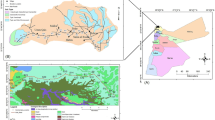
The central part of Wuhan City was chosen as soil sampling region to investigate the spatial distribution of heavy metals in roadside soils and the correlation between city road net and the spatial distribution of heavy metals. The total number of samples collected is 224 and the concentrations of As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in soils were detected. The spatial distribution of heavy metals in roadside soils was characterized by applying Universal Kriging interpolation model. The correlation between road net and the spatial distribution of heavy metals was analyzed based on Voronoi diagram. The results show that there is high correlation between the road net and the distribution of heavy metals in the range of 400 m on both sides of the main road of the study area. There is no strong relationship between road net and heavy metals in the soil of the whole study area which indicates that the road net of Wuhan is not the main source of heavy metal contaminate in soils.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren, Y., Wang, X., Ouyang, Z., Wang, Q., Hou, P.: The pollution characteristics of Beijing urban road sediments. Acta Ecologica Sinica 08, 2365–2371 (2013)
Zhang, J.-Q., Shiraishi, S., Watanabe, I.: Heavy Metal Pollution of Dust, Topsoil and Roadside Tree Nearby Main City Roadways. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University 01, 68–73 (2006)
Zhi, Y.-B., Wang, Z.-L., Ma, Z., Wang, Z.-S., Deng, Z.-F., Li, H.-L.: The speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals pollutions in soil along highway in Erdos. Acta Ecologica Sinica 05, 2030–2039 (2007)
Guo, J.-P., Zhang, Y.-X.: Spatial Sampling Methods and Their Applications in landscape pattern analysis for landscape ecological research. Scientia Geographica Sinica 05, 74–79 (2005)
Huang, M., Yang, H.-Z., Yu, C., Li, J.-J.: Accumulation Characteristics and Pollution Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Soils of Wuhan City. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 24(4), 135–139 (2010)
Jaber, S.M., Ibrahim, K.M., Al-Muhtaseb, M.: Comparative evaluation of the most common kriging techniques for measuring mineral resources using Geographic Information Systems. GIScience & Remote Sensing 50(1), 93–111 (2013)
Deza, M.M., Deza, E.: Voronoi Diagram Distances. In: Encyclopedia of Distances, pp. 339–347. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Gold, C.M.: The Meaning of “Neighbour”. In: Frank, A.U., Formentini, U., Campari, I. (eds.) GIS 1992. LNCS, vol. 639, pp. 220–235. Springer, Heidelberg (1992)
Luo, Y.: Trends in soil environmental pollution and the prevention-controlling-remediation strategies in China. Environmental Pollution & Control 12, 27–31 (2009)
Ding, X.W., Shen, Z.Y., Liu, R.M., et al.: Effects of ecological factors and human activities on nonpoint source pollution in the upper reach of the Yangtze River and its management strategies. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions 11(1), 691–721 (2014)
Carrero, J.A., Goienage, N., Barrutia, O., Artetxe, U.: Diagnosing the Impact of Traffic on Roadside Soils Through Chemometric Analysis on the Concentrations of More Than 60 Metals Measured by ICP/MS. Springer Science Business Media B.V. (2010)
Sun, X.-B., Li, Y.-C.: The Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metals and Variation Characteristics of Datong Abandoned Coal Mine Area in Huainan City. Scientia Geographica Sinica 10, 1238–1244 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shen, R., Li, J., Yang, M., Zeng, M., Zhou, M. (2015). Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Roadside Soils Based on Voronoi Diagram: A Case Study of Wuhan City. In: Bian, F., Xie, Y. (eds) Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem. GRMSE 2014. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 482. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45737-5_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-45737-5_71
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-45736-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-45737-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)