Abstract
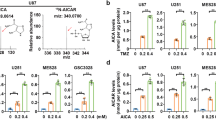
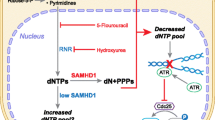
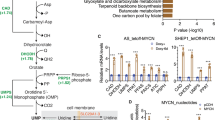
GTP has multi-faceted cellular functions. Apart from its role in metabolism, in biosynthesis of RNA, proteins, biopterins, UTP and tubulin, GTP is an intricate part of signal transduction mechanisms, production of c-GMP and adenylates, G-protein action and expression of ras oncogene family. Guanylates are indispensable in DNA biosynthesis, since from GDP dGDP is formed and then dGTP, which is rate-limiting as it is the smallest pool among the dNTPs1,2 (Fig. 1). Curtailing GTP and dGTP pools is an important chemotherapeutic objective. GTP de novo biosynthesis is governed by IMP dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.205), the rate-limiting enzyme1,2. GTP pools are influenced by the activity of GPRT (guanine-hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.8), the salvage enzyme, which can recycle guanine to GMP in one step. The significance of GTP in cancer biochemistry and chemotherapy was highlighted by the discovery that IMP dehydrogenase activity increased in a transformation- and progression-linked fashion in rat hepatomas of different growth rates1,2. IMP dehydrogenase activity increased in all murine and 4 human cancer cell lines and was particularly high in rapidly proliferating neoplastic cells such as leukemic cells1–3.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Weber, Biochemical strategy of cancer cells and the design of chemotherapy: G.H.A. Clowes Memorial Lecture, Cancer Res. 43: 3466 (1983).
R. C. Jackson, H. P. Morris and G. Weber, IMP dehydrogenase: A proliferation and malignancy-linked enzyme, Nature 256: 331 (1975).
G. Weber, N. Prajda and R. C. Jackson, Key enzymes of IMP metabolism: Transformation-and proliferation-linked alterations in gene expression, Advan. Enzyme Regul. 14:3 (1976).
G. Weber, M. Nagai, Y. Natsumeda, H. Nakamura, J. N. Eble, H. N. Jayaram, W. Zhen, E. Paulik, R. Hoffman and G. Tricot, Regulation of de novo and salvage pathways, Advan. Enzyme Regul. 31:45 (1991).
G. J. Tricot, H. N. Jayaram, E. Lapis, Y. Natsumeda, Y. Yamada, C. R. Nichols, P. Kneebone, N. Heerema, G. Weber and R. Hoffman, Biochemically directed therapy of leukemia with tiazofurin, a selective blocker of IMP dehydrogenase activity, Cancer Res. 49: 3696 (1989).
G. Tricot, H. N. Jayaram, G. Weber and R. Hoffman, Tiazofurin: Biological effects and clinical uses, Intl. J. Cell Cloning 8:161 (1990).
R. K. Robins, Nucleoside and nucleotide inhibitors of inosine monophosphate (IMP) dehydrogenase as potential antitumor inhibitors, Nucleosides and Nucleotides 1: 35 (1982).
H. N. Jayaram, Biochemical mechanisms of resistance to tiazofurin, Advan. Enzyme Regul. 24:67 (1986).
Y. Yamada, Y. Natsumeda, Y. Yamaji and G. Weber, Kinetic properties and TAD inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase in leukemic leukocytes, Leukemia Res. 13: 179 (1989).
H. N. Jayaram, K. Pillwein, C. R. Nichols, R. Hoffman and G. Weber, Selective sensitivity to tiazofurin of human leukemic cells, Biochem. Pharmacol. 35:2029 (1986).
G. Weber, H. N. Jayaram, E. Lapis, Y. Natsumeda, Y. Yamada, Y. Yamaji, G. J. Tricot and R. Hoffman, Enzyme-pattern-targeted chemotherapy in human leukemia, Advan. Enzyme Requl. 27:405 (1988).
G. Weber, M. Nagai, Y. Natsumeda, J. N. Eble, H. N. Jayaram, E. Paulik, W. Zhen, R. Hoffman and G. Tricot, Tiazofurin down-regulates expression of c-Ki-ras oncogene in a leukemic patient, Cancer Commun. 3: 51 (1991).
E. Olah, Y. Natsumeda, T. Ikegami, Z. Kote, M. Horanyi, J. Szelenyi, E. Paulik, T. Kremmer, S. R. Hollan, J. Sugar and G. Weber, Induction of erythroid differentiation and modulation of gene expression by tiazofurin in K-562 leukemia cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85:6533 (1988).
M. Nagai, Y. Natsumeda and G. Weber, Tiazofurin action in HL-60 cells, Submitted for publication (1991).
E. Olah, Z. Kote, Y. Natsumeda, Y. Yamaji, G. Jarai, E. Lapis, I. Financsek and G. Weber, Down-regulation of c-myc and c-Ha-ras gene expression by tiazofurin in rat hepatoma cells, Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 11:107 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Weber, G. (1991). IMP Dehydrogenase and GTP as Targets in Human Leukemia Treatment. In: Harkness, R.A., Elion, G.B., Zöllner, N. (eds) Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Man VII. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 309B. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7703-4_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7703-4_64
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4615-7705-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-7703-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive