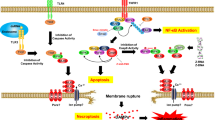
Abstract
RIP1 kinase plays a key role in regulating signaling pathways downstream of a number of innate immune receptors such as TNFRI and TLRs. The discovery of Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) as a small-molecule inhibitor of RIP1 kinase has been very instrumental in defining the necroptotic and other signalling pathways regulated by RIP1, but certain characteristics of Nec-1 limits its utility in experimental systems. Next generation RIP1 kinase inhibitors have been identified and the use of these tool inhibitors along with Nec-1 has revealed that RIP1 is emerging as a key driver of inflammation and tissue injury in the pathogenesis of various diseases. Further studying the role of RIP1 to carefully unravel the complex biology requires the selection of the correct tool small-molecule inhibitors. In addition, it is important to consider the proper application of current tool inhibitors and understand the current limitiations. Here we will discuss key parameters that need to be considered when selecting and applying tool inhibitors to novel biological assays and systems. General protocols to explore the in vitro and in vivo potency, cellular selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties of current small-molecule inhibitors of RIP1 kinase are provided.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger SB, Kasparcova V, Hoffman S, Swift B, Dare L, Schaeffer M, Capriotti C, Cook M, Finger J, Hughes-Earle A, Harris PA, Kaiser WJ, Mocarski ES, Bertin J, Gough PJ (2014) Cutting edge: RIP1 kinase activity is dispensable for normal development but is a key regulator of inflammation in SHARPIN-deficient mice. J Immunol 192(12):5476–5480. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1400499
Kelliher MA, Grimm S, Ishida Y, Kuo F, Stanger BZ, Leder P (1998) The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity 8(3):297–303
Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N, Kelliher MA (2004) The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem 279(32):33185–33191. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404206200
Berger SB, Bertin J, Gough PJ (2015) Drilling into RIP1 biology: what compounds are in your toolkit? Cell Death Dis 6:e1889. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.254
Berger SB, Harris P, Nagilla R, Kasparcova V, Hoffman S, Swift B, Dare L, Schaeffer M, Capriotti C, Ouellette M, King BW, Wisnoski D, Cox J, Reilly M, Marquis RW, Bertin J, Gough PJ (2015) Characterization of GSK'963: a structurally distinct, potent and selective inhibitor of RIP1 kinase. Cell Death Discov 1:15009. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.9
Harris PA, King BW, Bandyopadhyay D, Berger SB, Campobasso N, Capriotti CA, Cox JA, Dare L, Dong X, Finger JN, Grady LC, Hoffman SJ, Jeong JU, Kang J, Kasparcova V, Lakdawala AS, Lehr R, McNulty DE, Nagilla R, Ouellette MT, Pao CS, Rendina AR, Schaeffer MC, Summerfield JD, Swift BA, Totoritis RD, Ward P, Zhang A, Zhang D, Marquis RW, Bertin J, Gough PJ (2016) DNA-encoded library screening identifies Benzo[b][1,4]oxazepin-4-ones as highly potent and Monoselective receptor interacting protein 1 kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem 59(5):2163–2178. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01898
Degterev A, Zhou W, Maki JL, Yuan J (2014) Assays for necroptosis and activity of RIP kinases. Methods Enzymol 545:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801430-1.00001-9
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L, Wang X (2009) Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 137(6):1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X, Wang X (2012) Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 148(1–2):213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.031
Newton K, Dugger DL, Maltzman A, Greve JM, Hedehus M, Martin-McNulty B, Carano RA, Cao TC, van Bruggen N, Bernstein L, Lee WP, Wu X, DeVoss J, Zhang J, Jeet S, Peng I, McKenzie BS, Roose-Girma M, Caplazi P, Diehl L, Webster JD, Vucic D (2016) RIPK3 deficiency or catalytically inactive RIPK1 provides greater benefit than MLKL deficiency in mouse models of inflammation and tissue injury. Cell Death Differ 23(9):1565–1576. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.46
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, Hedrick SM, Gerber SA, Lugovskoy A, Yuan J (2008) Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 4(5):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.83
Degterev A, Maki JL, Yuan J (2013) Activity and specificity of necrostatin-1, small-molecule inhibitor of RIP1 kinase. Cell Death Differ 20(2):366. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.133
Muller AJ, DuHadaway JB, Donover PS, Sutanto-Ward E, Prendergast GC (2005) Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1, potentiates cancer chemotherapy. Nat Med 11(3):312–319. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1196
Teng X, Degterev A, Jagtap P, Xing X, Choi S, Denu R, Yuan J, Cuny GD (2005) Structure-activity relationship study of novel necroptosis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15(22):5039–5044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.07.077
Ren Y, Su Y, Sun L, He S, Meng L, Liao D, Liu X, Ma Y, Liu C, Li S, Ruan H, Lei X, Wang X, Zhang Z (2017) Discovery of a highly potent, selective, and metabolically stable inhibitor of receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) for the treatment of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Med Chem 60(3):972–986. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01196
Najjar M, Suebsuwong C, Ray SS, Thapa RJ, Maki JL, Nogusa S, Shah S, Saleh D, Gough PJ, Bertin J, Yuan J, Balachandran S, Cuny GD, Degterev A (2015) Structure guided design of potent and selective ponatinib-based hybrid inhibitors for RIPK1. Cell Rep 10(11):1850–1860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Beal, A.M., Bertin, J., Reilly, M.A. (2018). Use of RIP1 Kinase Small-Molecule Inhibitors in Studying Necroptosis. In: Ting, A. (eds) Programmed Necrosis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1857. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8754-2_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8754-2_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8753-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8754-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols