Abstract
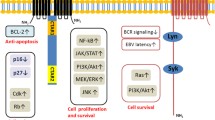
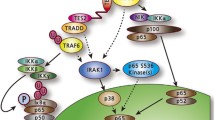
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a human herpesvirus that persistently infects its host for a lifetime through a strategy of growth transforming resting B-cells into continuously proliferating lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) while maintaining itself as an incomplete or “latent” virus in the infected cell nucleus. Immune surveillance is critical to maintaining this symbiosis as perturbations to T-cell immunity reveal the malignant potential of latent EBV-transformed B-cells. Epidemiological evidence further associates EBV infection with the development of other malignancies including Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Burkitt’s lymphoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Genetic and biochemical analyses have revealed that five viral proteins are essential for transformation by commandeering signal transduction pathways or intervening in transcriptional control. Latent infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1), a principal effector of transformation signaling, is a constitutively active receptor that exploits the tumor necrosis factor receptor-signaling pathway. This chapter reviews current models regarding the molecular mechanisms through which LMP1 enables EBV to transform B-cell growth.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbot SD, Rowe M, Cadwallader K, Ricksten A, Gordon J, Wang F, Rymo L, Rickinson AB (1990) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol 64: 2126–2134
Alfieri C, Birkenbach M, Kieff E (1991) Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes [published erratum appears in Virology 1991 Dec;185(2):946]. Virology 181: 595–608
Allday MJ, Crawford DH, Griffin BE (1989) Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol 70: 1755–1764
Allday MJ, Farrell PJ (1994) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA3C/6 expression maintains the level of latent membrane protein 1 in G1-arrested cells. J Virol 68: 3491–3498
Aman P, Rowe M, Kai C, Finke J, Rymo L, Klein E, Klein G (1990) Effect of the EBNA-2 gene on the surface antigen phenotype of transfected EBV-negative B-lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer 45: 77–82
Ambinder RF, Lemas MV, Moore S, Yang J, Fabian D, Krone C (1999) Epstein-Barr virus and lymphoma. Cancer Treat Res 99: 27–45
Babcock GJ, Decker LL, Volk M, Thorley-Lawson DA (1998) EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 9: 395–404
Babcock GJ, Decker LL, Freeman RB, Thorley-Lawson DA (1999) Epstein-barr virus-infected resting memory B cells, not proliferating lymphoblasts, accumulate in the peripheral blood of immunosuppressed patients. J Exp Med 190: 567–576
Baichwal VR, Sugden B (1987) Posttranslational processing of an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane protein expressed in cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 61: 866–875
Baichwal VR, Sugden B (1988) Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene 2: 461–467
Baud V, Liu ZG, Bennett B, Suzuki N, Xia Y, Karin M (1999) Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain. Genes Dev 13: 1297–1308
Birkenbach M, Liebowitz D, Wang F, Sample J, Kieff E (1989) Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein increases vimentin expression in human B-cell lines. J Virol 63: 4079–4084
Bradley JR, Pober JS (2001) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors ( TRAFs ). Oncogene 20: 6482–6491
Braeuninger A, Kuppers R, Strickler JG, Wacker HH, Rajewsky K, Hansmann ML (1997) Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin disease represent clonal populations of germinal center-derived tumor B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 9337–9342
Brodeur SR, Cheng G, Baltimore D, Thorley-Lawson DA (1997) Localization of the major NFkappaB-activating site and the sole TRAF3 binding site of LMP-1 defines two distinct signaling motifs. J Biol Chem 272: 19777–19784
Brooks L, Yao QY, Rickinson AB, Young LS (1992) Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol 66: 2689–2697
Burkhardt AL, Bolen JB, Kieff E, Longnecker R (1992) An Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated membrane protein interacts with src family tyrosine kinases. J Virol 66: 5161–5167
Busson P, McCoy R, Sadler R, Gilligan K, Tursz T, Raab-Traub N (1992) Consistent transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP2 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol 66: 3257–3262
Cahir McFarland ED, Izumi KM, Mosialos G (1999) Epstein-Barr virus transformation: involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Oncogene 18: 6959–6964
Caldwell RG, Wilson JB, Anderson SJ, Longnecker R (1998) Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity 9: 405–411
Caldwell RG, Brown RC, Longnecker R (2000) Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A-induced B-cell survival in two unique classes of EmuLMP2A transgenic mice. J Virol 74: 1101–1013
Chadee DN, Yuasa T, Kyriakis JM (2002) Direct activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase MEKK1 by the Ste20p homologue GCK and the adapter protein TRAF2. Mol Cell Biol 22: 737–749
Chen G, Goeddel DV (2002) TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science 296: 1634–1635
Cohen JI (1999) Epstein-Barr virus infections, including infectious mononucleosis. In: Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Isselbacher KJ, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL (eds) Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. McGraw-Hill, Boston, part 7, sect 12, chap 186
Cohen JI, Wang F, Mannick J, Kieff E (1989) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9558–9562
Cordier-Bussat M, Billaud M, Calender A, Lenoir GM (1993) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclearantigen-2-induced up-regulation of CD21 and CD23 molecules is dependent on a permissive cellular context. Int J Cancer 53: 153–160
Curran JA, Laverty FS, Campbell D, Macdiarmid J, Wilson JB (2001) Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein-1 induces epithelial cell proliferation and sensitizes transgenic mice to chemical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 61: 6730–6738
Dantuma NP, Heessen S, Lindsten K, Jenne M, Masucci MG (2000) Inhibition of proteasomal degradation by the gly-Ala repeat of Epstein-Barr virus is influenced by the length of the repeat and the strength of the degradation signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 8381–8385
Dawson CW, Rickinson AB, Young LS (1990) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature 344: 777–780
Devergne O, Hatzivassiliou E, Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kleijnen MF, Kieff E, Mosialos G (1996) Association of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 with an Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 domain important for B-lymphocyte transformation: role in NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 16: 7098–7108
Devergne O, McFarland EC, Mosialos G, Izumi KM, Ware CF, Kieff E (1998) Role of the TRAF binding site and NF-kappaB activation in Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-induced cell gene expression. J Virol 72: 7900–7908
D’Souza B, Rowe M, Walls D (2000) The bfl-1 gene is transcriptionally upregulated by the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1, and its expression promotes the survival of a Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line. J Virol 74: 6652–6658
Eliopoulos AG, Stack M, Dawson CW, Kaye KM, Hodgkin L, Sihota S, Rowe M, Young LS (1997) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and CD40 mediate IL-6 production in epithelial cells via an NF-kappaB pathway involving TNF receptor-associated factors. Oncogene 14: 2899–2916
Eliopoulos AG, Blake SM, Floettmann JE, Rowe M, Young LS (1999a) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the INK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2. J Virol 73: 1023–1035
Eliopoulos AG, Gallagher NJ, Blake SM, Dawson CW, Young LS (1999b) Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 coregulates interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 production. J Biol Chem 274: 16085–16096
Eliopoulos AG, Davies C, Blake SS, Murray P, Najafipour S, Tsichlis PN, Young LS (2002) The oncogenic protein kinase Tpl-2/Cot contributes to Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1-induced NF-kappaB signaling downstream of TRAF2. J Virol 76: 4567–4579
Fahraeus R, Jansson A, Ricksten A, Sjoblom A, Rymo L (1990) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 7390–7394
Fauci AS, Lane HC (1999) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease: AIDS and related disorders. In: Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Isselbacher KJ, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL (eds) Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. McGraw-Hill, Boston, sect 1, chap 308, p 12
Fennewald, S., van Santen, V. and Kieff, E. (1984) Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol 51 (2), 411–9.
Floettmann JE, Eliopoulos AG, Jones M, Young LS, Rowe M (1998) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) signalling is distinct from CD40 and involves physical cooperation of its two C-terminus functional regions. Oncogene 17: 2383–2392
Freedman AS (1999) Malignancies of lymphoid cells. In: Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Isselbacher KJ, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL (eds) Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. McGraw-Hill, Boston, part 6, sect 2, chap 113
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109: 581–96
Ghosh D, Kieff E (1990) cis-acting regulatory elements near the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein transcriptional start site. J Virol 64: 1855–1858
Gires O, Kohlhuber F, Kilger E, Baumann M, Kieser A, Kaiser C, Zeidler R, Scheffer B, Ueffing M, Hammerschmidt W (1999) Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus interacts with JAK3 and activates STAT proteins. EMBO J 18: 3064–3073
Gunven P, Klein G, Henle G, Henle W, Clifford P (1970) Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt’s lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Antibodies to EBV associated membrane and viral capsid antigens in Burkitt lymphoma patients. Nature 228: 1053–1056
Habeshaw G, Yao QY, Bell AI, Morton D, Rickinson AB (1999) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 sequences in endemic and sporadic Burkitt’s lymphoma reflect virus strains prevalent in different geographic areas. J Virol 73: 965–975
Hammarskjold ML, Simurda MC (1992) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein transactivates the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat through induction of NF-kappa B activity. J Virol 66: 6496–6501
Hammerschmidt W, Sugden B (1989) Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature 340: 393–397
Hammerschmidt W, Sugden B, Baichwal VR (1989) The transforming domain alone of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus is toxic to cells when expressed at high levels. J Virol 63: 2469–2475
Harada S, Kieff E (1997) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein LP stimulates EBNA-2 acidic domain-mediated transcriptional activation. J Virol 71: 6611–6618
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JK, Cleary ML, Delsol G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Falini B, Gatter KC (1994) A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 84: 1361–1392
Hatzivassiliou E, Miller WE, Raab-Traub N, Kieff E, Mosialos G (1998) A fusion of the EBV latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) transmembrane domains to the CD40 cytoplasmic domain is similar to LMP1 in constitutive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression, nuclear factor-kappa B, and stress-activated protein kinase. J Immunol 160: 1116–1121
Henderson S, Rowe M, Gregory C, Croom-Carter D, Wang F, Longnecker R, Kieff E, Rickinson A (1991) Induction of bd-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell 65: 1107–1115
Henle W, Ho HC, Henle G, Kwan HC (1973) Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Comparison of active cases with long-term survivors. J Natl Cancer Inst 51: 361–369
Hennessy K, Fennewald S, Hummel M, Cole T, Kieff E (1984) A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 7207–7211
Henriquez NV, Floettmann E, Salmon M, Rowe M, Rickinson AB (1999) Differential responses to CD40 ligation among Burkitt lymphoma lines that are uniformly responsive to Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. J Immunol 162: 3298–3307
Herbst H, Dallenbach F, Hummel M, Niedobitek G, Pileri S, Muller-Lantzsch N, Stein H (1991) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 4766–4770
Higuchi M, Kieff E, Izumi KM (2002) The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 putative Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) binding domain does not mediate JAK3 association or activation in B-lymphoma or lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol 76: 455–459
Hong SY, Yoon WH, Park JH, Kang SG, Ahn JH, Lee TH (2000) Involvement of two NF-kappa B binding elements in tumor necrosis factor alpha-, CD40-, and Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-mediated induction of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 gene. J Biol Chem 275: 18022–18028
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV (1995) The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 81: 495–504
Huen DS, Henderson SA, Croom-Carter D, Rowe M (1995) The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 ( LMPI) mediates activation of NF-kappa B and cell surface phenotype via two effector regions in its carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Oncogene 10: 549–560
IARC (1997) Proceedings of the IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8. Lyon, France, 17–24 June, 1997. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 70: 1–492
Izumi KM, Kieff ED (1997) The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12592–12597
Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kieff ED (1997) The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 1447–1452
Izumi KM, McFarland EC, Riley EA, Rizzo D, Chen Y, Kieff E (1999a) The residues between the two transformation effector sites of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 are not critical for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol 73: 9908–9916
Izumi KM, McFarland EC, Ting AT, Riley EA, Seed B, Kieff ED (1999b) The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated proteins TRADD and receptor-interacting protein ( RIP) but does not induce apoptosis or require RIP for NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 19: 5759–5767
Kaiser C, Laux G, Eick D, Jochner N, Bornkamm GW, Kempkes B (1999) The proto-oncogene c-myc is a direct target gene of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2. J Virol 73: 4481–4484
Kanzler H, Kuppers R, Helmes S, Wacker HH, Chott A, Hansmann ML, Rajewsky K (2000) Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia represent the outgrowth of single germinal-center B-cell-derived clones: potential precursors of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 95: 1023–1031
Karran L, Gao Y, Smith PR, Griffin BE (1992) Expression of a family of complementary-strand transcripts in Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8058–8062
Kaye KM, Izumi KM, Kieff E (1993) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 9150–9154
Kaye KM, Izumi KM, Mosialos G, Kieff E (1995) The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 cytoplasmic carboxy terminus is essential for B-lymphocyte transformation; fibroblast cocultivation complements a critical function within the terminal 155 residues. J Virol 69: 675–683
Kaye KM, Devergne O, Harada JN, Izumi KM, Yalamanchili R, Kieff E, Mosialos G (1996) Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2 is a mediator of NF- kappa B activation by latent infection membrane protein 1, the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 11085–11090
Kaye KM, Izumi KM, Li H, Johannsen E, Davidson D, Longnecker R, Kieff E (1999) An Epstein-Barr virus that expresses only the first 231 LMP1 amino acids efficiently initiates primary B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol 73: 10525–10530
Khan G, Miyashita EM, Yang B, Babcock GJ, Thorley-Lawson DA (1996) Is EBV persistence in vivo a model for B cell homeostasis? Immunity 5: 173–179
Kieff E, Rickinson A (2001) Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffen DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Virology, 4th edn. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins: Philadelphia, pp 2511–2573
Kieser A, Kilger E, Gires O, Ueffing M, Kolch W, Hammerschmidt W (1997) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 triggers AP-1 activity via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascade. EMBO J 16: 6478–6485
Kieser A, Kaiser C, Hammerschmidt W (1999) LMP1 signal transduction differs substantially from TNF receptor 1 signaling in the molecular functions of TRADD and TRAF2. EMBO J 18: 2511–2521
Knutson JC (1990) The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol 64: 2530–2536
Kulwichit W, Edwards RH, Davenport EM, Baskar JF, Godfrey V, Raab-Traub N (1998) Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces B cell lymphoma in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 11963–11968
Kuppers R, Rajewsky K (1998) The origin of Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg cells in Hodgkin’s disease. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 471–493
Kuppers R, Rajewsky K, Zhao M, Simons G, Laumann R, Fischer R, Hansmann ML (1994) Hodgkin disease: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells picked from histological sections show clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and appear to be derived from B cells at various stages of development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 10962–10966
Laherty CD, Hu HM, Opipari AW, Wang F, Dixit VM (1992) The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem 267: 24157–24160
Lee MA, Diamond ME, Yates JL (1999) Genetic evidence that EBNA- 1 is needed for efficient, stable latent infection by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 73: 2974–2982
Lenoir G, Philip P, Sonier R (1984) Burkitt’s type lymphoma: EBV association and cytogenetic markers in cases from various geographic origins. In: Magrath I, O’Conor G, Ramot B (eds) Environmental influences in the pathogenesis of leukaemias and lymphomas. Raven, New York, pp 283–295
Levitskaya J, Coram M, Levitsky V, Imreh S, Steigerwald-Mullen PM, Klein G, Kurilla MG, Masucci MG (1995) Inhibition of antigen processing by the internal repeat region of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1. Nature 375: 685–688
Levitskaya J, Sharipo A, Leonchiks A, Ciechanover A, Masucci MG (1997) Inhibition of ubiquitin/ proteasome-dependent protein degradation by the Gly-Ala repeat domain of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 12616–12621
Li SN, Chang YS, Liu ST (1996) Effect of a 10-amino acid deletion on the oncogenic activity of latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene 12: 2129–2135
Liebowitz D, Wang D, Kieff E (1986) Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 58: 233–237
Liebowitz D, Kopan R, Fuchs E, Sample J, Kieff E (1987) An Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein associates with vimentin in lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol 7: 2299–2308
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ (2001) The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104: 487–501
Longnecker R (2000) Epstein-Barr virus latency: LMP2, a regulator or means for Epstein-Barr virus persistence? Adv Cancer Res 79: 175–200
Magrath I (1990) The pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Adv Cancer Res 55: 133–270
Malinin NL, Boldin MP, Kovalenko AV, Wallach D (1997) MAP3K-related kinase involved in NFkappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 385: 540–544
Mann KP, Thorley-Lawson D (1987) Posttranslational processing of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded p63/LMP protein. J Virol 61: 2100–2108
Mann KP, Staunton D, Thorley-Lawson DA (1985) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol 55: 710–720
Mannick JB, Cohen JI, Birkenbach M, Marchini A, Kieff E (1991) The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein encoded by the leader of the EBNA RNAs is important in B-lymphocyte transformation. J Virol 65: 6826–6837
Marshall D, Sample C (1995) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C is a transcriptional regulator. J Virol 69: 3624–3630
Mehl AM, Fischer N, Rowe M, Hartmann F, Daus H, Trumper L, Pfreundschuh M, MullerLantzsch N, Grasser FA (1998) Isolation and analysis of two strongly transforming isoforms of the Epstein-Barr-virus(EBV)-encoded latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) from a single Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Int J Cancer 76: 194–200
Merchant M, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R (2000) The LMP2A ITAM is essential for providing B cells with development and survival signals in vivo. J Virol 74: 9115–9124
Miller CL, Longnecker R, Kieff E (1993) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A blocks calcium mobilization in B lymphocytes. J Virol 67: 3087–3094
Miller CL, Lee JH, Kieff E, Burkhardt AL, Bolen JB, Longnecker R (1994a) Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP2A regulates reactivation from latency by negatively regulating tyrosine kinases involved in slg-mediated signal transduction. Infect Agents Dis 3: 128–136
Miller CL, Lee JH, Kieff E, Longnecker R (1994b) An integral membrane protein (LMP2) blocks reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus from latency following surface immunoglobulin crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 772–776
Miller CL, Burkhardt AL, Lee JH, Stealey B, Longnecker R, Bolen JB, Kieff E (1995a) Integral membrane protein 2 of Epstein-Barr virus regulates reactivation from latency through dominant negative effects on protein-tyrosine kinases. Immunity 2: 155–166
Miller WE, Earp HS, Raab-Traub N (1995b) The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Virol 69: 4390–4398
Miller WE, Mosialos G, Kieff E, Raab-Traub N (1997) Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 induction of the epidermal growth factor receptor is mediated through a TRAF signaling pathway distinct from NF-kappaB activation. J Virol 71: 586–594
Miller WE, Cheshire JL, Baldwin AS Jr, Raab-Traub N (1998) The NPC derived C15 LMP1 protein confers enhanced activation of NF-kappa B and induction of the EGFR in epithelial cells. Oncogene 16: 1869–1877
Mitchell T, Sugden B (1995) Stimulation of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription by mutant derivatives of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 69: 2968–2976
Miyashita EM, Yang B, Lam KM, Crawford DH, Thorley-Lawson DA (1995) A novel form of Epstein-Barr virus latency in normal B cells in vivo. Cell 80: 593–601
Moorthy R, Thorley-Lawson DA (1990) Processing of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein p63/LMP. J Virol 64: 829–837
Moorthy R, Thorley-Lawson DA (1992) Mutational analysis of the transforming function of the EBV encoded LMP-1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 182: 359–365
Moorthy RK, Thorley-Lawson DA (1993a) All three domains of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein LMP-1 are required for transformation of rat-1 fibroblasts. J Virol 67: 1638–1646
Moorthy RK, Thorley-Lawson DA (1993b) Biochemical, genetic, and functional analyses of the phosphorylation sites on the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded oncogenic latent membrane protein LMP-1. J Virol 67: 2637–2645
Mosialos G, Birkenbach M, Yalamanchili R, VanArsdale T, Ware C, Kieff E (1995) The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell 80: 389–399
Murray PG, Niedobitek G, Kremmer E, Grasser F, Reynolds GM, Cruchley A, Williams DM, Muller-Lantzsch N, Young LS (1996) In situ detection of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded
nuclear antigen 1 in oral hairy leukoplakia and virus-associated carcinomas. J Pathol 178:44–47
Nakagomi H, Dolcetti R, Bejarano MT, Pisa P, Kiessling R, Masucci MG (1994) The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) induces interleukin-10 production in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer 57: 240–244
Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K, Ichijo H (1998) ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell 2: 389–395
Nitsche F, Bell A, Rickinson A (1997) Epstein-Barr virus leader protein enhances EBNA-2-mediated transactivation of latent membrane protein 1 expression: a role for the W 1 W2 repeat domain. J Virol 71: 6619–6628
Pallesen G, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Rowe M, Young LS (1991) Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin’s disease. Lancet 337: 320–322
Peng M, Lundgren E (1992) Transient expression of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene in human primary B cells induces cellular activation and DNA synthesis. Oncogene 7: 1775–1782
Polack A, Hortnagel K, Pajic A, Christoph B, Baier B, Falk M, Mautner J, Geltinger C, Bornkamm GW, Kempkes B (1996) c-myc activation renders proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)transformed cells independent of EBV nuclear antigen 2 and latent membrane protein 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 10411–10416
Rickinson A, Kieff E (2001) Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffen DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Virology, 4th edn. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 2573–2627
Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV (1994) A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78: 681–692
Rowe M, Rowe DT, Gregory CD, Young LS, Farrell PJ, Rupani H, Rickinson AB (1987) Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. EMBO J 6: 2743–2751
Rowe M, Peng-Pilon M, Huen DS, Hardy R, Croom-Carter D, Lundgren E, Rickinson AB (1994) Upregulation of bd-2 by the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein LMP1: a B-cellspecific response that is delayed relative to NF-kappa B activation and to induction of cell surface markers. J Virol 68: 5602–5612
Sandberg M, Hammerschmidt W, Sugden B (1997) Characterization of LMP-l’s association with TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3. J Virol 71: 4649–4656
Scholle F, Bendt KM, Raab-Traub N (2000) Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A transforms epithelial cells, inhibits cell differentiation, and activates Akt. J Virol 74: 10681–10689
Sharipo A, Imreh M, Leonchiks A, Branden C, Masucci MG (2001) cis-Inhibition of proteasomal degradation by viral repeats: impact of length and amino acid composition. FEBS Lett 499: 137–142
Shi CS, Kehrl JH (1997) Activation of stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase, but not NF-kappaB, by the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 through a TNF receptor-associated factor 2- and germinal center kinase related-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 272: 32102–32107
Smith PR, Griffin BE (1992) Transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus gene EBNA-1 from different promoters in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and B-lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol 66: 706–714
Sung NS, Kenney S, Gutsch D, Pagano JS (1991) EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid-specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 65: 2164–2169
Swart R, Ruf IK, Sample J, Longnecker R (2000) Latent membrane protein 2A-mediated effects on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Virol 74: 10838–10845
Sylla BS, Hung SC, Davidson DM, Hatzivassiliou E, Malinin NL, Wallach D, Gilmore TD, Kieff E, Mosialos G (1998) Epstein-Barr virus-transforming protein latent infection membrane protein 1 activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through a pathway that includes the NFkappaB-inducing kinase and the IkappaB kinases IKKalpha and IKKbeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 10106–10111
Thorley-Lawson DA, Babcock GJ (1999) A model for persistent infection with Epstein-Barr virus: the stealth virus of human B cells. Life Sci 65: 1433–1453
Tomkinson B, Robertson E, Kieff E (1993) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins EBNA-3A and EBNA-3C are essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol 67: 2014–2025
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E (1985) An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell 43: 831–840
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Wang F, Gregory C, Rickinson A, Larson R, Springer T, Kieff E (1988) Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol 62: 4173–4184
Wang F, Gregory C, Sample C, Rowe M, Liebowitz D, Murray R, Rickinson A, Kieff E (1990a) Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol 64: 2309–2318
Wang F, Tsang SF, Kurilla MG, Cohen JI, Kieff E (1990b) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol 64: 3407–3416
Wang S, Rowe M, Lundgren E (1996) Expression of the Epstein Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 causes a rapid and transient stimulation of the Bd-2 homologue Mc1–1 levels in B-cell lines. Cancer Res 56: 4610–4613
Weiss LM, Strickler JG, Warnke RA, Purtilo DT, Sklar J (1987) Epstein-Barr viral DNA in tissues of Hodgkin’s disease. Am J Pathol 129: 86–91
Wilson JB, Weinberg W, Johnson R,Yuspa S, Levine AJ (1990) Expression of the BNLF-1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus in the skin of transgenic mice induces hyperplasia and aberrant expression of keratin 6. Cell 61: 1315–1327
Wu TC, Mann RB, Charache P, Hayward SD, Staal S, Lambe BC, Ambinder RF (1990) Detection of EBV gene expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin’s disease. Int J Cancer 46: 801–804
Yates J, Warren N, Reisman D, Sugden B (1984) A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 3806–3810
Yoshizaki T, Sato H, Furukawa M, Pagano JS (1998) The expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 is enhanced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3621–3626
Yuasa T, Ohno S, Kehrl JH, Kyriakis JM (1998) Tumor necrosis factor signaling to stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)/Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38. Germinal center kinase couples TRAF2 to mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase 1 and SAPK while receptor interacting protein associates with a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase upstream of MKK6 and p38. J Biol Chem 273: 22681–22692
Zhao B, Sample CE (2000) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C activates the latent membrane protein 1 promoter in the presence of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 through sequences encompassing an spi-1/Spi-B binding site. J Virol 74: 5151–5160
Zimber-Strobl U, Suentzenich KO, Laux G, Eick D, Cordier M, Calender A, Billaud M, Lenoir GM, Bornkamm GW (1991) Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol 65: 415–423
zur Hausen H, Schulte-Holthausen H, Klein G, Henle W, Henle G, Clifford P, Santesson L (1970) EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature 228: 1056–1058
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Izumi, K.M. (2004). Epstein-Barr Virus Signal Transduction and B-Lymphocyte Growth Transformation. In: Alonso, C. (eds) Viruses and Apoptosis. Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology, vol 36. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74264-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74264-7_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-74263-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-74264-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive