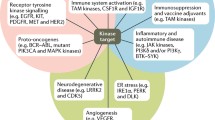
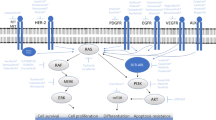
Abstract
The recognition that we may be approaching a plateau of effectiveness with traditional anticancer agents has led to the view that to gain more than incremental value against the major solid tumours will require a radically different strategy. Rather than the “black box” approach of random screening for cytotoxicity or cytostasis, or even the rational design of improved agents acting on conventional drug targets [1,2], many believe that this quantum leap will come from an exploitation of the identification of the genes and their encoded protein products which control proliferation, differentiation and cell death, combined with an understanding of their aberrant behaviour in malignant cells. Cancer is now described in extraordinary detail at the molecular level as a genetic disease. As a result of the remarkable advances in molecular oncology made over the last few years, the new central dogma of cancer drug discovery can be defined as: new biology → new targets → new therapies [3].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson RK: Screening methods in drug discovery. JNCI 1990 (82):1082–1083
Schwartsmann G and Workman P: Anticancer drug screening and discovery in the 1990s: A European perspective. Eur J Cancer 1993 (29A):3–14
Workman P (ed) New anticancer drug design based on advances in molecular oncology. Sem Cancer Biol 1992 (3):329–333
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: The multistep nature of cancer. Trends Genetics 1993 (9):138–141
Powis G: Signalling targets for anticancer drug development. Trends Pharm Sci 1991 (12):188–193
Brunton VG and Workman P: Cell-signalling targets for antitumour drug development. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1993 (32):1–19
Kenyon GL and Garcia GA: Design of kinase inhibitors. Med Res Rev 1987 (7):389–416
Levitski A: Tyrphostins — potential antiproliferative agents and novel molecular tools. Biochem Pharmac 1990 (40):313–318
Chang C-J and Geahlen RL: Protein-tyrosine kinase inhibition: mechanism-based discovery of antitumor agents. J Natural Products 1992 (11):1529–1560
Workman P, Brunton VG, Robins DJ: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Sem Cancer Biol 1992 (3):369–381
Burke TR: Protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Drugs of the Future 1992 (17):119–131
Spence P: Inhibitors of tyrosine kinase activity as anticancer therapeutics: recent developments. Current Opinion in Therapeutic Patents, December 1992
Dobrusin EM and Fry DW: Protein tyrosine kinases and cancer. Ann Rep Med Chem 1992 (27):169–176
Hunter T: A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell 1987(50):823–829
Gescher A: Towards selective pharmacological modulation of protein kinase C — opportunities for the development of novel antineoplastic agents. Br J Cancer 1992 (66):10–19
Grunicke HH and Uberall F: Protein kinase C modulation. Sem Cancer Biology 1992 (3):351–360
Fantl W, Johnson DE, Williams RT: Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Ann Rev Biochem 1993 (62):453–481
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL: Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987 (235):177–181
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA et al: Studies of HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989 (244):707–712
Bicknell R and Harris AL: Anticancer strategies involving vasculature: vascular targeting and the inhibition of angiogenesis. Sem Cancer Biology 1992(3):399–407
Bolen JB, Veillette A, Schwartz A, DeSeau V, Rosen N: Activation of pp60c-src protein kinase activity in human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1987 (84) :2251–2255
Ottenhoff-Kalff AE, Rijksen G, van Bearden EACM, Hennipman A, Michels AA, Staal GEJ: Characterization of protein tyrosine kinases from human breast cancer: Involvement of the c-src oncogene product. Cancer Res 1992 (52):4773–4778
Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E: Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature 1985 (315):550–554
Ullrich A and Schlessinger J: Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 1990 (61):203–213
Snyder MA, Bishop JM, McGrath JP, Levinson AD: A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60c-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol 1985 (5):1772–1779
Stein PL, Imamoto A, Soriano P: Genetic analysis of src-family tyrosine kinase mouse mutants. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 1993 (34):575
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T: The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phytogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 1988 (241):42–52
Knighton DR, Zheng J, Ten Eyck LF, Ashford VA, Xuong N-H, Taylor SS, Sowadski JM: Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 1991 (253):407–414
Zheng J, Knighton DR, Ten Eyck LF, Karlsson R, Xuong N-H, Taylor S, Sowadski JM: Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry 1993 (32):2154–2161
Bossemeyer D, Engh RA, Kinzel V, Ponstinyl H, Huber R: Phosphotransferase and substrate binding mechanism of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from porcine heart as deduced from the 2.0 Å structure of the complex with Mn2+ adenyl imidophosphate and inhibitor peptide PKI (5–24). EMBO J 1993 (3):849–859
De Bondt HL, Rosenblatt J, Jancarik J, Jones HD, Morgan DO, Kim S-H: Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Science 1993 (363):595–603
Knighton DR, Cadena DL, Zheng J, Ten Eyck LF, Taylor SS, Sowadski JM, Gill GN: Structural features that specify tyrosine kinase activity deduced from homology modelling of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1993 (90):5001–5005
Robinson S, Dean BJ, Petty BA: Characterization of A431 tumor xenograft as an in vivo model for testing epidermal growth factor-receptor antagonists. Int J Oncol 1992 (1):293–298
Hagiwara M, Inoue S, Tanaka T, Nunoki K, Ito M, Hidaka H: Differential effects of flavonoids as inhibitors of tyrosine protein kinases and serine/ threonine protein kinases. Biochem Pharmac 1988 (37):2987–2992
Okura A, Arakawa H, Oka H, Yoshinari T, Moden Y: Effect of genistein on topoisomerase activity and on the growth of Ha-ras-transformed NIH3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1988 (157):183–189
Cushman M, Nagarathnam D, Burg DL, Geahlen RL: Synthesis and protein tyrosine kinase inhibitory activities of flavonoid analogues. J Med Chem 1991 (34):798–806
Worland PJ, Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Sartor O, Sausville EA: Alteration of a p34cdc2 kinase by the flavone L86–8275 in breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmac 1993 (46):1831–1840
Geahlen RL and McLaughlin JL: Piceatannol (3,4,5′-tetrahydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a naturally occurring protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1989 (165):241–245
Cunningham BDM, Threadgill MD, Groundwater PW, Dale IL, Hickman JA: Synthesis and biological evaluation of protein tyrosine kinases. Anti-Cancer Drug Design 1992 (7):365–384
Umezawa H, Imoto M, Sawa T, Isshiki K, Matsuda N, Uchida T, Iinuma H, Hamada H, Hamada M, Takeuchi T: Studies on a new epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, erbstatin, produced by MH 435-hF3. J Antibiot 1986 (39):170–173
Yaish P, Gazit A, Gilon C, Levitski A: Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science 1988 (242):933–935
Gazit A, Osherov N, Posner I, Yaish P, Pradosy E, Gilon C, Levitski A: Tyrphostins 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and erbB2/neu tyrosine kinases. J Med Chem 1991 (34):1897–1907
Brunton VG, Lear MJ, Robins DJ, Williamson S, Workman P: Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of tyrphostins containing heteroaromatic moieties. Anti-Cancer Drug Design 1994 (in press)
Yoneda T, Lyall RM, Alsina MM, Persons PE, Spada AP, Levitski A, Zilbertstein A, Mundy GR: The antiproliferative effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors tyrphostins and a human squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Res 1991 (51):4430–4435
Shiraishi T, Domoto T, Imai N, Shimada Y, Watanabe K: Specific inhibitors of tyrosine specific protein kinase, synthetic 4-hydroxycinnamamide derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1987 (147):322–328
Traxler PM, Wacker O, Bach HL, Geissler JF, Kump W, Meyer T, Regenass U, Roesel JL, Lydon N: Sulfonylbenzoylnitrostyrenes: potential bisubstrate type inhibitors of the EGF-receptor tyrosine kinase. J Med Chem 1991 (34):2328–2337
Geissler JF, Traxler P, Regenass U, Murray BJ, Roessel JL, Meyer T, McGlynn E, Storni A, Lydon NB: Thiazolidine-diones. Biochemical and biological activity of a novel class of tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 1990 (265):22255–22261
Traxler P, Buchdunger E, Mett H, Meyer T, Regenass U, Roesel J, Trinks U, Lydon N: Amino-alkyl-acrylophenones as potent and selective inhibitors of the EGF-receptor protein tyrosine kinase. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 1992 (33):527
Kraker AJ, Wemple, Schemmel ME, Moore CW: Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase by 2-thioindoles, a new structural class of tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 1993 (34):408
Lydon N, Buchdunger E, Mett H, Regenass U, Muller M, Trinks U, Traxler P: Biological profile of CGP 52411: a tyrosine protein kinase inhibitor with selectivity for the EGF-receptor enzyme family. J Cell Biochem Suppl 1993 (17A):235
Buchdunger F et al: 4,5-dianilino-phthalimide: a novel tyrosine protein kinase inhibitor with selectivity for the EGF receptor signal transduction pathway and potent in vivo antitumour activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994 (in press)
Uchara Y, Hori M, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H: Screening of agents which convert ‘transformed morphology’: identification of an active agent as herbimycin and its inhibition of intracellular src kinase. Jpn J Cancer Res 1985 (76):672–675
Uchara Y, Fukazawa H, Murakami Y, Mizuno S: Irreversible inhibition of v-src tyrosine kinase activity by herbimycin A and its abrogation by sulphydryl compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1989 (163):803–809
Hamaguchi M, Xiao H, Uchara Y, Ohnishi Y, Nagai Y: Herbimycin A inhibits the association of p60v-src with the cytoskeletal structure and with phospha-tidylinositol 3′kinase. Oncogene 1993 (8):559–564
Pelech L: Networking with protein kinases. Current Biology 1993 (3):513–515
Moodie SA and Wolfman A: The 3 Rs of life: Ras, raf and growth regulation. Trends Genetics 1994 (10):44–48
Pawson T and Schlessinger J: SH2 and SH3 domains. Current Biology 1993 (3):434–442
Songyang Z, Schoelson SE, Chaudhuri M et al: SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell 1983 (72):767–778
McNamara DJ, Dobrusin E, Zhu G, Decker SJ, Saltiel AR: Inhibition of the binding of phospholipase Cγ1 SH2 domains to phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor by phosphorylated peptides. Int J Peptide Protein Res 1993 (42):240–248
McCormick F: How receptors turn ras on. Nature 1993(363):15–16
Wu J, Dent P, Jelinek T, Wolfman A, Weber M, Sturgill TW: Inhibition of the EGF-activated MAP kinase signalling pathway by adenosine 3′,5′-mono-phosphate. Science 1993 (262):1065–1069
Cook SJ and McCormick F: Inhibition by cAMP of ras-dependent activation of raf. Science 1993 (262):1069–1072
Graves LM, Bomfeldt KE, Raines EW, Potts BC, MacDonald SG, Ross R, Krebs EG: Protein kinase A antagonizes platelet-derived growth factor-induced signalling by mitogen-activated protein kinase in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 (90):10300–10304
Silvennoinen O, Schindler C, Schlessinger J, Levy DE: Ras-independent growth factor signalling by transcription factor tyrosine phosphorylation. Science 1993 (261):1736–1739
Sadowski HB, Shuai K, Darnell JE, Gilman MZ: A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science 1993 (261):1739–1743
Fu X-Y and Zhang J-J: Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell 1993 (74):1135–1145
Bos JL: Ras oncogenes and human cancer: A review. Cancer Res 1989 (49):4682–4689
James GL, Goldstein JL, Brown MS et al: Benzodiazepine peptidomimetics: Potent inhibitors of ras famesylation in animal cells. Science 1993 (260):1937–1942
Kohl NE, Mosser SD, de Solms J, Giuliani EA, Pompliano DL, Graham SL, Smith RL, Scolnick EM, Oliff A, Gibbs JB: Selective inhibition of ras- dependent transformation by a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Science 1993 (260):1934–1937
Waksman G, Kominos D, Robertson SC et al: Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature 1992 (358):646–653
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR: Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 1972 (26):239–157
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR: Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 1980 (68): 251–300
Dive C, Evans CE, Whetton AD: Induction of apoptosis — new targets for cancer chemotherapy. Sem Cancer Biology 1992 (3):417–427
Raff M: Social controls on cell survival and death. Nature 1992 (356):397–400
Fanidi A, Harrington EA, Evan GI: Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 oncogene. Nature 1992 (359):554–556
Workman P and Graham MA: Pharmacokinetics of Cancer Chemotherapy. Cancer Surveys, Vol 17. Cold Spring Harbor, 1993
Zachary I and Rozengurt E: Focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK): A point of convergence in the action of neuropeptides, integrins and oncogenes. Cell 1992 (71):891–894
Weiner TM, Liu EJ, Craven RJ Cance WG: Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer. Lancet 1993 (342):1024–1025
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risan W, Ullrich A: Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative flk-1 mutant. Nature 1994 (367):576–579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Workman, P., Brunton, V.G., Robins, D.J. (1994). Discovery and Design of Inhibitors of Oncogenic Tyrosine Kinases. In: Workman, P., D’lncalci, M. (eds) New Approaches in Cancer Pharmacology: Drug Design and Development. ESO Monographs. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-79088-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-79088-1_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-79090-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-79088-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive