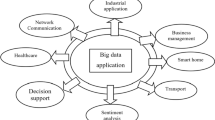
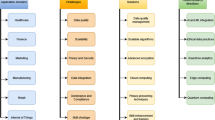
Abstract
Big Data has been gathering importance in the last few years, specially through bigger data generation, and, consequently, more accessible storage of said data. They are originated at social media or sensors, for example, and are stored to be transformed in useful information. The use of Big Data is becoming more common in several fields of business, mainly because it is a source of competitive differential, through the analysis of the stored data. This study has the objective of executing a systematic review towards presenting a broad vision of Big Data. Were analyzed 466 publications from 2005 until March 2016.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gartner Group. (2011). Gartner says worldwide enterprise IT spending to reach $2.7 Trillion in 2012. [Online]. Available: http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/1824919.
Davenport, T. (2014). Big data no trabalho. Brazil: Campus.
Chandarana, P., & Vijayalakshmi, M. (2014). Big data analytics frameworks. In Proceedings of the international conference on circuits, systems communication and information technology applications 2014 (pp. 430–434). Mumbai.
Laney, D. (2011). 3D data management: Controlling data volume, velocity, and variety. Information and Software Technology, 51(4), 769–784.
Liu, Z., Yang, P., & Zhang, L. (2013). A sketch of big data technologies. In 2013 seventh international conference on internet computing for engineering and science (pp. 26–29).
Ramesh, B. (2015). Big data: Architecture (vol. 11). India: Springer India.
Ward, J. S., & Barker, A. (2013). Undefined by data: A survey of big data definitions. arXiv.org, 1, 2.
Benjelloun, F.-Z., Lahcen, A. A., & Belfkih, S. (2015). An overview of big data opportunities, applications and tools. In Intelligent systems computer vision (ISCV), 2015 (pp. 1–6).
Maria, R. E., et al. (2015). Applying scrum in an interdisciplinary project using big data, internet of things, and credit cards. In Proceedings of 12th international conference on information technology: New generations ITNG 2015 (pp. 67–72). Linz.
Chen, M., Mao, S., & Liu, Y. (2014). Big data: A survey. January, 19, 171–209.
Schneider, R. D. (2012). Hadoop for dummies (1st ed.). EUA: John Wiley & Sons.
Demchenko, Y., Grosso, P., De Laat, C., & Membrey, P. (2013). Addressing big data issues in scientific data infrastructure. In Proceedings of 2013 international conference on collaboration technologies and systems (CTS 2013) (pp. 48–55).
Seay, C., Agrawal, R., Kadadi, A., & Barel, Y. (2015). Using hadoop on the mainframe: A big solution for the challenges of big data. In 12th international conference on information technology: New generations (ITNG), 2015 (pp. 765–769).
Zikopoulos, P., & Eaton, C. (2011). Understanding big data: Analytics for enterprise class hadoop and streaming data. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Kitchenham, B. (2004). Procedures for performing systematic reviews. United Kingdom: Keele University Technical Report.
Li, S., & Ni, J. (2015). Evolution of big-data-enhanced higher education systems. In 2015 eighth international conference on internet computing for science and engineering (pp. 253–258).
Raghupathi, W., & Raghupathi, V. (2014). Big data analytics in healthcare: Promise and potential. Health Information Science and Systems, 2, 1–10.
Katal, A., Wazid, M., & Goudar, R. H. (2013). Big data: Issues, challenges, tools and good practices. In Sixth international conference on contemporary computong, IC3 2013 (pp. 404–409).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Santos, A.F.C., Teles, Í.P., Siqueira, O.M.P., de Oliveira, A.A. (2018). Big Data: A Systematic Review. In: Latifi, S. (eds) Information Technology - New Generations. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 558. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54978-1_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54978-1_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-54977-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-54978-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)