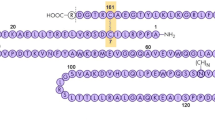
Abstract
Erythropoietin (EPO), the primary cytokine of erythropoiesis, stimulates both proliferation and differentiation of erythroid progenitors and their maturation to red blood cells. Basal EPO levels maintain the optimum levels of circulating red blood cells. However, during hypoxia, EPO secretion and its expression is elevated drastically in renal interstitial fibroblasts, thereby increasing the number of erythroid progenitors and accelerating their differentiation to mature erythrocytes. A tight regulation of this pathway is therefore of paramount importance. The biological response to EPO is commenced through the involvement of its cognate receptor, EPOR. The receptor–ligand complex results in homodimerization and conformational changes, which trigger downstream signaling events and cause activation or inactivation of critical transcription factors that promote erythroid expansion. In recent years, recombinant human EPO (rEPO) has been widely used as a therapeutic tool to treat a number of anemias induced by infection, and chemotherapy for various cancers. However, several studies have uncovered a tumor promoting ability of EPO in man, which likely occurs through EPOR or alternative receptor(s). On the other hand, some studies have demonstrated a strong anticancer activity of EPO, although the mechanism still remains unclear. A thorough investigation of EPOR signaling could yield enhanced understanding of the pathobiology for a variety of disorders, as well as the potential novel therapeutic strategies. In this chapter, in addition to the clinical relevance of EPO/EPOR signaling, we review its anticancer efficacy within various tumor microenvironments.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Youssoufian H, Longmore G, Neumann D, Yoshimura A, Lodish HF (1993) Structure, function, and activation of the erythropoietin receptor. Blood 81:2223–2236
Yasuda Y, Nagao M, Okano M, Masuda S, Sasaki R et al (1993) Localization of erythropoietin and erythropoietin-receptor in post-implantation mouse embryos. Dev Growth Differ 35(6):711–722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-169X.1993.00711.x
Snow MHL (1977) Gastrulation in the mouse: growth and regionalization of the epiblast. J Embryol Exp Morphol 42:293–303. https://dev.biologists.org/content/42/1/293
Yasuda Y, Fujita Y, Musha T, Tanaka H, Shiokawa S, Nakamatsu K et al (2001) Expression of erythropoietin in human female reproductive organs. Ital J Anat Embryol 106:215–222
Acs G, Zhang PJ, Rebbeck TR, Acs P, Verma A (2002) Immunohistochemical expression of erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor in breast carcinoma. Cancer 95:965–981. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.10787
Arcasoy MO, Amin K, Karayal AF, Chou SC, Raleigh JA et al (2002) Functional significance of erythropoietin receptor expression in breast cancer. Lab Investig 82:911–918. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.LAB.0000020415.72863.40
Feldman L, Wang Y, Rhim JS, Bhattacharya N, Loda M, Sytkowski AJ (2006) Erythropoietin stimulates growth and STAT5 phosphorylation in human prostate epithelial and prostate cancer cells. Prostate 66:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20310
Lopez TV, Lappin TRJ, Maxwell P, Shi Z, Lopez-Marure R, Aguilar C et al (2011) Autocrine/paracrine erythropoietin signaling promotes JAK/STAT-dependent proliferation of human cervical cancer cells. Int J Cancer 129:2566–2576. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25935
Yasuda Y, Fujita Y, Matsuo T, Koinuma S, Hara S, Tazaki A et al (2003) Erythropoietin regulates tumour growth of human malignancies. Carcinogenesis 24:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgg060
Mittelman M, Neumann D, Peled A, Kanter P, Haran-Ghera N (2003) Erythropoietin induces tumor regression and antitumor immune responses in murine myeloma models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(9):5181–5186. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Erythropoietin+induces+tumor+regression+and+antitumor+immune+responses+in+murine+myeloma+models
Cervi D, Shaked Y, Haeri M, Usenko T, Lee CR et al (2007) Enhanced natural-killer cell and erythropoietic activities in VEGF-A-overexpressing mice delay F-MuLV-induced erythroleukemia. Blood 109(5):2139–2146. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-11-026823
Cervi D, Truong AH, Lee JS, Sukhai N, Li YJ, Koki A, Ben-David Y (2004) Phosphorylation status of c-kit and EPO receptors, and the presence of wild-type p53 confer in vitro resistance of murine erythroleukemic cells to Celecoxib. Oncogene 23(13):2305–2314. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207400
Deshet-Unger N, Hiram-Bab S, Haim-Ohana Y, Mittelman M, Gabet Y, Neumann D (2016) Erythropoietin treatment in murine multiple myeloma: immune gain and bone loss. Sci Rep 6:30998. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30998
Katz O, Gil L, Lifshitz L, Prutchi-Sagiv S, Gassmann M, Mittelman M, Neumann D (2007) Erythropoietin enhances immune responses in mice. Eur J Immunol 37(6):1584–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200637025
Lamanuzzi A, Saltarella I, Ferrucci A, Ria R, Ruggieri S, Racanelli V et al (2016) Role of erythropoietin in the angiogenic activity of bone marrow endothelial cells of MGUS and multiple myeloma patients. Oncotarget 7(12):14510–14521. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7587
Vatsveen TK, Sponaas AM, Tian E, Zhang Q, Misund K, Sundan A et al (2016) Erythropoietin (EPO)-receptor signaling induces cell death of primary myeloma cells in vitro. Hematol Oncol 9(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0306-x
Miyake T, Kung CK, Goldwasser E (1977) Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem 252(15):5558–5564
Obara N, Imagawa S, Nakano Y, Suzuki N, Yamamoto M, Nagasawa T (2003) Suppression of erythropoietin gene expression by cadmium depends on inhibition of HIF-1, not stimulation of GATA-2. Arch Toxicol 77(5):267–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-003-0444-0
Tabata M, Tarumoto T, Ohmine K, Furukawa Y, Hatake K, Ozawa K et al (2003) Stimulation of GATA-2 as a mechanism of hydrogen peroxide suppression in hypoxia-induced erythropoietin gene expression. J Cell Physiol 186(2):260–267. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4652(200002)186:2<260::AID-JCP1025>3.0.CO;2-K
Haase VH (2013) Regulation of erythropoiesis by hypoxia-inducible factors. Blood Rev 27(1):41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2012.12.003
Ebert BL, Bunn HF (1999) Regulation of the erythropoietin gene. Blood 94(6):1864–1877
Fisher JW (2003) Erythropoietin: physiology and pharmacology update. Exp Biol Med 228(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/153537020322800101
Lacombe C, Mayeux P (1998) Biology of erythropoietin. Haematologica 83(8):724–732
Sasaki R, Masuda S, Nagao M (2000) Erythropoietin: multiple physiological functions and regulation of biosynthesis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1775–1793. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.64.1775
Jelkmann W (2003) Erythropoietin. J Endocrinol Investig 26:832–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345232
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Hou J, Shang YC (2008) Erythropoietin and oxidative stress. Curr Neurovasc Res 5:125–142
Toyoda T, Itai T, Arakawa T, Aoki KH, Yamaguchi H (2000) Stabilization of human recombinant erythropoietin through interactions with the highly branched N-glycans. J Biochem 128:731–737. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022809
Singbartl G (1994) Adverse events of erythropoietin in long-term and in acute/short-term treatment. Clin Investig 72(6):36–43
Vazquez-Mellado MJ, Monjaras-Embriz V, Rocha-Zavaleta L (2017) Erythropoietin, stem cell factor, and cancer cell migration. Vitam Horm 105:273–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2017.02.008
D’Andrea AD, Zon LI (1990) Erythropoietin receptor. Subunit structure and activation. J Clin Invest 86(3):681–687. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI114763
Huang LJ, Constantinescu SN, Lodish HF (2001) The N-terminal domain of Janus kinase 2 is required for Golgi processing and cell surface expression of erythropoietin receptor. Mol Cell 8(6):1327–1338. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00401-4
Kuhrt D, Wojchowski DM (2015) Emerging EPO and EPO receptor regulators and signal transducers. Blood 125(23):3536–3541. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-11-575357
Temkin SM, Hellmann M, Serur E, Lee YC, Abulafia O (2006) Erythropoietin administration during primary treatment for locally advanced cervical carcinoma is associated with poor response to radiation. Int J Gynecol Cancer 16:1855–1861. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00709.x
Rankin EB, Wu C, Khatri R, Wilson TL, Andersen R, Araldi E et al (2012) The HIF signaling pathway in osteoblasts directly modulates erythropoiesis through the production of EPO. Cell 149(1):63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.051
McGee SJ, Havens AM, Shiozawa Y, Jung Y, Taichman RS (2012) Effects of erythropoietin on the bone microenvironment. Growth Factors 30(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.3109/08977194.2011.637034
Munugalavadla V, Kapur R (2005) Role of c-kit and erythropoietin receptor in erythropoiesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 54:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2004.11.005
Witthuhn BA, Quelle FW, Silvennoinen O, Yi T, Tang B, Miura O et al (1993) JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell 74:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90414-l
Kirito K, Nakajima K, Watanabe T, Uchida M, Tanaka M et al (2002) Identification of the human erythropoietin receptor region required for Stat1 and Stat3 activation. Blood 99:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v99.1.102
Klingmuller U, Bergelson S, Hsiao JG, Lodish HF (1996) Multiple tyrosine residues in the cytosolic domain of the erythropoietin receptor promote activation of STAT5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:8324–8328. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.16.8324
Bao H, Jacobs-Helber SM, Lawson AE, Penta K, Wickrema A, Sawyer ST (1999) Protein kinase B (c-Akt), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and STAT5 are activated by erythropoietin (EPO) in HCD57 erythroid cells but are constitutively active in an EPO-independent, apoptosis-resistant sub clone (HCD57-SREI cells). Blood 93:3757–3773
Damen JE, Wakao H, Miyajima A, Krosl J, Humphries RK, Cutler RL et al (1995) Tyrosine 343 in the erythropoietin receptor positively regulates erythropoietin-induced cell proliferation and Stat5 activation. EMBO J 14:5557–5568. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00243.x
Lin JS, Chen YS, Chiang HS, Ma MC (2008) Hypoxic preconditioning protects rat hearts against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: role of erythropoietin on progenitor cell mobilization. J Physiol 586:5757–5769. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160887
Liu N, Tian J, Cheng J, Zhang J (2013) Effect of erythropoietin on the migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the acute kidney injury microenvironment. Exp Cell Res 319:2019–2027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.04.008
Satoh K, Kagaya Y, Nakano M, Ito Y, Ohta J, Tada H et al (2006) Important role of endogenous erythropoietin system in recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Circulation 113:1442–1450. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.583732
Heeschen C, Aicher A, Lehmann R, Fichtlscherer S, Vasa M, Urbich C et al (2003) Erythropoietin is a potent physiologic stimulus for endothelial progenitor cell mobilization. Blood 102:1340–1346. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-01-0223
Hoch M, Fischer P, Stapel B, Missol-Kolka E, Sekkali B, Scherr M et al (2011) Erythropoietin preserves the endothelial differentiation capacity of cardiac progenitor cells and reduces heart failure during anticancer therapies. Cell Stem Cell 9(2):131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.07.001
Ropers HH, Craig IW (1989) REPOrt of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 12 and 13. Cytogenet Cell Genet 51:259–279. https://doi.org/10.1159/000132794
Hsu YR, Wu GM, Mendiaz EA, Syed R, Wypych J, Toso R et al (1997) The majority of stem cell factor exists as monomer under physiological conditions. Implications for dimerization mediating biological activity. J Biol Chem 272:6406–6415. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.10.6406
Langley KE, Bennett LG, Wypych J, Yancik SA, Liu XD, Westcott KR et al (1993) Soluble stem cell factor in human serum. Blood 81:656–660
Liu H, Chen X, Focia PJ, He X (2007) Structural basis for stem cell factor-kit signaling and activation of class III receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 26:891–901. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601545
Ronnstrand L (2004) Signal transduction via the stem cell factor receptor/c-kit. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2535–2548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4189-6
Matsui Y, Zsebo KM, Hogan BL (1990) Embryonic expression of a haematopoietic growth factor encoded by the Sl locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature 347:667–669. https://doi.org/10.1038/347667a0
Matsui J, Wakabayashi T, Asada M, Yoshimatsu K, Okada M (2004) Stem cell factor/c-kit signaling promotes the survival, migration, and capillary tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:18600–18607. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311643200
Guo J, Jie W, Shen Z, Li M, Lan Y, Kong Y et al (2014) SCF increases cardiac stem cell migration through PI3K/AKT and MMP-2/−9 signaling. Int J Mol Med 34:112–118. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1773
Brown WM, Maxwell P, Graham AN, Yakkundi A, Dunlop EA, Shi Z et al (2007) Erythropoietin receptor expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma: a question of antibody specificity. Stem Cells 25:718–722. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2006-0687
Elliott S, Busse L, Bass MB, Lu H, Sarosi I, Sinclair AM et al (2006) Anti-EPO receptor antibodies do not predict EPO receptor expression. Blood 107:1892–1895. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-10-4066
Doleschel D, Mundigl O, Wessner A, Gremse F, Bachmann J, Rodriguez A et al (2012) Targeted near-infrared imaging of the erythropoietin receptor in human lung cancer xenografts. J Nucl Med 53:304–311. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.111.091124
Fuge F, Doleschel D, Rix A, Gremse F, Wessner A, Winz O et al (2015) In-vivo detection of the erythropoietin receptor in tumours using positron emission tomography. Eur Radiol 25:472–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3413-5
Shi Z, Hodges VM, Dunlop EA, Percy MJ, Maxwell AP, El-Tanani M et al (2010) Erythropoietin-induced activation of the JAK2/STAT6, PI3K/Akt, and Ras/ERK pathways promotes malignant cell behaviour in a modified breast cancer cell line. Mol Cancer Res 8:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0264
Um M, Gross AW, Lodish HF (2007) A “classical” homodimeric erythropoietin receptor is essential for the antiapoptotic effects of erythropoietin on differentiated neuroblastomaSH-SY5Y and pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells. Cell Signal 19:634–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.08.014
Liang K, Qiu S, Lu Y, Fan Z (2014) Autocrine/paracrine erythropoietin regulates migration and invasion potential and the stemness of human breast cancer cell. Cancer Biol Ther 15:89–98. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.26717
Pradeep S, Huang J, Mora EM, Nick AM, Cho MS, Wu SY et al (2015) Erythropoietin stimulates tumor growth via EphB4. Cancer Cell 28(5):610–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.008
Jeong JY, Feldman L, Solar P, Szenajch J, Sytkowski J (2008) Characterization of erythropoietin receptor and erythropoietin expression and function in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Cancer 122:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23068
Solar P, Hrckova G, Varinska L, Solarova Z, Kriska J, Uhrinova I et al (2012) Location and the functionality of erythropoietin receptor(s) in A2780 cells. Oncol Rep 28:141–146. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1795
Rozsas A, Berta J, Rojko L, Horvath LZ, Keszthelyi M, Kenessey I et al (2013) Erythropoietin receptor expression is a potential prognostic factor in human lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One 8:e77459. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077459
Mittelman M, Neumann D, Peled A, Kanter P, Haran-Ghera N (2001) Erythropoietin induces tumor regression and antitumor immune responses in murine myeloma models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(9):5181–5186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.081275298
Howard JC, Berger L, Bani MR, Hawley RG, Ben-David Y (1996) Activation of the erythropoietin gene in the majority of F-MuLV induced erythroleukemias results in growth factor independence and enhanced tumorigenicity. Oncogene 12:1405–1415
Howard JC, Yosefi S, Cheong G, Bernstein A, Ben-David Y (1993) Temporal order of the mutation of Fli-1, p53 and erythropoietin genes during the multistep erythroleukemias induced by F-MuLV. Oncogene 8:2721–2729
Shaked Y, Cervi D, Neuman M, Klement G, Michaud CR, Haeri M et al (2005) The splenic microenvironment is a source of angiogenesis/inflammatory mediators accelerating the expansion of murine erythroleukemic cells. Blood 105:4500–4507. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-08-3210
Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Cervi D, Haeri M, Li Y, Nagy A, Ben-David Y (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor--a positive and negative regulator of tumor growth. Cancer Res 70(3):863–867. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3592
Usenko T, Li YJ, Haeri M, Li Y, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Zhao X et al (2009) Enrichment of Sca1+ hematopoietic progenitors in polycythemic mice inhibits leukemogenesis. Blood 114:1831–1841. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-11-187419
Cui JW, Li YJ, Sarkar A, Brown J, Tan YH et al (2007) Retroviral insertional activation of the Fli-3 locus in erythroleukemias encoding a cluster of microRNAs that convert EPO-induced differentiation to proliferation. Blood 110:2631–2640. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-10-053850
Li Y, Luo H, Liu T, Zachsenhaus E, Ben-David Y (2015) The transcription factor Fli-1 in development, cancer and disease. Oncogene 35:2022–2031. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.162
Knight K, Wade S, Balducci L (2004) Prevalence and outcomes of anemia in cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Am J Med. 116:11S–26S. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15050883
Debeljak N, Solár P, Sytkowski AJ (2014) Erythropoietin and cancer: the unintended consequences of anemia correction. Front Immunol 5:563. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00563
Moebus V, Jackisch C, Schneeweiss A, Huober J, Lueck HJ, du Bois A et al (2013) Adding EPOetin alfa to intense dose-dense adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: randomized clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 105(14):1018–2610. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djt145
Tonia T, Mettler A, Robert N, Schwarzer G, Seidenfeld J, Weingart O et al (2012) Erythropoietin or darbEPOetin for patients with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD003407. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003407.pub5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Liu, W., Varier, K.M., Sample, K.M., Zacksenhaus, E., Gajendran, B., Ben-David, Y. (2020). Erythropoietin Signaling in the Microenvironment of Tumors and Healthy Tissues. In: Birbrair, A. (eds) Tumor Microenvironment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1223. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35582-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35582-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-35581-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-35582-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)