Abstract
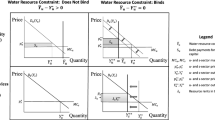
This chapter discusses basic issues in project analysis and shows how these issues can be resolved in a computable general equilibrium (CGE) framework. The role of border prices and intersectoral linkages is explored. The CGE framework is compared to less comprehensive frameworks, including benefit-cost analysis, input-output models, multimarket models, and models based on social accounting matrices (SAM’s). An illustrative CGE model of the southern portion of the San Joaquin Valley (Valley) is constructed and is used to find the effects of reducing water inputs to agriculture on aggregate Valley gross domestic product (GDP) and on sectoral output, employment, and land use. The model is also used to determine demand curves for water by the southern portion of the Valley, given alternative specifications of production technology.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman, I., 1984. Beyond Export Led Growth, World Development, 12(9), pp. 937–950.
Alward, G.; Siverts, E.; Olson, D.; Wagner, J.; Senf, D.; and Lindall, S., 1989. Micro Implan: Software Manual. Regents of the University of Minnesota, Minneappolis/St.Paul.
Bell, C. and Devarajan, S., 1987. Intertemporally Consistent Shadow Prices in an Open Economy, Estimates for Cyprus, Journal of Public Economics, 32, pp. 263–285.
Bell, C. and Devarajan, S., 1985. Social Cost-Benefit Analysis in a Semi-Input-Output Framework: An Application to the Muda Irrigation Project. In: Pyatt, G. and Round, J. I. (Eds.), Social Accounting Matrices: A Basis for Planning, The World Bank, Washington, DC.
Braverman, A. and Hammer, J., 1988. Computer Models for Agricultural Policy Analysis, Finance and Development, 25(2).
Brooke A.; Kendrick, D.; and Meeraus, A., 1988. GAMS: A User’s Guide. The Scientific Press, Redwood City, CA.
Dervis, K.; de Melo, J.; and Robinson, S., 1982. General Equilibrium Models for Development Policy. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY.
Diamond, P. and Mirrlees, J., 1971. Optimal Taxation and Public Production: I. Production Efficiency, American Economic Review, 61(1), pp. 8–27.
Goreux, L. M. and Manne, A S. (Eds.), 1973. Multi-Level Planning: Case Studies in Mexico. North-Holland, Amsterdam.
Ginsburgh, V. and Waelbroeck, J., 1981. Activity Analysis and General Equilibrium Modelling. North-Holland, Amsterdam.
Hanemann, M.; Lichtenberg, E.; Zilberman, D.; Chapman, D.; Dixon, L.; Ellis, G.; and Hukkinen, J., 1987. Economic Implications of Proposed Water Quality Objectives for the San Joaquin River Basin. Report to the California State Water Resources Control Board.
Little, I. M. D. and Mirrlees, J. A., 1974. Project Appraisal and Planning for Developing Countries. Basic Books, New York, NY.
Pyatt, G. and Round, J. I. (Eds.), 1985. Social Accounting Matrices: A Basis for Planning. The World Bank, Washington, DC.
Varian, H. R., 1989. Measuring the Deadweight Costs of DUP and Rent Seeking Activities, Economics and Politics, 1(1), pp. 81–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Berck, P., Robinson, S., Goldman, G. (1991). The Use of Computable General Equilibrium Models to Assess Water Policies. In: Dinar, A., Zilberman, D. (eds) The Economics and Management of Water and Drainage in Agriculture. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4028-1_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4028-1_25
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6801-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-4028-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive