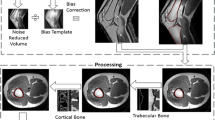
Abstract
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is routinely employed to assess muscular response and presence of inflammatory reactions in patients treated with metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty, driving the decision for revision surgery. However, MRI is lacking contrast for bony structures and as a result orthopaedic surgical planning is mostly performed on computed tomography images. In this paper, we combine the complementary information of both modalities into a novel framework for the joint segmentation of healthy and pathological musculoskeletal structures as well as implants on all images. Our processing pipeline is fully automated and was designed to handle the highly anisotropic resolution of clinical MR images by means of super resolution reconstruction. The accuracy of the intra-subject multimodal registration was improved by employing a non-linear registration algorithm with hard constraints on the deformation of bony structures, while a multi-atlas segmentation propagation approach provided robustness to the large shape variability in the population. The suggested framework was evaluated in a leave-one-out cross-validation study on 20 hip sides. The proposed pipeline has potential for the extraction of clinically relevant imaging biomarkers for implant failure detection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UK National Joint Registry: 13th Annual Report (December 2015) (2016)
Berber, R., Khoo, M., Cook, E., Guppy, A., Hua, J., Miles, J., Carrington, R., Skinner, J., Hart, A.: Muscle atrophy and metal-on-metal hip implants: a serial MRI study of 74 hips. Acta Orthop. 86(3), 351–357 (2015)
MHRA of the Department of Health: Medical Device Alert. MHRA Database, pp. 1–7 (2012). http://www.mhra.gov.uk
Bogner, E., Sofka, C.: CT evaluation of total hip arthroplasty complication: Dissociation of acetabular component. HSS J. 3(1), 112–114 (2007)
Pedoia, V., Majumdar, S., Link, T.: Segmentation of joint and musculoskeletal tissue in the study of arthritis. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phy. 29(2), 207–221 (2016)
Seim, H., Kainmüller, D., Heller, M., Lamecker, H., Zachow, S., Hege, H.C.: Automatic segmentation of the pelvic bones from CT data based on a statistical shape model. In: Proceedings of the 1st Eurographics Conference on Visual Computing for Biomedicine - EG VCBM 2008, pp. 93–100 (2008)
Yokota, F., Okada, T., Takao, M., Sugano, N., Tada, Y., Tomiyama, N., Sato, Y.: Automated CT segmentation of diseased hip using hierarchical and conditional statistical shape models. In: Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., Barillot, C., Navab, N. (eds.) MICCAI 2013. LNCS, vol. 8150, pp. 190–197. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_24
Pettersson, J., Knutsson, H., Borga, M.: Automatic hip bone segmentation using non-rigid registration. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition - ICPR 2006, vol. 3, pp. 946–949. IEEE (2006)
Chu, C., Chen, C., Liu, L., Zheng, G.: FACTS: fully automatic CT segmentation of a hip joint. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43(5), 1247–1259 (2015)
Prescott, J., Best, T., Swanson, M., Haq, F., Jackson, R., Gurcan, M.: Anatomically anchored template-based level set segmentation: application to quadriceps muscles in MR images from the osteoarthritis initiative. J. Digit. Imaging 24(1), 28–43 (2011)
Ahmad, E., Yap, M., Degens, H., McPhee, J.: Atlas-registration based image segmentation of MRI human thigh muscles in 3D space. In: Mello-Thoms, C.R., Kupinski, M. (eds.) Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2014: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment, vol. 9037, p. 90371L. SPIE (2014)
Gilles, B., Magnenat-Thalmann, N.: Musculoskeletal MRI segmentation using multi-resolution simplex meshes with medial representations. Med. Image Anal. 14(3), 291–302 (2010)
Klemt, C., Modat, M., Pichat, J., Cardoso, M., Henckel, J., Hart, A., Ourselin, S.: Automatic assessment of volume asymmetries applied to hip abductor muscles in patients with hip arthroplasty. In: Ourselin, S., Styner, M. (eds.) Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2015: Image Processing, vol. 9413, p. 94131M. SPIE (2015)
Castro-Mateos, I., Pozo, J., Lazary, A., Frangi, A.: Automatic construction of patient-specific finite-element mesh of the spine from IVDs and vertebra segmentations. In: Gimi, B., Krol, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2016: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging, vol. 9788, p. 97881U. SPIE (2016)
Sabah, S., Mitchell, A., Henckel, J., Sandison, A., Skinner, J., Hart, A.: Magnetic resonance imaging findings in painful metal-on-metal hips: a prospective study. J. Arthroplasty 26(1), 71–76 (2011)
Gorgolewski, K., Burns, C., Madison, C., Clark, D., Halchenko, Y., Waskom, M., Ghosh, S.: Nipype: a flexible, lightweight and extensible neuroimaging data processing framework in python. Front. Neuroinf. 5, 13 (2011)
Van Leemput, K., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P.: Automated model-based bias field correction of MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 18(10), 885–896 (1999)
Ebner, M., Chouhan, M., Patel, P.A., Atkinson, D., Amin, Z., Read, S., Punwani, S., Taylor, S., Vercauteren, T., Ourselin, S.: Point-spread-function-aware slice-to-volume registration: application to upper abdominal MRI super-resolution. In: Zuluaga, M.A., Bhatia, K., Kainz, B., Moghari, M.H., Pace, D.F. (eds.) RAMBO/HVSMR -2016. LNCS, vol. 10129, pp. 3–13. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52280-7_1
Modat, M., Cash, D., Daga, P., Winston, G., Duncan, J., Ourselin, S.: Global image registration using a symmetric block-matching approach. J. Med. Imaging 1(2), 024003 (2014)
Haber, E., Heldmann, S., Modersitzki, J.: A computational framework for image-based constrained registration. Linear Algebra Appl. 431(3–4), 459–470 (2009)
Ashburner, J., Ridgway, G.: Symmetric diffeomorphic modeling of longitudinal structural MRI. Front. Neurosci. 6, 197 (2013)
Modat, M., Daga, P., Cardoso, M., Ourselin, S., Ridgway, G., Ashburner, J.: Parametric non-rigid registration using a stationary velocity field. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis - MMBIA 2012, pp. 145–150 (2012)
Staring, M., Klein, S., Pluim, J.: A rigidity penalty term for nonrigid registration. Med. Phys. 34(11), 4098–4108 (2007)
Cardoso, J., Leung, K., Modat, M., Keihaninejad, S., Cash, D., Barnes, J., Fox, N., Ourselin, S.: STEPS: similarity and truth estimation for propagated segmentations and its application to hippocampal segmentation and brain parcelation. Med. Image Anal. 17(6), 671–684 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the EPSRC-funded UCL Centre for Doctoral Training in Medical Imaging [EP/L016478/1], the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust, the Department of Healths NIHR-funded Biomedical Research Centre at University College London Hospitals and Innovative Engineering for Health award by the Wellcome Trust [WT101957] and EPSRC [NS/A000027/1], and by Wellcome/EPSRC [203145Z/16/Z].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ranzini, M.B.M. et al. (2018). Joint Multimodal Segmentation of Clinical CT and MR from Hip Arthroplasty Patients. In: Glocker, B., Yao, J., Vrtovec, T., Frangi, A., Zheng, G. (eds) Computational Methods and Clinical Applications in Musculoskeletal Imaging. MSKI 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10734. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74113-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74113-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-74112-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-74113-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)