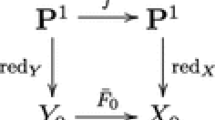
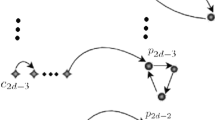
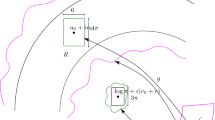
Abstract
The dynamical classification of rational maps is a central concern of holomorphic dynamics. Much progress has been made, especially on the classification of polynomials and some approachable one-parameter families of rational maps; the goal of finding a classification of general rational maps is so far elusive. Newton maps (rational maps that arise when applying Newton’s method to a polynomial) form a most natural family to be studied from the dynamical perspective. Using Thurston’s characterization and rigidity theorem, a complete combinatorial classification of postcritically finite Newton maps is given in terms of a finite connected graph satisfying certain explicit conditions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
We denote the n-th iterate of a dynamical system f : X → X by fn : X → X.
References
B. Bielefeld, Y. Fisher, J. Hubbard, The classification of critically preperiodic polynomials as dynamical systems. J. Am. Math. Soc. 5, 721–762 (1992)
X. Buff, A. Epstein, S. Koch, Twisted matings and equipotential gluings. Ann. Fac. Sci. Toulouse Math. 6(21), 995–1031 (2012)
X. Buff, G. Cui, L. Tan, Teichmüller spaces and holomorphic dynamics, in Handbook of Teichmüller Theory, ed. by A. Papadopoulos, vol. IV (European Mathematical Society, 2014), pp. 717–756
K. Cordwell, S. Gilbertson, N. Nuechterlein, K. Pilgrim, S. Pinella, On the classification of critically fixed rational maps. Conform. Geom. Dyn. 19, 51–94 (2015)
A. Douady, J. Hubbard, A proof of Thurston’s topological characterization of rational functions. Acta Math. 171, 263–297 (1993)
K. Drach, D. Schleicher, Rigidity of Newton dynamics (2018). arXiv:1812.11919
K. Drach, Y. Mikulich, J. Rückert, D. Schleicher, A combinatorial classification of postcritically fixed Newton maps. Ergodic Theory Dyn. Syst. 39(11), 2983–3014 (2019)
K. Drach, R. Lodge, D. Schleicher, M. Sowinski, Puzzles and the Fatou-Shishikura injection for rational Newton maps. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 374, 2753–2784 (2021)
B. Farb, D. Margalit, A Primer on Mapping Class Groups. Princeton Mathematical Series, vol. 49 (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2011)
L. Geyer, Classification of critically fixed anti-rational maps (2020). arXiv:2006.10788
J. Head, The combinatorics of Newton’s method for cubic polynomials. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University (1987)
M. Hlushchanka, Tischler graphs of critically fixed rational maps and their applications (2019). arXiv:1904.04759v1
J. Hubbard, D. Schleicher, S. Sutherland, How to find all roots of complex polynomials by Newton’s method. Invent. Math. 146, 1–33 (2001)
R. Lodge, Y. Luo, S. Mukherjee, Circle packings, kissing reflection groups and critically fixed anti-rational maps. Forum Math. Sigma (2020). arXiv:2007.03558
R. Lodge, Y. Mikulich, D. Schleicher, Combinatorial properties of Newton maps. Indiana Univ. Math. J. 70(5), 1833–1867 (2021)
J. Luo, Combinatorics and holomorphic dynamics: captures, matings, Newton’s method. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University (1995)
K. Mamayusupov, A characterization of postcritically minimal Newton maps of complex exponential functions. Ergodic Theory Dyn. Syst. 39(10), 2855–2880 (2019)
C. McMullen, Complex Dynamics and Renormalization. Annals of Mathematics Studies, vol. 135 (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1994)
Y. Mikulich, A classification of postcritically finite Newton maps. Ph.D. Thesis, Jacobs University Bremen (2011)
J. Milnor, Dynamics in One Complex Variable. Annals of Mathematics Studies, vol. 160 (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2006)
K. Pilgrim, L. Tan, Combining rational maps and controlling obstructions. Ergodic Theory Dyn. Syst. 18, 221–245 (1998)
A. Poirier, Hubbard trees. Fundam. Math. 208(3), 193–248 (2010)
M. Randig, D. Schleicher, R. Stoll, Newton’s method in practice II: the iterated refinement Newton method and near-optimal complexity for finding all roots of some polynomials of very large degrees (2017). arXiv:1703.05847
P. Roesch, Y. Yin, J. Zeng, Rigidity of non-renormalizable Newton maps (2018). arXiv:1811.09978
J. Rückert, Newton’s method as a dynamical system. Ph.D. Thesis, International University Bremen (2006)
D. Schleicher, On the efficient global dynamics of Newton’s method for complex polynomials (2011). arXiv:1108.5773
D. Schleicher, R. Stoll, Newton’s method in practice: finding all roots of polynomials of degree one million efficiently. Theor. Comput. Sci. 681, 146–166 (2017)
S. Shemyakov, R. Chernov, D. Rumiantsau, D. Schleicher, S. Schmitt, A. Shemyakov, Finding polynomial roots by dynamical systems — a case study. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 40(12), 6945–6965 (2020)
L. Tan, Branched coverings and cubic Newton maps. Fundam. Math. 154, 207–259 (1997)
X. Wang, Y. Yin, J. Zeng, Dynamics of Newton maps (2018). arXiv:1805.11478
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), as well as the Advanced Grant 695621 HOLOGRAM of the European Research Council (ERC), which is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are most grateful to the anonymous referee for very helpful comments that have led to marked improvements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lodge, R., Mikulich, Y., Schleicher, D. (2022). A Classification of Postcritically Finite Newton Maps. In: Ohshika, K., Papadopoulos, A. (eds) In the Tradition of Thurston II. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97560-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97560-9_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97559-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97560-9
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)