Abstract
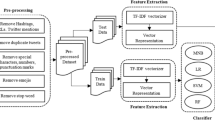
The present work is done as part of shared task in Sentiment Analysis in Indian Languages (SAIL 2015), under constrained category. The task is to classify the twitter data into three polarity categories such as positive, negative and neutral. For training, twitter dataset under three languages were provided Hindi, Bengali and Tamil. In this shared task, ours is the only team who participated in all the three languages. Each dataset contained three separate categories of twitter data namely positive, negative and neutral. The proposed method used binary features, statistical features generated from SentiWordNet, and word presence (binary feature). Due to the sparse nature of the generated features, the input features were mapped to a random Fourier feature space to get a separation and performed a linear classification using regularized least square method. The proposed method identified more negative tweets in the test data provided Hindi and Bengali language. In test tweet for Tamil language, positive tweets were identified more than other two polarity categories. Due to the lack of language specific features and sentiment oriented features, the tweets under neutral were less identified and also caused misclassifications in all the three polarity categories. This motivates to take forward our research in this area with the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://aci.info/2014/07/12/the-data-explosion-in-2014-minute-by-minute-infographic. Accessed 25 August 2015
http://wikibon.org/blog/big-data-statistics/. Accessed 25 August 2015
http://www.scidev.net/global/data/feature/big-data-for-development-facts-and-figures.html. Accessed 25 August 2015
Seungyeon, K., Fuxin, L., Guy, L., Irfan, E.: Beyond Sentiment: The Manifold of Human Emotions (2012)
Amitava D., Sivaji B.: SentiWordNet for Indian languages. In: Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Asian Language Resources (ALR), pp. 56–63, August 2010
Maite, T., Julian, B., Milan, T., Kimberly, V., Manfred, S.: Lexiconbased methods for sentiment analysis. Comput. Linguist. 37(2), 267–307 (2011)
Abilhoa, W.D., de Castro, L.N.: A keyword extraction method from twitter messages represented as graphs. Appl. Math. Comput. 240, 308–325 (2014)
Aman, S., Szpakowicz, S.: Identifying expressions of emotion in text. In: Matoušek, V., Mautner, P. (eds.) TSD 2007. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 4629, pp. 196–205. Springer, Heidelberg (2007)
Changhua Y., Hsin-Yih L.K., Hsin-Hsi, C.: Building emotion lexicon from weblog corpora. In: Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting of the ACL on Interactive Poster and Demonstration Sessions Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 133–136 (2007)
Hiroya, T., Takashi, I., Manabu, O.: Extracting semantic orientations of words using spin model. In: Proceedings of the 43rd AnnualMeeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2005), pp. 133–140 (2005)
Stefano, B., Andrea, E., Fabrizio, S.: Sentiwordnet 3.0: an enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the 7th conference on International Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2010), Valletta, Malta (2010)
Theresa, W., Janyce, W., Paul, H.: Recognizing contextual polarity in phrase-level sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the HLT/EMNLP, Vancouver, Canada (2005)
Maite, T., Anthony, C., Voll, K.: Creating semantic orientation dictionaries. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC), Genoa, pp. 427–432 (2006)
Yoshimitsu, T., Dipankar, D., Sivaji, B., Manabu, O.: Proceedings of 2nd workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity and Sentimental Analaysis, ACL-HLT, pp. 80–86 (2011)
Bo, P., Lee, L., Vaithyanathan S.: Thumbs up? sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In: The Proceedings of EMNLP, pp. 79–86 (2002)
Kreutzer, J., Witte, N.: Opinion Mining using SentiWordNet. Uppsala University (2013)
Wiebe, J., Mihalcea, R.: Word sense and subjectivity. In: The Proceedings of COLING/ACL-2006, pp. 1065–1072 (2006)
Pooja, P., Sharvari, G.: A framework for sentiment analysis in Hindi using HSWN. IJCA 119, 975–8887 (2015)
Namita, M., Basant, A., Garvit, C., Nitin, B., Prateek, P.: Sentiment analysis of Hindi review based on negation and discourse relation. In: International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Nagoya, Japan, October 2013
Joshi, A., Balamurali, A.R., Bhattacharyya, P.: A fall-back strategy for sentiment analysis in Hindi: a case study. In: Proceedings of the 8th ICON (2010)
Amitava D., Sivaji, B.: SentiWordNet for Indian Languages. Asian Federation for Natural Language Processing (COLING), China, pp. 56–63, (2010)
Sumit K.G., Gunjan, A.: Sentiment analysis in Hindi language: a survey. In: IJMTER (2014)
Richa, S., Shweta, N., Rekha, J.: Opinion mining in Hindi language: a survey. IJFCST 4(2), 41 (2014)
Pooja, P., Sharvari, G.: A survey of sentiment classification techniques used for Indian regional languages. IJCSA 5(2), 13–26 (2015)
Anu, S.: Sentiment analyzer using Punjabi language. In: IJIRCCE, vol. 2 (2014)
Thangarasu, M., Manavalan, R.: Tree-based mining with sentiment analysis for discovering patterns of human interaction in meetings Tamil document. IJCII 3(3), 151–159 (2013)
Arun, S., Kumar, M.A., Soman, K.P.: Sentiment analysis of Tamil movie reviews via Feature Frequency Count, in Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (2015)
Neethu, M., Nair, J.P.S., Govindaru, V.: Domain specific sentence level mood extraction from malayalam text. In: Advances in Computing and Communications (2012)
Deepu, S. N., Jisha, P.J., Rajeev, R.R., Elizabeth, S.: SentiMa-sentiment extraction for Malayalam. In: ICACCI, pp. 1719–1723 (2014)
Sandeep, C., Bhadran, V.K., Santhosh, G., Manoj, K.P.: Document level Sentiment Extraction for Malayalam (Feature based Domain Independent Approach). In: IJARTET (2015)
Kishorjith, N., Dilipkumar, K., Wangkheimayum, H., Shinghajith, K., Sivaji, B.: Verb based Manipuri sentiment analysis. IJNLC 3(3), 1307–2278 (2014)
Alekh, A., Pushpak, B.: Sentiment analysis: a new approach for effective use of linguistic knowledge and exploiting similarities in a set of documents to be classified. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Language Processing (2005)
Balamurali, A. R., Aditya, J., Pushpak, B.: Cross-lingual sentiment analysis for Indian languages using linked wordnets. In: COLLINS (Poster), pp. 73–82 (2012)
http://amitavadas.com/SAIL/index.html. Accessed on 25 August 2015
Olena, K., Jacques, S.: Feature selection in sentiment analysis. In: CORIA (2012)
Hussam, H., Patrice, B., Fredric, B.: The imapact of Zscore on twitter sentiment analysis. In: International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, pp. 636–641 (2014)
Tacchetti, A., Pavan, S.M., Santoro, M., Rosasco, L.: A toolbox for regularised least squares learning, GURLS (2012)
Rifkin, R., Gene, Y., Tomaso, P.: Regularized least-squares classification. Nato Sci. Ser. Sub Ser. III Comput. Syst. Sci. 190, 131–154 (2003)
Rahimi, A., Benjamin, R.: Random features for large-scale kernel machines. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2007)
Somla, A.J., Scholkopf, B., Muller, K.R.: The connection between regularization operators and support vector kernels. Neural Netw. 11, 637–649 (1997)
Patra, B.G., Das, D., Das, A., Prasath, R.: Shared Task on Sentiment Analysis in Indian Languages (SAIL) Tweets - An Overview (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, S.S., Premjith, B., Kumar, M.A., Soman, K.P. (2015). AMRITA_CEN-NLP@SAIL2015: Sentiment Analysis in Indian Language Using Regularized Least Square Approach with Randomized Feature Learning. In: Prasath, R., Vuppala, A., Kathirvalavakumar, T. (eds) Mining Intelligence and Knowledge Exploration. MIKE 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 9468. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-26832-3_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-26832-3_64
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-26831-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-26832-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)