Abstract
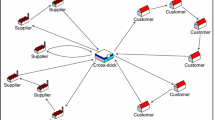
Cross-docking is a logistics strategy that aims at less transportation costs and fast customer deliveries. Incorporating an efficient vehicle routing could increase the benefits of the cross-docking. In this paper, the vehicle routing problem with reverse cross-docking (VRP-RCD) is studied. Reverse logistics has attracted more attention due to its ability to gain more profit and maintain the competitiveness of a company. VRP-RCD includes a four-level supply chain network: suppliers, cross-dock, customers, and outlets, with the objective of minimizing vehicle operational and transportation costs. A two-phase heuristic that employs an adaptive large neighborhood search (ALNS) with various destroy and repair operators is proposed to solve benchmark instances. The simulated annealing framework is embedded to discover a vast search space during the search process. Experimental results show that our proposed ALNS obtains optimal solutions for 24 out of 30 problems of the first set of benchmark instances while getting better results for all instances in the second set of benchmark instances compared to optimization software.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Brito, M.P., Dekker, R.: A framework for reverse logistics. In: Dekker, R., Fleischmann, M., Inderfurth, K., Van Wassenhove, L.N. (eds.) Reverse Logistics, pp. 3–27. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24803-3_1
Demir, E., Bektaş, T., Laporte, G.: An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the pollution-routing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 223(2), 346–359 (2012)
Grangier, P., Gendreau, M., Lehuédé, F., Rousseau, L.M.: A matheuristic based on large neighborhood search for the vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. Comput. Oper. Res. 84, 116–126 (2017)
Gunawan, A., Widjaja, A.T., Vansteenwegen, P., Yu, V.F.: Adaptive large neighborhood search for vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (WCCI) (2020, accepted for publication)
Gunawan, A., Widjaja, A.T., Vansteenwegen, P., Yu, V.F.: A matheuristic algorithm for solving the vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. In: Kotsireas, I.S., Pardalos, P.M. (eds.) LION 2020. LNCS, vol. 12096, pp. 9–15. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53552-0_2
Hasani-Goodarzi, A., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.: Capacitated vehicle routing problem for multi-product cross-docking with split deliveries and pickups. Proc. - Soc. Behav. Sci. 62, 1360–1365 (2011)
Hemmelmayr, V.C., Cordeau, J.F., Crainic, T.G.: An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for two-echelon vehicle routing problems arising in city logistics. Comput. Oper. Res. 39(12), 3215–3228 (2012)
Jayaraman, V., Luo, Y.: Creating competitive advantages through new value creation: a reverse logistics perspective. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 21(2), 56–73 (2007)
Kaboudani, Y., Ghodsypour, S.H., Kia, H., Shahmardan, A.: Vehicle routing and scheduling in cross docks with forward and reverse logistics. Oper. Res. Int. J 20, 1589–1622 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0396-z
Lambert, S., Riopel, D., Abdul-Kader, W.: A reverse logistics decisions conceptual framework. Comput. Ind. Eng. 61(3), 561–581 (2011)
Lee, Y.H., Jung, J.W., Lee, K.M.: Vehicle routing scheduling for cross-docking in the supply chain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 51(2), 247–256 (2006)
Liao, C.J., Lin, Y., Shih, S.C.: Vehicle routing with cross-docking in the supply chain. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(10), 6868–6873 (2010)
Lutz, R.: Adaptive large neighborhood search. Bachelor thesis, Universität Ulm (2015)
Nikolopoulou, A.I., Repoussis, P.P., Tarantilis, C.D., Zachariadis, E.E.: Moving products between location pairs: cross-docking versus direct-shipping. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 256(3), 803–819 (2017)
Rezaei, S., Kheirkhah, A.: Applying forward and reverse cross-docking in a multi-product integrated supply chain network. Prod. Eng. 11(4–5), 495–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-017-0743-6
Ropke, S., Pisinger, D.: An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for the pickup and delivery problem with time windows. Transp. Sci. 40(4), 455–472 (2006)
Sacramento, D., Pisinger, D., Ropke, S.: An adaptive large neighborhood search metaheuristic for the vehicle routing problem with drones. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 102, 289–315 (2019)
Shaw, P.: Using constraint programming and local search methods to solve vehicle routing problems. In: Maher, M., Puget, J.-F. (eds.) CP 1998. LNCS, vol. 1520, pp. 417–431. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49481-2_30
Wen, M., Larsen, J., Clausen, J., Cordeau, J.F., Laporte, G.: Vehicle routing with cross-docking. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 60(12), 1708–1718 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2008.108
Widjaja, A.T., Gunawan, A., Jodiawan, P., Yu, V.F.: Incorporating a reverse logistics scheme in a vehicle routing problem with cross-docking network: a modelling approach. In: 2020 7th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications, pp. 854–858. IEEE (2020)
Yu, V.F., Jewpanya, P., Redi, A.P.: Open vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. Comput. Ind. Eng. 94, 6–17 (2016)
Zuluaga, J.P.S., Thiell, M., Perales, R.C.: Reverse cross-docking. Omega 66, 48–57 (2017)
Acknowledgment
This research is supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) Academic Research Fund (AcRF) Tier 1 grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gunawan, A., Widjaja, A.T., Vansteenwegen, P., Yu, V.F. (2020). Vehicle Routing Problem with Reverse Cross-Docking: An Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search Algorithm. In: Lalla-Ruiz, E., Mes, M., Voß, S. (eds) Computational Logistics. ICCL 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12433. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59747-4_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59747-4_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59746-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59747-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)