Abstract
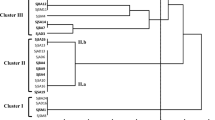
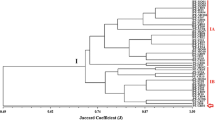
Three Bradyrhizobium species are currently recognized, e.g. B. japonicum,B. elkanii and B. liaoningense, all three nodulating soybeans. A rapidly increasing number of slow growing strains are being isolated from all Leguminosae sub-families, especially in the tropics and subtropics. Particularly the isolates from woody legumes have an uncertain taxonomic status. Several 16S rDNA sequences (partial and nearly full-length) are available for some of these strains. Their analysis revealed that even isolates with remarkable and distinct phenotypes, like those capable of photosynthesis and nodulating stems of aquatic legumes, or those having extremely slow growth rates, are close relatives of well known B. japonicum or B. elkanii strains, irrespective of their hosts or geographical origin (e.g. Wong et al., 1994; Moreira et al., 1998).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaluza K, Hahn M, and Hennecke H 1985. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J. Bacteriol. 162, 535–542.
Laguerre G, Mavingui P, Allard MR, Charnay MP, Louvrier P, Mazurier SI, Rigottier-Gois L, and Amarger N 1996. Typing of rhizobia by PCR and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of chromosomal and symbiotic gene regions: application to Rhizobium leguminosarum and its different biovars. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 2029–2036.
Moreira FMS, Haukka K, and Young JPW 1998. Biodiversity of rhizobia isolated from a wide range of forest legumes in Brazil. Mol. Ecol. 7: 889–895.
So R, Ladha JK, and Young JPW 1994. Photosynthetic symbionts of Aeschynomene spp. form a cluster with bradyrhizobia on the basis of fatty acids and rRNA analysis Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44, 392–403.
Van Rossum D, Schuurmans FP, Gillis M, Muyotcha A, van Verseveld HW, Stouthamer AH, and Boogerd FC 1995. Genetic and phenetic analysis of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61,1599–1609.
Vinuesa P, Rademaker JLW, de Bruijn FJ, and Werner D 1998. Genotypic characterization of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating endemic woody legumes of the Canary Islands by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA (16S rDNA) and 16S–23S rDNA inter-genic spacers, repetitive extragenic palindromic PCR genomic fingerprinting, and partial 16S rDNA sequencing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2096–2104.
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, and Lane DJ 1991. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 173, 697–703.
Wong FYK, Stackebrandt E, Ladha JK, Fleischman DE, Date RA, and Fuerst JA 1994. Phylogenetic analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and photosynthetic stem-nodulating bacteria from Aeschynomene species grown in separate geographical regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 940–946.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Vinuesa, P., Rademaker, L.W.J., de Bruijn, F.J., Werner, D. (1999). Characterization of Bradyrhizobium SPP. Strains by Rflp analysis of Amplified 16s rDNA and rDNA Intergenic Spacer Regions. In: Martĺnez, E., Hernández, G. (eds) Highlights of Nitrogen Fixation Research. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4795-2_56
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4795-2_56
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7172-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-4795-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive