Abstract
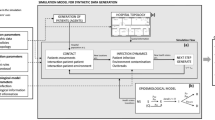
A Multi-Agent simulator made in Unity 3D is proposed to track the spread of Hospital Acquired Infections transmitted by contact in hospital wards. The tool generates a real-time contamination risk map for both people and spaces, depending on the profile, behavior and activities of virtual agents, the characteristics of pathogens and the role of inanimate objects and places.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klevens, R.M., et al.: Estimating health care-associated infections and deaths in U.S. Hospitals, 2002. Public Health Rep. 122, 160–166 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1177/003335490712200205
Scott, R.D.: The direct medical costs of healthcare-associated infections in U.S. hospitals and the benefits of prevention. In: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009)
Davies, J.: Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 74, 417–433 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00016-10
Beggs, C.B., Shepherd, S.J., Kerr, K.G.: Increasing the frequency of hand washing by healthcare workers does not lead to commensurate reductions in staphylococcal infection in a hospital ward. BMC Infect. Dis. 8, 114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-8-114
Schaumann, D., et al.: A computational framework to simulate human spatial behavior in built environments. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Simulation for Architecture and Urban Design, pp. 121–128 (2016)
Simeone, D., Yehuda, E., Schaumann, D., Carrara, G.: Adding users’ dimension to BIM. In: Morello, E., Piga, B.E.A. (eds.) 11th Conference of the European Envisioning Architecture: Design, Evaluation, Communication, pp. 483–490. Architectural Envisioning Association, Milano (2013)
World Health Organization: Prevention of hospital-acquired infections: a practical guide (2002). No. WHO/CDS/CSR/EPH/2002.12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formalization and writing D.E.; software, review and editing D.E., D.S.; supervision and project administration D.C. and Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Esposito, D., Schaumann, D., Camarda, D., Kalay, Y.E. (2020). A Multi-Agent Simulator for Infection Spread in a Healthcare Environment. In: Demazeau, Y., Holvoet, T., Corchado, J., Costantini, S. (eds) Advances in Practical Applications of Agents, Multi-Agent Systems, and Trustworthiness. The PAAMS Collection. PAAMS 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12092. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49778-1_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49778-1_36
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-49777-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-49778-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)