Abstract
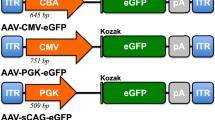
The retinal expression patterns were analyzed following the injection of serotype 8 adeno-associated virus (AAV8) vectors that utilize two broadly active and commonly used sets of transcription regulatory sequences. These include the human cytomegalovirus (CMV) immediate early (IE) enhancer/promoter and the hybrid CAG element (also known as CAGGS or CBA) composed of a partial human CMV IE enhancer and the chicken β-actin promoter and intron. Subretinal delivery to postnatal day 0 (P0) or 6 (P6) mouse eyes resulted in efficient labeling of retinal cells, but with very distinct patterns. With P0 delivery, AAV8-CMV-GFP selectively labelled photoreceptors, while AAV8-CAG-GFP efficiently labeled both outer and inner retinal neurons, including photoreceptors, horizontal cells, amacrine cells and retinal ganglion cells. With P6 delivery, both vectors led to efficient labeling of photoreceptors and Müller glia cells, but not of inner retinal neurons. Our results suggest that the cell types that express the genes encoded by subretinally delivered AAV8 vectors are determined by both the timing of the injection and the regulatory sequences.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allocca M, Mussolino C, Garcia-Hoyos M et al (2007) Novel adeno-associated virus serotypes efficiently transduce murine photoreceptors. J Virol 81:11372–11380
Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G et al (1985) A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell 41:521–530
Cronin T, Vandenberghe LH, Hantz P et al (2014) Efficient transduction and optogenetic stimulation of retinal bipolar cells by a synthetic adeno-associated virus capsid and promoter. EMBO Mol Med 6(9):1175–1190
Doroudchi MM, Greenberg KP, Liu J et al (2011) Virally delivered channelrhodopsin-2 safely and effectively restores visual function in multiple mouse models of blindness. Mol Ther 19:1220–1229
Macé E, Caplette R, Marre O et al (2015) Targeting channelrhodopsin-2 to ON-bipolar cells with vitreally administered AAV restores ON and OFF visual responses in blind mice. Mol Ther 23(1):7–16
Matsuda T, Cepko CL (2004) Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:16–22
McCarty DM, Young SM, Samulski RJ (2004) Integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) and recombinant AAV vectors. Annu Rev Genet 38:819–845
Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J (1991) Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 108:193–199
Qin JY, Zhang L, Clift KL et al (2010) Systematic comparison of constitutive promoters and the doxycycline-inducible promoter. PLoS One 5:e10611
Uga S, Smelser GK (1973) Electron microscopic study of the development of retinal Müllerian cells. Invest Ophthalmol 12:295–307
Vandenberghe LH, Xiao R, Lock M et al (2010) Efficient serotype-dependent release of functional vector into the culture medium during adeno-associated virus manufacturing. Hum Gene Ther 21:1251–1257
Wang S, Sengel C, Emerson M et al (2014) The binary decision of rod and bipolar fate in the vertebrate retina is controlled by a gene regulatory network. Dev Cell 30:513–527
Watanabe S, Sanuki R, Ueno S et al (2013) Tropisms of AAV for subretinal delivery to the neonatal mouse retina and its application for in vivo rescue of developmental photoreceptor disorders. PLoS One 8:e54146
Young RW (1985) Cell differentiation in the retina of the mouse. Anat Rec 212:199–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiong, W., Cepko, C. (2016). Distinct Expression Patterns of AAV8 Vectors with Broadly Active Promoters from Subretinal Injections of Neonatal Mouse Eyes at Two Different Ages. In: Bowes Rickman, C., LaVail, M., Anderson, R., Grimm, C., Hollyfield, J., Ash, J. (eds) Retinal Degenerative Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 854. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_67
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_67
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-17120-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-17121-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)