Abstract
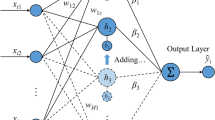
This work proposes a novel approach to Soft Sensor modelling, where the Soft Sensor is built by a set of experts which are artificial neural networks with randomly generated topology. For each of the experts a meta neural network is trained, the gating Artificial Neural Network. The role of the gating network is to learn the performance of the experts in dependency on the input data samples. The final prediction of the Soft Sensor is a weighted sum of the individual experts predictions. The proposed meta-learning method is evaluated on two different process industry data sets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jolliffe, I.T.: Principal Component Analysis. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Bishop, C.M.: Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1995)
Jang, J.S.R., Sun, C.T., Mizutani, E.: Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing. Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, Englewood Cliffs (1997)
Angelov, P.P., Filev, D.P.: Flexible models with evolving structure. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 19(4), 327–340 (2004)
Angelov, P.P., Filev, D.P.: An approach to online identification of takagi-sugeno fuzzy models. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part B, IEEE Transactions on 34(1), 484–498 (2004)
Kasabov, N.K., Song, Q.: Denfis: dynamic evolving neural-fuzzy inference system and itsapplication for time-series prediction. Fuzzy Systems, IEEE Transactions on 10(2), 144–154 (2002)
Gabrys, B., Bargiela, A.: Neural networks based decision support in presence of uncertainties. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 125(5), 272–280 (1999)
Champagne, M., Dudzic, M., Inc, T., Temiscaming, Q.: Industrial use of multivariate statistical analysis for process monitoring and control. In: American Control Conference, 2002 Proceedings of the 2002, vol. 1 (2002)
Li, W., Yue, H.H., Valle-Cervantes, S., Qin, S.J.: Recursive pca for adaptive process monitoring. Journal of Process Control 10(5), 471–486 (2000)
Fortuna, L.: Soft Sensors for Monitoring and Control of Industrial Processes. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Dunia, R., Qin, J., Edgar, T.F., McAvoy, T.J.: Sensor fault identification and reconstruction using principal component analysis. In: Proceedings of the 13th Triennial World Congress, pp. 259–264 (1996)
Dunia, R., Qin, S.J.: Joint diagnosis of process and sensor faults using principal component analysis. Control Engineering Practice 6(4), 457–469 (1998)
Amazouz, M., Pantea, R.: Use of multivariate data analysis for lumber drying process monitoring and fault detection. In: Crone, S.F., Stahlbock, S.L., R. (eds.) International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 329–332 (2006)
Macias, J.J., Zhou, P.X.: A method for predicting quality of the crude oil distillation. In: Evolving Fuzzy Systems, 2006 International Symposium on, pp. 214–220 (2006)
Jordan, M.I., Barto, A.G.: Task decomposition through competition in a modular connectionist architecture: The what and where vision tasks. Cognitive Science 15, 219–250 (1991)
Jacobs, R.: Adaptive mixtures of local experts. Neural Computation 3(1), 79–87 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kadlec, P., Gabrys, B. (2008). Gating Artificial Neural Network Based Soft Sensor. In: Nguyen, N.T., Katarzyniak, R. (eds) New Challenges in Applied Intelligence Technologies. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 134. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79355-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79355-7_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-79354-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-79355-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)