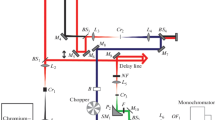
Abstract
Time resolved coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy has proven to be a powerful tool for studying the dephasing of molecular vibrations /1/. Excitation and delayed probing is usually performed with single high power picosecond pulses from Nd glass lasers. Up to now widespread application of this technique to study the decay of coherent optical phonons in solids was excluded by the lack of suitable sources for simultaneous generation of picosecond pulses with a material dependent difference frequency. In this paper a CARS-spectrometer with two synchronously mode-locked cw dye lasers parallely pumped by a mode-locked Ar+ laser is described. It has been applied to explore the decay of coherent lattice vibrations in GaP and the dephasing of molecular vibrations in Toluene.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
A. Laubereau and W. Kaiser, Rev. of Modern Physics Vol. 50, 607 (1978).
J.P. Heritage, Appl. Phys. Lett. 34, 470 (1979).
N.P. Economou, R.R. Freeman, J.P.-Heritage, and P.F. Liao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 36, 21 (1980).
R. KaaFTi, Ya. Aaviksoo, A. Freiberg, and P. Saari, Toim. Eesti NSV Tead. Akad. Fuus. Mat. (USSR) Vol. 29, 181 (1980).
M.C. Sceats, F. Kamga, and D. Podolski in Picosecond Phenomena II, ed. by R.M. Hochstrasser, W. Kaiser, and C.V. Shank, Springer Verlag Heidelberg (1980).
P.G. Klemens, Phys. Rev. 148, 845 (1966).
D. von der Linde, J. Kuhl, and H. Klingenberg, Phys. Rev. Lett. 44, 1505 (1980).
A.S. Barker, Phys. Rev. 165, 917 (1968).
S. Ushioda and J.D. McMuTrin, Solid State Commun. 11, 299 (1972).
A. Laubereau, D. von der Linde, and W. Kaiser, Opt Comm. 7, 173 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1982 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kuhl, J., von der Linde, D. (1982). A Picosecond CARS-Spectrometer Using Two Synchronously Mode-Locked CW Dye Lasers. In: Eisenthal, K.B., Hochstrasser, R.M., Kaiser, W., Laubereau, A. (eds) Picosecond Phenomena III. Springer Series in Chemical Physics, vol 23. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-87864-0_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-87864-0_50
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-87866-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-87864-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive