Abstract
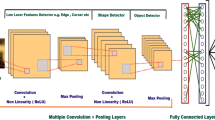
Deep learning (DL) methods have gained considerable attention since 2014. In this chapter we briefly review the state of the art in DL and then give several examples of applications from diverse areas of application. We will focus on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which have since the seminal work of Krizhevsky et al. (ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25, pp. 1097–1105, 2012) revolutionized image classification and even started surpassing human performance on some benchmark data sets (Ciresan et al., Multi-column deep neural network for traffic sign classification, 2012a; He et al., Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. CoRR, Vol. 1502.01852, 2015a). While deep neural networks have become popular primarily for image classification tasks, they can also be successfully applied to other areas and problems with some local structure in the data. We will first present a classical application of CNNs on image-like data, in particular, phenotype classification of cells based on their morphology, and then extend the task to clustering voices based on their spectrograms. Next, we will describe DL applications to semantic segmentation of newspaper pages into their corresponding articles based on clues in the pixels, and outlier detection in a predictive maintenance setting. We conclude by giving advice on how to work with DL having limited resources (e.g., training data).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aucouturier, J.-J., Defreville, B., & Pachet, F. (2007). The bag-of-frames approach to audio pattern recognition: A sufficient model for urban soundscapes but not for polyphonic music. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 122(2), 881–891.
Beigi, H. (2011). Fundamentals of speaker recognition. Springer Science & Business Media.
Bersimis, S., Psarakis, S., & Panaretos, J. (2007). Multivariate statistical process control charts: An overview. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 23, 517–543.
Bishop, C. M. (2006). Pattern recognition and machine learning. Springer.
Bouma, G. (2009). Normalized (pointwise) mutual information in collocation extraction. In: From form to meaning: Processing texts automatically, Proceedings of the Biennial GSCL Conference 2009 (pp. 31–40). https://svn.spraakdata.gu.se/repos/gerlof/pub/www/Docs/npmi-pfd.pdf
Chung, J. S., Senior, A. W., Vinyals, O., & Zisserman, A. (2016). Lip reading sentences in the wild. CoRR, Vol. 1611.05358. http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.05358
Ciresan, D., Meier, U., Masci, J., & Schmidhuber, J. (2012a). Multi-column deep neural network for traffic sign classification. http://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/nn2012traffic.pdf
Ciresan, D., Giusti, A., Gambardella, L. M., & Schmidhuber, J. (2012b). Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 25, 2843–2851.
Dehak, N., Kenny, P., Dehak, R., Dumouchel, P., & Ouellet, P. (2011). Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(4), 788–798.
Dieleman, S., & Schrauwen, B. (2014). End-to-end learning for music audio. In Proceedings of ICASSP (pp. 6964–6968).
Domingos, P. (2012). A few useful things to know about machine learning. Communications of the ACM, 55(10), 78–87.
Dürr, O., Duval, F., Nichols, A., Lang, P., Brodte, A., Heyse, S., & Besson, D. (2007). Robust hit identification by quality assurance and multivariate data analysis of a high-content, cell-based assay. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 12(8), 1042–1049.
Ester, M., Kriegel, H.-P., Sander, J., & Xu, X. (1996). A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD-96) (pp. 226–231) AAAI Press.
Fernández-Francos, D., Martínez-Rego, D., Fontenla-Romero, O., & Alonso-Betanzos, A. (2013). Automatic bearing fault diagnosis based on one-class ν-SVM. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 64(1), 357–365.
Fukushima, K. (1980). Neocognitron: A self-organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biological Cybernetics, 36(4), 193–202.
Ganchev, T., Fakotakis, N., & Kokkinakis, G. (2005). Comparative evaluation of various MFCC implementations on the speaker verification task. In Proceedings of SPECOM 2005 (Vol. 1, pp. 191–194).
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep learning. MIT Press. http://www.deeplearningbook.org.
Gustafsdottir, S. M., Ljosa, V., Sokolnicki, K. L., Wilson, J. A., Walpita, D., Kemp, M. M., Petri Seiler, K., Carrel, H. A., Golub, T. R., Schreiber, S. L., Clemons, P. A., Carpenter, A. E., & Shamji, A. F. (2013). Multiplex cytological profiling assay to measure diverse cellular states. PLoS One, 12, e80999.
Han, S., Mao, H., & Dally, W. J. (2015). Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and Huffman coding. CoRR, Vol. 1510.00149. https://arxiv.org/abs/1510.00149
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015a). Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. CoRR, Vol. 1502.01852. http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.01852
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015b). Deep residual learning for image recognition. CoRR, Vol. 1512.03385. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
Hinton, G. E., Srivastava, N., & Swersky, K. (2012). Lecture 6a: Overview of mini-batch gradient descent. In Neural Networks for Machine Learning, University of Toronto. https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks
Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8), 1735–1780.
Hsu, Y.-C., & Kira, Z. (2015). Neural network-based clustering using pairwise constraints. CoRR, Vol. 1511.06321. https://arxiv.org/abs/1501.03084
Hubel, D. H., & Wiesel, T. N. (1959). Receptive fields of single neurons in the cat’s striate cortex. Journal of Physiology, 148, 574–591.
Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In International Conference on Machine Learning (Vol. 37, pp. 448–456). https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03167.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. CoRR, Vol. 1412.6980. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding variational Bayes. CoRR, Vol. 1312.6114. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114
Kingma, D. P., Mohamed, S., Rezende, D. J., & Welling, M. (2014). Semi-supervised learning with deep generative models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 3581–3589). https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5352-semi-supervised-learning-with-deep-generative-models
Kotti, M., Moschou, V., & Kotropoulos, C. (2008). Speaker segmentation and clustering. Signal Processing, 88(5), 1091–1124.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2012). ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 25, 1097–1105.
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., & Haffner, P. (1998a). Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11), 2278–2324.
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Orr, G. B., & Mueller, K.-R. (1998b). Efficient BackProp. In G. B. Orr, & K.-R. Mueller (Eds.), Neural networks: Tricks of the trade, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Vol. 1524, pp. 9–50).
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. E. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521, 436–444.
Lee, J., Qiu, H., Yu, G., & Lin, J. (2007). Bearing data set. IMS, University of Cincinnati, NASA Ames Prognostics Data Repository, Rexnord Technical Services. https://ti.arc.nasa.gov/tech/dash/pcoe/prognostic-data-repository/
Ljosa, V., Sokolnicki, K. L., & Carpenter, A. E. (2009). Annotated high-throughput microscopy image sets for validation. Nature Methods, 9, 637.
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., & Darrell, T. (2014). Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~jonlong/long_shelhamer_fcn.pdf
Lukic, Y. X., Vogt, C., Dürr, O., & Stadelmann, T. (2016). Speaker identification and clustering using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of IEEE MLSP 2016.
Lukic, Y. X., Vogt, C., Dürr, O., & Stadelmann, T. (2017). Learning embeddings for speaker clustering based on voice quality. In Proceedings of IEEE MLSP 2017.
MacQueen, J. B. (1967). Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability (Vol. 1, pp. 281–297). Berkeley: University of California Press.
Meier, B., Stadelmann, T., Stampfli, J., Arnold, M., & Cieliebak, M. (2017). Fully convolutional neural networks for newspaper article segmentation. In Proceedings of ICDAR 2017.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G. S., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 3111–3119). https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5021-distributed-representations-of-words-and-phrases-and-their-compositionality.pdf
Mitchell, T. M. (1980). The need for biases in learning generalizations. Technical Report, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ. http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~pszbsl/G52HPA/articles/Mitchell:80a.pdf
Moravcik, M., Schmid, M., Burch, N., Lisy, V., Morrill, D., Bard, N., Davis, T., Waugh, K., Johanson, M., & Bowling, M. H. (2017). DeepStack: Expert-level artificial intelligence in no-limit poker, CoRR, Vol. 1701.01724. http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.01724
Mori, S., Nishida, H., & Yamada, H. (1999). Optical character recognition. New York, NY: Wiley. ISBN 0471308196.
Ng, A. (2016). Nuts and bolts of building AI applications using deep learning. NIPS Tutorial.
Ng, A. (2019, in press). Machine learning yearning. http://www.mlyearning.org/
Nielsen, M. A. (2015). Neural networks and deep learning. Determination Press. http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com.
Nielsen, F. A. (2017). Status on human vs. machines, post on “Finn Årup Nielsen’s blog”. https://finnaarupnielsen.wordpress.com/2015/03/15/status-on-human-vs-machines/
Pan, S. J., & Yang, Q. (2010). A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 22(10), 1345–1359. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5288526/.
Pimentel, M. A. F., Clifton, D. A., Clifton, L., & Tarassenko, L. (2014). A review of novelty detection. Signal Processing, 215–249.
Randall, R. B., & Antoni, J. (2011). Rolling element bearing diagnostics—A tutorial. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 25(2), 485–520.
Razavian, A. S., Azizpour, H., Sullivan, J., & Carlsson, S. (2014). CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition. CVPR 2014 (pp. 806–813). https://arxiv.org/abs/1403.6382
Reynolds, D. A., & Rose, R. C. (1995). Robust text-independent speaker identification using Gaussian mixture speaker models. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 3(1), 72–83.
Reynolds, D. A., Quatieri, T. F., & Dunn, R. B. (2000). Speaker verification using adapted Gaussian mixture models. Digital Signal Processing, 10(1), 19–41.
Romanov, A., & Rumshisky, A. (2017). Forced to learn: Discovering disentangled representations without exhaustive labels. ICRL 2017. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=SkCmfeSFg
Rosenblatt, F. (1957). The perceptron – A perceiving and recognizing automaton. Technical report 85-460-1, Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., & Williams, R. J. (1988). Learning representations by back-propagating errors. In Neurocomputing: Foundations of Research (pp. 696–699). MIT Press. http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/absps/naturebp.pdf
Schmidhuber, J. (2014). Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. https://arxiv.org/abs/1404.7828
Schölkopf, B., & Smola, A. J. (2002). Learning with kernels: Support vector machines, regularization, optimization, and beyond. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Silver, D., Huang, A., Maddison, C. J., Guez, A., Sifre, L., van den Driessche, G., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Panneershelvam, V., Lanctot, M., Dieleman, S., Grewe, D., Nham, J., Kalchbrenner, N., Sutskever, I., Lillicrap, T., Leach, M., Kavukcuoglu, K., Graepel, T., & Hassabis, D. (2016). Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 529, 484–503.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. CoRR, vol. 1409.1556. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G. E., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1), 1929–1958.
Stadelmann, T., & Freisleben, B. (2009). Unfolding speaker clustering potential: A biomimetic approach. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 185–194). ACM.
Stadelmann, T., Musy, T., Duerr, O., & Eyyi, G. (2016). Machine learning-style experimental evaluation of classic condition monitoring approaches on CWRU data. Technical report, ZHAW Datalab (unpublished).
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., & Rabinovich, A. (2014). Going deeper with convolutions. CoRR, Vol. 1409.4842. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.4842
Szeliski, R. (2010). Computer vision: Algorithms and applications. Texts in Computer Science. New York: Springer. http://szeliski.org/Book/.
van der Maaten, L., & Hinton, G. E. (2008). Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 9(Nov), 2579–2605.
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., & Manzagol, P.-A. (2010). Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 11, 3371–3408.
Weyand, T., Kostrikov I., & Philbin, J. (2016). PlaNet – Photo geolocation with convolutional neural networks. CoRR, Vol. 1602.05314. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.05314
Xiong, W., Droppo, J., Huang, X., Seide, F., Seltzer, M., Stolcke, A., Yu, D., & Zweig, G. (2016). Achieving human parity in conversational speech recognition. CoRR, Vol. 1610.05256. http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.05256
Zagoruyko, S., & Komodakis, N. (2016). Wide residual networks. In Wilson, R. C., Hancock, E. R., & Smith, W. A. P. (Eds.), Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) (pp. 87.1–87. 12. BMVA Press.
Zeiler, M. D. (2012). ADADELTA: An adaptive learning rate method. CoRR, Vol. 1212.5701. http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701
Zheng, F., Zhang, G., & Song, Z. (2001). Comparison of different implementations of MFCC. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 16(6), 582–589.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support by CTI grants 17719.1 PFES-ES, 17729.1 PFES-ES, and 19139.1 PFES-ES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Stadelmann, T., Tolkachev, V., Sick, B., Stampfli, J., Dürr, O. (2019). Beyond ImageNet: Deep Learning in Industrial Practice. In: Braschler, M., Stadelmann, T., Stockinger, K. (eds) Applied Data Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11821-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11821-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-11820-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-11821-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)