Abstract
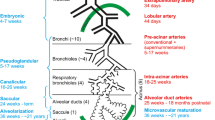
In the current literature (although not officially sanctioned by the third edition of Nomina Embryologica, 1989) lung development is generally divided into four successive, but partially overlapping, phases, known as the pseudo-glandular, canalicular, saccular, and alveolar stages. Based on recent structural observations, we have advocated the idea that alveolization does not represent the final step in lung development and have proposed the introduction into the nomenclature of a stage of microvascular maturation [1]. As will become evident in this chapter, the process of alveoli formation depends upon the presence of a specific morphology of the parenchymal1 capillaries, i.e., on the presence of a double capillary network within the intersaccular and interalveolar walls [2–5]. The adult mature interalveolar septa, however, are slender and contain only a single capillary system, allowing gas exchange on both of its faces. The transformation of the postalveolar to the adult pulmonary capillary system therefore requires a stage of microvascular maturation before pulmonary development may be considered to be complete.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeltner TB, Burri PH. The postnatal development and growth of the human lung. II. Morphology. Respir Physiol 67: 269–282, 1987.
Burri PH. The postnatal growth of the rat lung. III. Morphology. Anat Rec 180: 77–98, 1974.
Amy RWM, Bowes D, Burri PH, Haines J, Thurlbeck WM. Postnatal growth of the mouse lung. J Anat 124: 131–151, 1977.
Caduff JH, Fischer LC, Burri PH. Scanning electron microscopic study of the developing microvasculature in the postnatal rat lung. Anat Rec 216: 154–164, 1986.
Burri PH. Development and growth of the human lung. In: Fishman, AP, Fisher AB (ed.), Handbook of Physiology, Section 3: The Respiratory System, American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, pp 1–46, 1985.
Bucher U, Reid L. Development of the intrasegmental bronchial tree: The pattern of branching and development of cartilage at various stages of intra-uterine life. Thorax 16: 207–218, 1961.
Ten Have-Opbroek AAW. The development of the lung in mammals: An analysis of concepts and findings. Am J Anat 162: 201–219, 1981.
Boyden EA. Development and growth of the airways. In: Hodson WA (ed.), Lung Biology in Health and Disease. Development of the Lung. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 3–35, 1977.
Gil J, Reiss OK. Isolation and characterization of lamellar bodies and tubular myelin from rat lung homogenates. J Cell Biol 58: 152–171, 1973.
Burri PH. Fetal and postnatal development of the lung. Ann Rev Physiol 46: 617–628, 1984.
Dubreuil G, Lacoste A, Raymond R. Observations sur le développement du poumon humain. Bull Histol Tech Microsc 13: 235–245, 1936.
Davies G, Reid L. Growth of the alveoli and pulmonary arteries in childhood. Thorax 25: 669–681, 1970.
Langston C, Kida K, Reed M, Thurlbeck WM. Human lung growth in late gestation and in the neonate. Am Rev Respir Dis 129: 607–613, 1984.
Dunnill MS. Postnatal growth of the lung. Thorax 17: 329–333, 1962.
Emery JL, Wilcock PF. The postnatal development of the lung. Acta Anat 65: 10–29, 1966.
Zeltner TB, Caduff JH, Gehr P, Pfenninger, J, Burri PH. The postnatal development and growth of the human lung. I. Morphometry. Respir Physiol 67: 247–267, 1987.
Weibel ER. Morphometry of the Human Lung, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 1963.
Angus GE, Thurlbeck WM. Number of alveoli in the human lung. J Appl Physiol 32: 483–485, 1972.
Hansen JE, Ampaya EP. Lung morphometry: A fallacy in the use of the counting principle. J Physiol 37: 951–954, 1974.
Sterio DC. The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the dissector. J Microsc 134: 127–136, 1984.
Cruz-Orive LM. Arbitrary particles can be counted using a dissector of unknown thickness: the selector. J Microsc 145: 121–142, 1986.
Burri PH, Dbaly J, Weibel ER. The postnatal growth of the rat lung. I. Morphometry. Anat Rec 178: 711–730, 1974.
Gil J, Bachofen H, Gehr P, Weibel ER. Alveolar volume-surface area relation in air- and saline-filled lungs fixed by vascular perfusion. J Appl Physiol 47: 990–1001, 1979.
Weibel ER, Gil J. Structure-function relationships at the alveolar level. In: West JB (ed.), Bioengineering Aspects of the Lung, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–81, 1977.
Miller WS. The Lung, 2nd ed., Charles C Thomas, Springfield, IL, pp 74–88, 1947.
Weibel ER. The Pathway for Oxygen. Structure and Function in the Mammalian Respiratory System. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 1–425, 1984.
Folkman J. Angiogenesis: Initiation and control. Ann NY Acad Sci 401: 212–227, 1982.
Nicosia RF, Tchao R, Leighton J. Histotypic angiogenesis in vitro: Light microscopic, ultrastructural, and radio-autographic studies. In Vitro 18: 538–549, 1982.
Simpson JG, Fraser RA, Thompson WD. Angiogenese und Angiogenese-Faktoren. In: Messmer K, Hammersen F (eds.), Struktur und Funktion endothelialer Zellen. S. Karger, Basel, pp 80–96, 1983.
Tano Y, Chandler DB, Machemer R. Vascular casts of experimental retinal neovascularization. Am J Ophtalmol 92: 110–120, 1981.
Burger PC, Chandler DB, Klintworth GK. Scanning electron microscopy of vascular casts. J Electron Microsc Tech 1: 341–348, 1984.
Yoshida Y, Ikura F, Watabe K, Nagata T. Developmental microvascular architecture of the rat cerebellar cortex. Anat Embryol 171: 129–138, 1985.
Burri PH, Tarek MR. A novel mechanism of capillary growth in the rat pulmonary microcirculation. Anat Record, 228: 35–45, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Burri, P.H. (1992). Postnatal Development and Growth of the Pulmonary Microvasculature. In: Motta, P.M., Murakami, T., Fujita, H. (eds) Scanning Electron Microscopy of Vascular Casts: Methods and Applications. Electron Microscopy in Biology and Medicine, vol 10. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3488-4_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3488-4_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6546-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3488-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive