Abstract
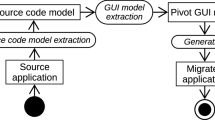
The legacy of mainframe terminal applications has generally limited the complexity level in desktop applications’ user interfaces. Nevertheless the apparition of the new Internet-related technologies is driving to the migration of traditional desktop applications into the web to benefit from the internet technology services. However, GUI’s modernization is a new software engineering field that requires a thorough analysis to build and preserve the important characteristics and functionality of the user interfaces. It provides support for transforming existing system’s user interfaces to new ones that satisfy new demands. In this work, we have focused on the Architecture-driven modernization ADM approach as a best solution for the legacy system’s evolution. The OMG ADM Task Force defines a set of standards to facilitate interoperability between modernization tools. We cite the Knowledge Discovery Metamodel and Abstract Syntax Tree Metamodel. For our work, these two standards will help us to capture design knowledge needed for the construction of modern Nooj user interfaces. We present along this work a reengineering of Nooj application GUIs. We explain its migration process to transform the old desktop GUIs into modern ones respecting web technologies. The process consists of a deep analysis that affects both the structural and behavioral aspects of a GUI, and sophisticated reverse engineering algorithms that must be designed to cope with it.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pérez-Castillo, R., de Guzmán, I.G.R., Piattini, M.: Architecture-driven modernization. In: Modern Software Engineering Concepts and Practices: Advanced Approaches, p. 75. IGI Global, Hershey (2010)
OMG: Architecture-Driven Modernization. http://adm.omg.org
OMG: Abstract Syntax Tree Metamodel. http://www.omg.org/spec/ASTM/
OMG: Architecture-Driven Modernization: Knowledge Discovery Meta-Model, v1.4. http://www.omg.org/spec/KDM/1.4/
Chikofsky, E.J.: Reverse engineering and design recovery: a taxonomy. J. Softw. IEEE 7(1), 13–17 (1990)
Pérez-Castillo, R., de Guzman, I.G.R., Piattini, M., Ebert, C.: Reengineering technologies. IEEE Softw. 28(6), 13–17 (2011)
Miller, J., Mukerji, J.: MDA Guide Version 1.0.1. Object Management Group, Needham (2003)
Blanc, X., Salvatori, O.: MDA en action: Ingénierie logicielle guidée par les modèles. Editions Eyrolles, paris (2011)
OMG: QVT. Meta Object Facility 2.0, Query/View/Transformation Specification. http://www.omg.org/spec/QVT/1.0/PDF/. Accessed June 2014
Silberztein, M.: NooJ’s dictionaries. Proc. LTC 5, 291–295 (2005)
CodePro Analytix. https://developers.google.com/java-dev-tools/codepro/doc
JDT: Eclipse Java development tools. https://eclipse.org/jdt
Gotti, Z., Mbarki, S.: Java swing modernization approach-complete abstract representation based on static and dynamic analysis. In: ICSOFT-EA, pp. 210–219 (2016)
Laaz, N., Mbarki, S.: A model-driven approach for generating RIA interfaces using IFML and ontologies. In: Information Science and Technology (CiSt) (2016)
Gotti, S., Mbarki, S.: Toward IFVM virtual machine: a model driven IFML interpretation. In: ICSOFT-EA, pp. 220–225 (2016)
Silva, J.C., Silva, C.E., Campos, J.C., Saraiva, J.A.: GUI behavior from source code analysis. In: Interacç ao 2010, Quarta Conferência Nacional em Interacçao Humano-Computador, Universidade de Aveiro, October 2010
Eclipse: MoDisco. http://www.eclipse.org/MoDisco
Memon, A.M., Banerjee, I., Nagarajan, A.: GUI ripping: reverse engineering of graphical user interfaces for testing. In: WCRE, vol. 3, p. 260, November 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gotti, Z., Mbarki, S., Gotti, S., Laaz, N. (2018). Nooj Graphical User Interfaces Modernization. In: Mbarki, S., Mourchid, M., Silberztein, M. (eds) Formalizing Natural Languages with NooJ and Its Natural Language Processing Applications. NooJ 2017. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 811. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73420-0_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73420-0_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-73419-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-73420-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)