Abstract
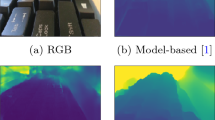
Depth from focus (DFF) is one of the classical ill-posed inverse problems in computer vision. Most approaches recover the depth at each pixel based on the focal setting which exhibits maximal sharpness. Yet, it is not obvious how to reliably estimate the sharpness level, particularly in low-textured areas. In this paper, we propose ‘Deep Depth From Focus (DDFF)’ as the first end-to-end learning approach to this problem. One of the main challenges we face is the hunger for data of deep neural networks. In order to obtain a significant amount of focal stacks with corresponding groundtruth depth, we propose to leverage a light-field camera with a co-calibrated RGB-D sensor. This allows us to digitally create focal stacks of varying sizes. Compared to existing benchmarks our dataset is 25 times larger, enabling the use of machine learning for this inverse problem. We compare our results with state-of-the-art DFF methods and we also analyze the effect of several key deep architectural components. These experiments show that our proposed method ‘DDFFNet’ achieves state-of-the-art performance in all scenes, reducing depth error by more than 75% compared to the classical DFF methods.
This research was partially funded by the Humboldt Foundation through the Sofja Kovalevskaja Award and ERC Consolidator Grant “3D Reloaded”.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
Lytro ILLUM lightfield camera, illum.lytro.com, accessed: 2016-11-07.
- 3.
- 4.
References
Adelson, E., Wang, J.: Single lens stereo with a plenoptic camera. PAMI 1(2), 99–106 (1992)
Asif, M., Choi, T.: Learning shape from focus using multilayer neural networks. In: SPIE, Vision Geometry VIII (1999)
Badrinarayanan, V., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. PAMI 39(12), 2481–2495 (2017)
Bok, Y., Jeon, H.G., Kweon, I.S.: Geometric calibration of micro-lens-based light field cameras using line features. PAMI 39(2), 287–300 (2017)
Cho, D., Lee, M., Kim, S., Tai, Y.W.: Modeling the calibration pipeline of the lytro camera for high quality light-field image reconstruction. In: ICCV (2013)
Dansereau, D., Pizarro, O., Williams, B.: Decoding, calibration and rectification for lenselet-based plenoptic cameras. In: CVPR (2013)
Diebold, M., Goldluecke, B.: Epipolar plane image refocusing for improved depth estimation and occlusion handling. In: ICCV (2013)
Dosovitskiy, A., et al.: FlowNet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: ICCV (2015)
Dosovitskiy, A., Tobias Springenberg, J., Brox, T.: Learning to generate chairs with convolutional neural networks. In: CVPR (2015)
Eigen, D., Puhrsch, C., Fergus, R.: Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. In: NIPS (2014)
Galliani, S., Schindler, K.: Just look at the image: viewpoint-specific surface normal prediction for improved multi-view reconstruction. In: CVPR (2016)
Garg, R., B.G., V.K., Carneiro, G., Reid, I.: Unsupervised CNN for single view depth estimation: geometry to the rescue. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 740–756. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_45
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. In: ICCV (2015)
Hazirbas, C., Ma, L., Domokos, C., Cremers, D.: FuseNet: incorporating depth into semantic segmentation via fusion-based CNN architecture. In: Lai, S.-H., Lepetit, V., Nishino, K., Sato, Y. (eds.) ACCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 10111, pp. 213–228. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54181-5_14
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: ICCV (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Heber, S., Pock, T.: Convolutional networks for shape from light field. In: CVPR (2016)
Heber, S., Yu, W., Pock, T.: Neural EPI-volume networks for shape from light field. In: ICCV (2017)
Honauer, K., Johannsen, O., Kondermann, D., Goldluecke, B.: A dataset and evaluation methodology for depth estimation on 4D light fields. In: Lai, S.-H., Lepetit, V., Nishino, K., Sato, Y. (eds.) ACCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 10113, pp. 19–34. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54187-7_2
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: ICML (2015)
Jeon, H.G., et al.: Accurate depth map estimation from a lenslet light field camera. In: CVPR (2015)
Kendall, A., Badrinarayanan, V., Cipolla, R.: Bayesian SegNet: model uncertainty in deep convolutional encoder-decoder architectures for scene understanding. In: BMVC (2017)
Kendall, A., Grimes, M., Cipolla, R.: PoseNet: a convolutional network for real-time 6-DOF camera relocalization. In: ICCV (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Li, B., Shen, C., Dai, Y., van den Hengel, A., He, M.: Depth and surface normal estimation from monocular images using regression on deep features and hierarchical CRFs. In: CVPR (2015)
Lin, H., Chen, C., Kang, S.B., Yu, J.: Depth recovery from light field using focal stack symmetry. In: ICCV (2015)
Liu, F., Shen, C., Lin, G., Reid, I.D.: Learning depth from single monocular images using deep convolutional neural fields. PAMI 38(10), 2024–2039 (2016)
Liu, M.Y., Tuzel, O., Taguchi, Y.: Joint geodesic upsampling of depth images. In: CVPR (2013)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2015)
Mahmood, M.: Shape from focus by total variation. In: IVMSP Workshop (2013)
Mahmood, M., Choi, T.S.: Nonlinear approach for enhancement of image focus volume in shape from focus. TIP 21(5), 2866–2873 (2012)
Moeller, M., Benning, M., Schönlieb, C., Cremers, D.: Variational depth from focus reconstruction. TIP 24(12), 5369–5378 (2015)
Ng, R., Levoy, M., Brédif, M., Duval, G., Horowitz, M., Hanrahan, P.: Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Technical report, Stanford University Computer Science Tech Report CSTR 2005-02 (2005)
Noh, H., Hong, S., Han, B.: Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: ICCV (2015)
Park, J., Kim, H., Tai, Y.W., Brown, M.S., Kweon, I.: High quality depth map upsampling for 3D-TOF cameras. In: ICCV (2011)
Park, J., Kim, H., Tai, Y., Brown, M.S., Kweon, I.: High-quality depth map upsampling and completion for RGB-D cameras. TIP 23(12), 5559–5572 (2014)
Pérez-Nava, F., Lüke, J.P.: Simultaneous estimation of super-resolved depth and all-in-focus images from a plenoptic camera. In: 3DTV-CON (2009)
Pertuz, S., Puig, D., Garcia, M.A.: Analysis of focus measure operators for shape-from-focus. Pattern Recogn. 46(5), 1415–1432 (2013)
Russakovsky, O., et al.: ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. IJCV 115(3), 211–252 (2015)
Shen, J., Cheung, S.C.S.: Layer depth denoising and completion for structured-light RGB-D cameras. In: CVPR (2013)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: ICLR (2015)
Suwajanakorn, S., Hernandez, C., Seitz, S.M.: Depth from focus with your mobile phone. In: CVPR (2015)
Thelen, A., Frey, S., Hirsch, S., Hering, P.: Improvements in shape-from-focus for holographic reconstructions with regard to focus operators, neighborhood-size, and height value interpolation. TIP 18(1), 151–157 (2009)
Walch, F., Hazirbas, C., Leal-Taixe, L., Sattler, T., Hilsenbeck, S., Cremers, D.: Image-based localization using lstms for structured feature correlation. In: ICCV (2017)
Wanner, S., Meister, S., Goldlücke, B.: Datasets and benchmarks for densely sampled 4D light fields. In: VMV (2013)
Wilburn, B., et al.: High performance imaging using large camera arrays. In: TOG (2005)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hazirbas, C., Soyer, S.G., Staab, M.C., Leal-Taixé, L., Cremers, D. (2019). Deep Depth from Focus. In: Jawahar, C., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2018. ACCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11363. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20893-6_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20893-6_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-20892-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-20893-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)