Abstract
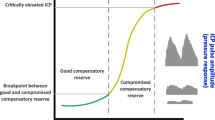
Objectives: The detection of increasing intracranial pressure (ICP) is important in preventing secondary brain injuries. Before mean ICP increases critically, transient ICP elevations may be observed. We have observed ICP transients of less than 10 min duration ,which occurred simultaneously with transient increases in heart rate (HR). These simultaneous events in HR and ICP suggest a direct interaction or communication between the heart and the brain. Methods: This chapter describes four mathematical methods and their applicability in detecting the above heart–brain cross-talk events during long-term monitoring of ICP. Results: Recurrence plots, cross-correlation function and wavelet analysis confirmed the relationship between ICP and HR time series. Using the peaks detection algorithm with a sliding window approach we found an average of 37 cross-talk events (± SD 39). The number of events detected varied among patients, from 1 to more than 150 events. Conclusion: Our analysis suggested that the peaks detection algorithm based on a sliding window approach is feasible for detecting simultaneous peaks, e.g. cross-talk events in the ICP and HR signals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu X, et al. Morphological clustering and analysis of continuous intracranial pressure. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2009;56:696–705.
Hu X, et al. Estimation of hidden state variables of the intracranial system using constrained nonlinear Kalman filters. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007;54:597–610.
Hu X, et al. Adaptive computation of approximate entropy and its application in integrative analysis of irregularity of heart rate variability and intracranial pressure signals. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30:631–9.
Hu X, et al. Characterization of interdependency between intracranial pressure and heart variability signals: a causal spectral measure and a generalized synchronization measure. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007;54:1407–17.
Marwan N, Romano MC, Thiel M, Kurths J. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys Rep. 2007;438(5–6):237–329.
Eckmann J-P, Oliffson Kamphorst S, David R. Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys Lett. 1987;4:973.
Fabretti A, Ausloos M. Recurrence plot and recurrence quantification analysis techniques for detecting a critical regime. Examples from financial market indices. Int J Mod Phys C. 2005;16(05):671–706.
Takens F. Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. Dynamical systems and turbulence, Warwick 1980. Berlin: Springer; 1981. p. 366–81.
Kapinchev K, Bradu A, Barnes F, Podoleanu A. GPU implementation of cross-correlation for image generation in real time. ICSPCS 2015. 2015.
Tian F, et al. Wavelet coherence analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neuroimage Clin. 2016;11:124–32.
Mallat SG. A wavelet tour of signal processing. San Diego: Academic Press; 1999.
Grinsted A, Moore JC, Jevrejeva S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Proc Geophys. 2004;11:561–6.
Palshikar G. Simple algorithms for peak detection in time-series. Proc. 1st Int. Conf. Advanced Data Analysis, Business Analytics and Intelligence. 2009.
Conflicts of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dimitri, G.M. et al. (2018). Simultaneous Transients of Intracranial Pressure and Heart Rate in Traumatic Brain Injury: Methods of Analysis. In: Heldt, T. (eds) Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, vol 126. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65798-1_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65798-1_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-65797-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-65798-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)