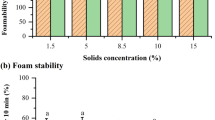
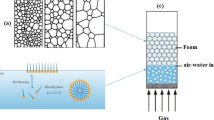
Abstract
In dairy industry, foaming of milk can be undesirable in many processes (e.g. bottle filling, milk transportation in the pipe systems or reconstitution of milk powders) or desirable for many products (e.g. cappuccino-style drinks, milkshake, ice cream or whipped cream). For foam-based products, the quality of foam imparts the body, smoothness and lightness to the products, and constitutes to the main sensory appeal to the consumers. Depending on the continuous phase in which air bubbles are dispersed, the foam-based products can be categorized into liquid or solid foams in which the continuous phase exists as liquid phase or transforms to (semi-) solid phase, respectively. The formation and stability of milk foam are determined by many factors including properties of milk (origin, age, composition, protein/solid concentration, presence of surfactants, fat content, etc.), processing conditions (foaming method, heating treatment, homogenization, or temperature and/or pH at which foam is created), even seasonality or added substances. Among these factors, milk fat has both detrimental and beneficial effects on the development of foam and its stability depending on its physical state and type of foam (liquid or solid foam). In this chapter, together with description of importance of foam or foaming in the manufacture of aerated dairy products and mechanism of the foaming process, a particular emphasis is placed on the impact of the milk fat on the foaming behavior of both liquid and solid foams, aiming to provide an insight on the foaming process, by which the foaming of milk can be controlled on demand for a particular application. Effects of the other factors on the foaming process are not in the scope of this chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aime, D., Arntfield, S., Malcolmson, L., & Ryland, D. (2001). Textural analysis of fat reduced vanilla ice cream products. Food Research International, 34, 237–246.
Anderson, M., & Brooker, B. E. (1988). Dairy foams. In E. Dickinson & G. Stainsby (Eds.), Advances in food emulsions and foams (pp. 221–225). London, UK: Elsevier Applied Science Publisher.
Barford, N. M., Krog, N., Larsen, G., & Buchheim, W. (1991). Effects of emulsifiers on protein-fat interaction in ice cream mix during ageing. I: Quantitative analyses. Lipids, 93, 24–29.
Berk, Z. (2008). Food process engineering and technology. Oxford, UK: Academic Press.
Biasutti, M., Venir, E., Marino, M., Maifreni, M., & Innocente, N. (2013). Effects of high pressure homogenisation of ice cream mix on the physical and structural properties of ice cream. International Dairy Journal, 32, 40–45.
Blecker, C., Paquot, M., Lamberti, I., Sensidoni, A., Lognay, G., & Deroanne, C. (1997). Improved emulsifying and foaming of whey proteins after enzymic fat hydrolysis. Journal of Food Science, 62, 48.
NIIR Board. (2013). Modern technology of milk processing & dairy products (4th ed.). Delhi, India: NIIR Project Consultancy Services.
Bogdan, Z., & Chandrapala, J. (2015). High power ultrasound processing in milk and dairy products. In N. Datta & P. M. Tomasula (Eds.), Emerging dairy processing technologies: Opportunities for the dairy industry (pp. 149–180). Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Borcherding, K., Hoffmann, W., Lorenzen, P. C., & Schrader, K. (2008). Effect of milk homogenisation and foaming temperature on properties and microstructure of foams from pasteurised whole milk. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 41, 2036–2043.
Buchanan, R. (1965). Lipolysis and the frothing of milk. Australian Journal of Dairy Technology, 20, 62–66.
Campbell, G. M., & Mougeot, E. (1999). Creation and characterisation of aerated food products. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 10, 283–296.
Chandan, R. C., Kilara, A., & Shah, N. P. (2009). Dairy processing and quality assurance (2nd ed.). Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Chee, C. H., & Chow, M. C. (2006). Edible emulsions. In P. Somasundaran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science (Vol. 3, pp. 1846–1856). Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis.
Clarke, C. (2006). The science of ice cream. Cambridge, UK: RSC Publishing, The Royal Chemistry Society.
Day, E. A. (1966). Role of milk lipids in flavors of dairy products (Advances in chemistry series) (p. 94). Washington, DC: American Chemical Society.
Deeth, H., & Smith, R. (1983). Lipolysis and other factors affecting the steam frothing capacity of milk. Australian Journal of Dairy Technology, 38, 14.
Deeth, H. C. (2006). Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis in milk. International Dairy Journal, 16, 555–562.
Drewnowski, A. (1997). Why do we like fat? Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 97, S58–S62.
Euston, S. R. (1997). Emulsifiers in dairy products and dairy substitutes. In G. L. Hasenhuettl & R. W. Hartel (Eds.), Food emulsifiers and their applications (pp. 173–210). Boston, MA: Springer US.
Euston, S. R. (2008). Emulsifiers in dairy products and dairy substitutes. In G. L. Hasenhuettl & R. W. Hartel (Eds.), Food emulsifiers and their applications (2nd ed., pp. 195–232). New York, NY: Springer.
Gamboa, G. V., & Barraquio, V. L. (2013). Foaming properties at different fat levels and age of milk. The Philippine Agricultural Scientist, 95, 416–421.
Gantner, V., Mijić, P., Baban, M., Škrtić, Z., & Turalija, A. (2015). The overall and fat composition of milk of various species. Mljekarstvo/Dairy, 65, 223–231.
Goff, H. D. (1997). Colloidal aspects of ice cream - A review. International Dairy Journal, 7, 363–373.
Goff, H. D., & Hartel, R. W. (2013a). Ice cream structure. In Ice cream (pp. 313–352). New York, NY: Springer.
Goff, H. D., & Hartel, R. W. (2013b). Mix processing and properties. In Ice cream (pp. 121–154). New York, NY: Springer.
Goh, J., Kravchuk, O., & Deeth, H. (2009). Comparison of mechanical agitation, steam injection and air bubbling for foaming milk of different types. Milchwissenschaft, 64, 121–124.
Golding, M., & Pelan, E. (2008). Application of emulsifiers to reduce fat and enhance nutritional quality. In G. L. Hasenhuettl & R. W. Hartel (Eds.), Food emulsifiers and their applications (2nd ed., pp. 327–348). New York, NY: Springer.
Gordon, M. H. (2013). Milk lipids. In Y. W. Park & G. F. W. Haenlein (Eds.), Milk and dairy products in human nutrition: Production, composition and health (pp. 65–79). Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Granger, C., Leger, A., Barey, P., Langendorff, V., & Cansell, M. (2005). Influence of formulation on the structural networks in ice cream. International Dairy Journal, 15, 255–262.
Gray, I. (1973). Seasonal variations in the composition and thermal properties of New Zealand milk fat: I. Fatty-acid composition. Journal of Dairy Research, 40, 207–214.
Grummer, R. R. (1991). Effect of feed on the composition of milk fat. Journal of Dairy Science, 74, 3244–3257.
Hayes, M. G., Lefrancois, A. C., Waldron, D. S., Goff, H. D., & Kelly, A. L. (2003). Influence of high pressure homogenisation on some characteristics of ice cream. Milchwissenschaft-Milk Science International, 58, 519–523.
Hidden, F., Boomsma, J., Schins, A., & Van den Berg, E. (2012). Cappuccino and specific heat versus heat of vaporization. The Physics Teacher, 50, 103–104.
Huppertz, T. (2010). Foaming properties of milk: A review of the influence of composition and processing. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 63, 477–488.
Huppertz, T., Smiddy, M. A., Goff, H. D., & Kelly, A. L. (2011). Effects of high pressure treatment of mix on ice cream manufacture. International Dairy Journal, 21, 718–726.
Innocente, N., Biasutti, M., Venir, E., Spaziani, M., & Marchesini, G. (2009). Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distribution and rheological properties of ice cream mixes. Journal of Dairy Science, 92, 1864–1875.
Jensen, R. G. (2002). The composition of bovine milk lipids: January 1995 to December 2000. Journal of Dairy Science, 85, 295–350.
Kamath, S., Huppertz, T., Houlihan, A. V., & Deeth, H. C. (2008). The influence of temperature on the foaming of milk. International Dairy Journal, 18, 994–1002.
Kamath, S., Wulandewi, A., & Deeth, H. (2008). Relationship between surface tension, free fatty acid concentration and foaming properties of milk. Food Research International, 41, 623–629.
Karleskind, D., Laye, I., Mei, F. I., & Morr, C. V. (1995). Foaming properties of lipid-reduced and calcium-reduced whey-protein concentrates. Journal of Food Science, 60, 738–741.
Khezri, M., Shahriari, S., & Shahsavani, L. (2017). The effect of xanthan gum and temperature on foam stability of milk-based espresso coffees. Journal of Food Biosciences and Technology, 7, 15–22.
Kim, S. H., Morr, C. V., Seo, A., & Surak, J. G. (1989). Effect of whey pretreatment on composition and functional-properties of whey-protein concentrate. Journal of Food Science, 54, 25–29.
Kitchen, B., & Cranston, K. (1969). Lipase activation in farm milk supplies. Australian Journal of Dairy Technology, 24, 107–112.
Koeferli, C. R. S., Piccinali, P., & Sigrist, S. (1996). The influence of fat, sugar and non-fat milk solids on selected taste, flavor and texture parameters of a vanilla ice-cream. Food Quality and Preference, 7, 69–79.
Kontkanen, H., Rokka, S., Kemppinen, A., Miettinen, H., Hellstrom, J., Kruus, K., et al. (2011). Enzymatic and physical modification of milk fat: A review. International Dairy Journal, 21, 3–13.
Koxholt, M. M. R., Eisenmann, B., & Hinrichs, J. (2001). Effect of the fat globule sizes on the meltdown of ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 84, 31–37.
Li, Z., Marshall, R., Heymann, H., & Fernando, L. (1997). Effect of milk fat content on flavor perception of vanilla ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 80, 3133–3141.
Lilbaek, H. M., Fatum, T. M., Ipsen, R., & Sorensen, N. K. (2007). Modification of milk and whey surface properties by enzymatic hydrolysis of milk phospholipids. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 2970–2978.
Long, Z., Zhao, M. M., Zhao, Q. Z., Yang, B., & Liu, L. Y. (2012). Effect of homogenisation and storage time on surface and rheology properties of whipping cream. Food Chemistry, 131, 748–753.
MacGibbon, A. K. H., & Taylor, M. W. (2006). Composition and structure of bovine milk lipids. In P. F. Fox & P. L. H. McSweeney (Eds.), Advanced dairy chemistry volume 2: Lipids (pp. 1–42). Boston, MA: Springer.
Madden, J. (1989). Ice cream. In A. Wilson (Ed.), Foams: Physics, chemistry and structure (pp. 185–196). London, UK: Springer.
Marshall, R. T., & Arbuckle, W. S. (1996). Ice cream. New York, NY: International Thomson Publishing.
Norris, G. E., Gray, I., & Dolby, R. (1973). Seasonal variations in the composition and thermal properties of New Zealand milk fat: II. Thermal properties of milk fat and their relation to composition. Journal of Dairy Research, 40, 311–321.
Nylander, T., Arnebrant, T., Bos, M., & Wilde, P. (2008). Protein/emulsifier interactions. In G. L. Hasenhuettl & R. W. Hartel (Eds.), Food emulsifiers and their applications (2nd ed., pp. 89–171). New York, NY: Springer.
Olson, D. W., White, C. H., & Watson, C. E. (2003). Properties of frozen dairy desserts processed by microfluidization of their mixes. Journal of Dairy Science, 86, 1157–1162.
Palmquist, D., Beaulieu, A. D., & Barbano, D. (1993). Feed and animal factors influencing milk fat composition. Journal of Dairy Science, 76, 1753–1771.
Patel, M. T., & Kilara, A. (1990). Studies on whey protein concentrates. 2. Foaming and emulsifying properties and their relationships with physicochemical properties. Journal of Dairy Science, 73, 2731–2740.
Pei, Z., & Schmidt, K. (2010). Ice cream: Foam formation and stabilization - a review. Food Reviews International, 26, 122–137.
Peltonen-Shalaby, R., & Mangino, M. (1986). Compositional factors that affect the emulsifying and foaming properties of whey protein concentrates. Journal of Food Science, 51, 91–95.
Pilhofer, G. M., Lee, H.-C., McCarthy, M. J., Tong, P. S., & Bruce German, J. (1994). Functionality of milk fat in foam formation and stability. Journal of Dairy Science, 77, 55–63.
Prindiville, E., Marshall, R., & Heymann, H. (1999). Effect of milk fat on the sensory properties of chocolate ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 82, 1425–1432.
Ranjith, P. H. M., & Wijewardene, U. (2006). Lipid emulsifiers and surfactants in dairy and bakery products. In F. D. Gunstone (Ed.), Modifying lipids for use in food (pp. 393–428). Cambridge, UK: Woodhead Publishing.
Rego, O. A., Cabrita, A. R., Rosa, H. J., Alves, S. P., Duarte, V., Fonseca, A. J., et al. (2016). Changes in milk production and milk fatty acid composition of cows switched from pasture to a total mixed ration diet and back to pasture. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 15, 76–86.
Rinn, J.-C., Morr, C., Seo, A., & Surak, J. (1990). Evaluation of nine semi-pilot scale whey pretreatment modifications for producing whey protein concentrate. Journal of Food Science, 55, 510–515.
Roland, A. M., Phillips, L. G., & Boor, K. J. (1999). Effects of fat content on the sensory properties, melting, color, and hardness of ice cream. Journal of Dairy Science, 82, 32–38.
Samkova, E., Spicka, J., Pesek, M., Pelikanova, T., & Hanus, O. (2012). Animal factors affecting fatty acid composition of cow milk fat: A review. South African Journal of Animal Science, 42, 83–100.
Truong, T., Bansal, N., & Bhandari, B. (2014). Effect of emulsion droplet size on foaming properties of milk fat emulsions. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 3416–3428.
Truong, T., Palmer, M., Bansal, N., & Bhandari, B. (2016). Methodologies to vary milk fat globule size. In Effect of milk fat globule size on the physical functionality of dairy products (pp. 15–30). New York, NY: Springer International Publishing.
Vaghela, M. N., & Kilara, A. (1996). Foaming and emulsifying properties of whey protein concentrates as affected by lipid composition. Journal of Food Science, 61, 275–280.
Venkatachalam, S., John, S. G., & Kuppuswamy, K. (2015). Foam mat drying of food materials: A review. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 39, 3165–3174.
Walker, G. P., Wijesundera, C., Dunshea, F. R., & Doyle, P. T. (2013). Seasonal and stage of lactation effects on milk fat composition in northern Victoria. Animal Production Science, 53, 560–572.
Walstra, P. (1989). Principles of foam formation and stability. In A. Wilson (Ed.), Foams: Physics, chemistry and structure (pp. 1–15). London, UK: Springer.
Walstra, P., Geurts, T. J., Noomen, A., Jellema, A., & vanBoekel, M. A. J. S. (1999). Dairy technology: Principles of milk properties and processes. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc..
Wright, A. J., & Marangoni, A. G. (2006). Crystallization and rheological properties of milk fat. In P. F. Fox & P. L. H. McSweeney (Eds.), Advanced dairy chemistry volume 2: Lipids (pp. 245–291). Boston, MA: Springer.
Zayas, J. F. (1997). Foaming properties of proteins. In Functionality of proteins in food (pp. 260–309). New York, NY: Springer.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded through Australian Research Council’s Industrial Transformation Research Hub (ARC-ITRH) grant with Lion Dairy and Drinks as an industry partner. The ARC Dairy Innovation Hub is a collaboration between The University of Melbourne, The University of Queensland and Dairy Innovation Australia Ltd. The authors acknowledge the facilities, and the scientific and technical assistance, of the School of Agriculture and Food Sciences at The University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ho, T.M., Bhandari, B., Bansal, N. (2020). Influence of Milk Fat on Foam Formation, Foam Stability and Functionality of Aerated Dairy Products. In: Truong, T., Lopez, C., Bhandari, B., Prakash, S. (eds) Dairy Fat Products and Functionality. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41661-4_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41661-4_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-41660-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-41661-4
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)