Abstract
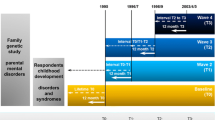
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of early predictors of the onset and course of schizophrenia, with special emphasis on the results from the temporally most advanced prospective study of children of schizophrenic mothers, launched in Copenhagen in 1962 by Mednick and Schulsinger (1965), the so-called Copenhagen High Risk Project. The focus will be on predictors of onset rather than those related to course.
Supported by National Institute of Mental Health grant MH 41 469 to Dr. Parnas
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth MD (1962) The effects of maternal deprivation: a review of findings and controversy in the context of research strategy. In: Deprivation of maternal care: a reassessment of its effects. WHO, Geneva (Public Health papers no 14)
Asarnow RF, Neuchterlein KH, Marder SR (1983) Span of apprehension performance, neuropsychological functioning, and indices of psychosis proneness. J Nerv Ment Dis 171:662–669
Baron M, Gruen R, Rainer JD, Kain J, Asnis L, Lord S (1985) A family study of schizophrenic and normal control probands: implications for the spectrum concept of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 142:447–455
Beliak L (1979) Schizophrenic syndrome related to minimal brain dysfunction: a possible neurologic subgroup. Schizophr Bull 5:480–489
Bleuler E (1911/1950) Dementia praecox for the group of schizophrenias. International University Press, New York
Bowlby J (1988) Developmental psychology comes from aging. Am J Psychiatry 145:1–10
Brown GW, Harris T (1978) Social origins of depression. Free Press, New York
Burman B, Mednick SA, Machon RA, Parnas J, Schulsinger F (1987) Children at high risk for schizophrenia: parent and offspring perception of family relationships. J Abnorm Psychol 96:364–366
Cannon TD, Mednick SA, Parnas J (1989a) Two pathways to schizophrenia in children at risk. In: Robins L, Rutter M (eds) Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 328–350
Cannon TD, Mednick SA, Parnas J (1989b) Genetic and perinatal determinants of structural brain deficits in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:883–889
Chapman JL, Chapman JP (1985) Psychosis proneness. In: Alpert M (ed) Controversies in schizophrenia. Guilford, New York, pp 157–174
Chapman JL, Chapmann JP (1987) The search for symptoms predictive of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:497–504
Ciompi L (1988) The psyche and schizophrenia: the bond between affect and logic. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Cohen P, Cohen J (1984) The clinician’s illusion. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:1178–1182
Conrad AJ, Scheibel AB (1987) Schizophrenia and the hippocampus: the embryological hypothesis extended. Schizophr Bull 13:577–588
Conrad K (1968) Die beginnende Schizophrenie. Thieme, Stuttgart
Dalén S (1975) Season of birth: a study of schizophrenia and other mental disorders. North Holland, Amsterdam
De Clerambault G (1942) Oeuvre psychiatrique. Presses Universitaires de France, Paris
Dohrenwend BP, Dohrenwend BS (1982) Perspectives on the past and future of psychiatric epidemiology. Am J Public Health 72:1271–1279
Dohrenwend BP, Shrout P, Link BG, Martin JL, Skodel AE (1986) Overview and initial results from a risk factor study of depression and schizophrenia. In: Barrett JE (ed) Mental disorders in the community: progress and challenge. Guilford, New York, pp 184–215
Endicott J, Spitzer R (1972) Current and past psychopathology scales (CAPPS). Arch Gen Psychiatry 27:678–687
Erlenmeyer-Kimling L, Marcuse Y, Comblatt B, Friedman D, Reiner JD, Rutchman J (1984) The New York High Risk Project. In: Watt NF, Anthony EJ, Wynne LC, Rolf JE (eds) Children at risk for schizophrenia: a longitudinal perspective. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 169–189
Erlenmeyer-Kimling L, Comblatt B (1987) The New York high risk project: a follow-up report. Schizophr Bull 13:451
Essen Moller E, Larsson H, Uddenberg CE, White G (1956) Individual traits and morbidity in a Swedish rural population. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand [Suppl] 100
Fish B (1977) Neurobiologic antecedents of schizophrenia in children: evidence for an inherited, congenital, neurointegrative defect. Arch Gen Psychiatry 34:1297–1313
Fish B (1987) Infant predictors of the longitudinal course of schizophrenic development. Schizophr Bull 13:395–410
Freedman BJ, Chapman LJ (1973) Early subjective experience in schizophrenic episodes. J Abnorm Psychol 82:46–54
Freedman BJ, Madison W (1974) The subjective experience of perceptual and cognitive disturbances in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 30:333–340
Goldstein MJ (1987) The UCLA high risk project. Schizophr Bull 13:505–514
Gottesman EE, Shields J (1982) The epigenetic puzzle. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gray JA (1987) The neuropsychology of anxiety. Oxford Science, Oxford
Guze SB, Cloninger CR, Martin RL, Clayton PJ (1983) A follow-up and family study of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:1273–1276
Heinrichs DW, Buchannan RW (1988) Significance and meaning of neurological signs in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 145:11–18
Huber G (1969) Klinische und neuroradiologische Untersuchungen an chronisch Schizophrenen. Nervenarzt 32:7–15
Huber G (1983) Das Konzept substratnaher Basissymptome und seine Bedeutung für Theorie und Therapie schizophrener Erkrankungen. Nervenarzt 54:23–32
Jorgensen AA, Parnas J (1990) The Copenhagen High Risk Study: premorbid and clinical dimensions of maternal schizophrenia. J Nerv Ment Dis 178:370–376
Jorgensen AA, Teasdale TW, Parnas J, Schulsinger F, Schulsinger H, Mednick SA (1987) The Copenhagen High Risk Project. The diagnosis of maternal schizophrenia and its relation to offspring diagnosis. Br J Psychiatry 151:753–757
Kendler KS (1988) Familial aggregation of schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:377–383
Kendler KS, Gruenberg AM, Strauss JS (1981) An independent analysis of the Copenhagen sample of the Danish adoption study. The relationship between schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 38:982–984
Kety SS (1988) Schizophrenic illness in the families of schizophrenic adoptees. Schizophr Bull 14:217–222
Klosterkötter J (1988) Basissymptome und Endphänomene der Schizophrenie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kraepelin E (1919/1971) Dementia praecox and paraphrenia. Krieger, New York
Leff J, Kuipers L, Berkowitz R, Eberlein-Vries R, Sturgeon D (1982) A controlled trial of social intervention in the families of schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry 141:121–134
Machon RA, Mednick SA, Schulsinger F (1983) The interaction of seasonality, place of birth, genetic risk, and subsequent schizophrenia in a high risk sample. Br J Psychiatry 55:316–327
Marcus J, Hans SL, Nagler S, Auerbach JG, Mirsky AF, Aubrey A (1987) Review of the NIMH Israeli Kibbutz-City study and the Jerusalem infant development study. Schizophr Bull 13:425–438
Matussek P (1952) Untersuchungen über die Wahnwahrnehmung. Arch Psychiatr Z Neurol 189:279–318
McGhie A, Chapman J (1961) Disorders of attention and perception in early schizophrenia. Br J Med Psychol 34:103–116
McNeil TF, Kaij L (1978) Obstetric factors in the development of schizophrenia: complications in the birth of preschizophrenics and in the reproduction by schizophrenic parents. In: Wynne LC, Cromwell RL, Matthysse S (eds) The nature of schizophrenia. Wiley, New York, pp 401–429
Mednick SA (1958) A learning theory approach to research in schizophrenia. Psychol Bull 55:316–327
Mednick SA (1960) The early and advanced schizophrenic. In: Mednick SA, Higgins J (eds) Current research in schizophrenia. Edwards, Ann Arbor, pp 69–78
Mednick SA, McNeil TF (1968) Current methodology in research on the etiology of schizophrenia: serious difficulties which suggest the use of the high-risk group method. Psychol Bull 21:681–693
Mednick SA, Schulsinger F (1965) A longitudinal study of children with a high-risk for schizophrenia: a preliminary report. In: Vandenberg S (ed) Methods and goals in human behavior genetics. Academic, New York, pp 255–296
Mednick SA, Silverton L (1988) High risk studies of the etiology of schizophrenia. In: Tsuang MT, Simpson JC (eds) Handbook of schizophrenia, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 543–562
Mednick SA, Machon RA, Huttunen MO, Bonett D (1988) Adult schizophrenia following prenatal exposure to an influenza epidemic. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:189–192
Meehl PE (1962) Schizotaxia, schizotypy, schizophrenia. Am Psychol 17:827–838
Meehl PE (1972) A critical afterword. In: Gottesman EE, Shields J (eds) Schizophrenia and genetics: a twin study vantage point. Academic, New York, pp 367–415
Minkowski E (1927) La schizophrénie. Psychopathologie des schizoïdes et des schizophrènes. Payot, Paris
Parnas J (1985) Mates of schizophrenic mothers: a study of assortative mating from the American/Danish High Risk Project. Br J Psychiatry 146:490–497
Parnas J, Jorgensen AA (1989) Premorbid psychopathology in schizophrenia spectrum. Br J Psychiatry 155:623–627
Parnas J, Schulsinger H (1986) Continuity of formal thought disorder from childhood to adulthood in a high risk sample. Acta Psychiatr Scand 74:246–251
Parnas J, Teasdale TW (1987) Treated versus untreated schizophrenia spectrum cases: a matched paired high risk population study. Acta Psychiatr Scand 75:44–50
Parnas J, Schulsinger F, Schulsinger H, Teasdale TW, Mednick SA (1982a) Behavioral precursors of the schizophrenia spectrum. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:658–664
Parnas J, Schulsinger F, Teasdale TW, Schulsinger H, Feldman PN, Mednick SA (1982b) Perinatal complications and clinical outcome within the schizophrenia spectrum. Br J Psychiatry 140:416–420
Parnas J, Teasdale TW, Schulsinger H (1985) Institutional rearing and diagnostic outcome in children of schizophrenic mothers: a prospective high risk study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:762–769
Patterson T (1987) Studies toward the subcortical pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:555–576
Piaget J (1951) Principle factors determining intellectual evolution from childhood to adult life. In: Rappaport D (ed) Organization and pathology of thought. Columbia University Press, New York, pp 154–175
Popper K (1959) The logic of scientific discovery. Basic Books, New York
Schulsinger H (1976) A ten-year follow up of children of schizophrenic mothers: a clinical assessment. Acta Psychiatr Scand 53:371–386
Schulsinger F, Pamas J, Petersen ET, Schulsinger H, Teasdale TW, Mednick SA, Moller L, Silverton L (1984) Cerebral ventricular size in the offspring of schizophrenic mothers: a preliminary study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:602–606
Spitz RA (1965) The first year of life. International Universities Press, New York
Spring B (1981) Stress and schizophrenia: some definitional issues. Schizophr Bull 7:24–33
Stransky E (1903) Zur Kenntnis gewisser erworbener Blödsinnsformen. Neurol Zentralbl 24:1–149
Stransky E (1904) Zur Auffassung gewisser Symptome der Dementia Praecox. Neurol Zentralbl 24:1074–1085, 1137–1143
Susser M (1973) Causal thinking in the health sciences. Oxford University Press, New York
Tatossian A (1979) Phénomenologie des psychoses. Masson, Paris
Tennant C (1984) Stress and schizophrenia. A review. Integrative Psychiatry 3:248–261
Tienari P, Sorri A, Lakti I, Naarala M, Walhberg HE, Moring J, Pohjola J, Wynne LC (1987) Genetic and psychosocial factors in schizophrenia: the Finnish adoptive family study. Schizophr Bull 13:477–484
Tsuang MT, Winokur G, Crowe RR (1980) Morbidity risk of schizophrenia and affective disorders among first degree relatives of patients with schizophrenia, mania, depression, and surgical conditions. Br J Psychiatry 136:497–504
Varsamis J, Adamson JD (1971) Early schizophrenia. Can Psychiatr Assoc J 16:487–497
Weintraub S (1987) Risk factors in schizophrenia: the Stony Brook high risk project. Schizophr Bull 13:439–450
Wing JK, Brown DW (1970) Institutionalism and schizophrenia. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wing JK, Cooper JE, Sartorius N (1974) The measurement and classification of psychiatric syndromes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1990 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Parnas, J., Mednick, S.A. (1990). Early Predictors of Onset and Course of Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum. In: Häfner, H., Gattaz, W.F. (eds) Search for the Causes of Schizophrenia. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-74881-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-74881-3_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-74883-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-74881-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive