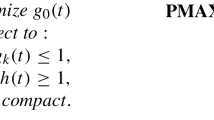Abstract
We shall deal with the numerical solution of optimization problems of the following type
where
-
1.
L is a constant matrix of rank k < n and
-
2.
the semi-infinite constraint functions ƒ 1,. . . , ƒ m are assumed to be concave in y (at least on the domain where they are positive, see the function (det(y))1/n on y ≥ 0, i.e. on the set of positive semidefinite matrices). Note that “finite” constraints ƒ j (x) ≥ 0 are formally incorporated by just selecting a j = b j .
-
3.
The functions ƒ i , i = 0, . . .,m are assumed to be algebraically simple and rather smooth, e.g. analytic on their domains of definition, both in x and y. This condition may seem rather stringent at first, it is however of great importance. Analyticity is, of course, a very broad property. We shall show that for important classes of constraints the arising analytic functions are of special type, e. g. like the Stieltjes functions, such that they can be approximated very effectively by suitable, low complexity algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.S. Bahvalow, Methodes Numeriques, ed. Nauka (Mir) Moscow, 1980.
P.J. Davis, P. Rabinovitz, Methods of Numerical Integration, Academic Press, New York, 1975.
P.D. Domich et al., Optimal 3-dimensional methods for linear programming, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, NISTIR 89–4225.
M.C. Ferris, A.B. Philpott, An interior point method for semi-infinite programming, Mathematical Programming (43) 1989 pp. 257–276.
R. Hettich, ed., Semi-Infinite Programming, Lect. Notes in Control and Inf Sciences, Vol. 15, Springer Verlag 1979.
F. Jarre, Interior Point Methods for convex programming, to appear in Applied Math. and Optimization, 1993.
J.C. Lagarias, M.J. Todd, eds., Mathematical Developments Arising from Linear Programming, Contemporary Mathematics, Vol. 114, Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, 1989.
G. Lopes, Conditions for convergence of multipoint Padé approximations for functions of Stieltjes type, Math. USSR Sbornik, Vol. 35 (1979), No. 3.
I.J. Lustig, R.E. Marsten, D.F.Shanno, Computational Experience with a Primal-Dual Interior Point Method for Linear Programming Techniques, Industrial and Syst. Engineering Rep. Ser., Rep. J-89-11, Inst. of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia.
U. Schättier, An interior point method for semi-infinite programming problems, Doct. Dissertation, Univ. Würzburg, Inst. f. Angew. Math. 1992.
G. Sonnevend, J. Stoer, G. Zhao, On the complexity of following the central path by linear extrapolation in linear programs, Mathematical Programming, 1991, pp. 527–553.
G. Sonnevend, Constructing feedback control in differential games by the use of central trajectories, DFG Report, Nr. 385/1992, Inst. für Angewandte Mathematik, Univ. Würzburg (July 1992), 37 p., to appear in ZAMM.
G. Sonnevend, J. Stoer, Global ellipsoidal approximations and homotopy methods for smooth, convex, analytic programs, Applied Math. and Appl., 21 (1980) pp. 139–165.
G. Sonnevend, Applications of Analytic Centers, NATO ASI Ser. F, Vol. 70, “Numerical Linear Algebra and Digital Signal Processing” (P. van Dooren, and G.Golub eds.), Reidel 1988.
G. Sonnevend, Application of analytic centers for the numerical solution of semi-infinite, convex programs arising in control theory, 15 p., DFG Report , Anwendungsbezogene Optimierung und Steuerung, Nr. 170/1989, Inst. für Angewandte Mathematik, Univ,. Würzburg.
T. Tsuchiya, M. Murarmatsu, Global convergence of a long-step affine scaling algorithm for degenerate linear programming problems, Res. Memo. Nr. 423, Inst. of Statistical Math., Tokyo 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1994 Birkhäuser Verlag Basel
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sonnevend, G. (1994). A New Class of a High Order Interior Point Method for the Solution of Convex Semiinfinite Optimization Problems. In: Bulirsch, R., Kraft, D. (eds) Computational Optimal Control. ISNM International Series of Numerical Mathematics, vol 115. Birkhäuser Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8497-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8497-6_16
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-7643-5015-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-8497-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive