Abstract
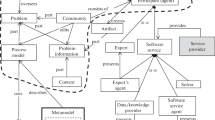
Efficient collaboration of humans and machines has the great potential for improving many knowledge-intensive processes in variety of applications. Therefore, developing means supporting such collaboration and making it efficient is an important area of research. The paper presents a part of research aimed on the development of a collective intelligence environment that would support joint work of humans and machines on decision support problems, allowing participants to self-organize (define and adapt the plan of actions). In particular, it describes an approach to solving semantic interoperability issues in supporting human-machine collective intelligence for decision-making scenarios. The proposed approach is based on using multi-aspect ontologies and ontology-based smart spaces.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulkarni, A., Can, M., Hartmann, B.: Collaboratively crowdsourcing workflows with turkomatic. In: Proceedings of the ACM 2012 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work - CSCW 2012, p. 1003. ACM Press, New York (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2145204.2145354
Retelny, D., Bernstein, M.S., Valentine, M.A.: No workflow can ever be enough: how crowdsourcing workflows constrain complex work. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 1, Article 89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3134724
Karacapilidis, N., Tampakas, V.: On the exploitation of collaborative argumentation structures for inducing reasoning behavior. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on WWW/Internet 2019, pp. 78–84. IADIS Press (2019). https://doi.org/10.33965/icwi2019_201913L010
Gruber, T.R.: Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing? Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 43, 907–928 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1006/ijhc.1995.1081
OWL 2 Web Ontology Language Document Overview. https://www.w3.org/TR/owl2-overview/
RDF 1.1 Concepts and Abstract Syntax. https://www.w3.org/TR/rdf11-concepts/
Schneider, C., Weinmann, M., vom Brocke, J.: Digital nudging. Commun. ACM 61, 67–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3213765
Guo, K.L.: DECIDE: a decision-making model for more effective decision making by health care managers. Health Care Manager 27, 118–127 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.HCM.0000285046.27290.90
Smirnov, A., Shilov, N., Parfenov, V.: Building a multi-aspect ontology for semantic interoperability in PLM. In: Product Lifecycle Management in the Digital Twin Era. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, pp. 107–115. Springer (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42250-9_10
Luc, D.T.: Pareto optimality. In: Pareto Optimality, Game Theory and Equilibria. Springer Optimization and Its Applications, vol. 17. pp. 481–515. Springer, New York (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77247-9_18
Korzun, D.: On the smart spaces approach to semantic-driven design of service-oriented information systems (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40180-5_13
Roffia, L., Azzoni, P., Aguzzi, C., Viola, F., Antoniazzi, F., Salmon Cinotti, T.: Dynamic linked data: a SPARQL event processing architecture. Future Internet 10, 36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10040036
Acknowledgments
The research is funded by Russian Science Foundation, project 19-11-00126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Smirnov, A., Ponomarev, A. (2021). Supporting Collective Intelligence of Human-Machine Teams in Decision-Making Scenarios. In: Russo, D., Ahram, T., Karwowski, W., Di Bucchianico, G., Taiar, R. (eds) Intelligent Human Systems Integration 2021. IHSI 2021. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1322. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68017-6_115
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68017-6_115
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68016-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68017-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)