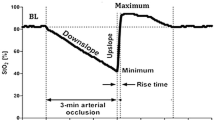
Abstract
Adequate assessment of tissue oxygen tension has been proven a reliable indicator of tissue blood perfusion1. Monitoring of tissue oxygen tension therefore offers a useful method in the clinical management of patients. Several devices for measurement of tissue oxygenation are available, however no single one is universally accepted. A method for measuring oxygen tension (PO2) inside tissue is tissue tonometry. This method uses a tonometer consisting of an implanted silastic tube through which an anoxic fluid comes in equilibrium with the surrounding tissue. The tonometer also can be used to insert PO2 electrodes. It has its limitations, it is difficult to use routinely, time consuming, sensitive to movement, and requires frequent recalibration. We evaluated a commercially available intravascular oxygen sensor which was inserted into microsurgically revascularized muscle transplants. This oxygen sensor overcomes numerous difficulties faced with tissue tonometry.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Gottrup, R. Firmin, N. Chang, et al., Continuous direct tissue oxygen tension measurement by a new method using an implantable silastic tonometer and oxygen polarography, Am. J. Sure. 146: 399 (1983).
K. Jonsson, J. A. Jensen, W. H. Goodson III, et al., Assessment of perfusion in postoperative patients using tissue oxygen measurements, Br. J. Surg. 74: 263 (1987).
P. W. Davies, The oxygen cathode, in: “Physical techniques in biological research. Vol IV, Special methods,” W. L. Nastuk, ed., Academic Press, New York, London (1962).
I. A. Silver, Polarography and its biological applications, Phys. Med. Biol. 12: 285 (1967).
A. J. Kleij van der,.in: “Skeletal muscle PO2 in shock,” Thesis, Nijmegen, The Netherlands (1984).
F. Gottrup, S. Gellett, L. Kirkegaard, et al., Effect of hemorrhage and resuscitation on subcutaneous, conjunctival, and transcutaneous oxygen tension in relation to hemodynamic variables, Crit. Care. Med. 17: 904 (1989).
T. K. Hunt, B.H. Zederfeldt, T. K. Goldstick et al., Tissue oxygen tensions during controlled hemorrhage, Sure. Forum 18: 3 (1967).
A. J. Kleij van der, J. Koning de, J. Beerthuizen, et al., H. P. Kimmich, Early detection of hemorrhagic hypovolemia by muscle oxygen pressure assessment: Preliminary report, Surgery 93: 518 (1983).
J. L. Mahoney, F. R. Lista, Variations in flap blood flow and tissue PO2: a new technique for monitoring flap viability, Ann. Plast. Sure. 20: 43 (1988).
S. O. P. Hofer, E. J. F. Timmenga, R. Christiano, et al., An intravascular oxygen tension monitoring device used in myocutaneous transplants (submitted, 1991 ).
P. J. Sheffield, Tissue oxygen measurements, In: “Problem wounds: The role of oxygen,” J. C. Davis, T. K. Hunt, eds., Elsevier, New York, (1988).
T. R. S. Harward, J. Volny, F. Goldbranson, et al., Oxygen inhalationinduced transcutaneous PO2 changes as a predictor of amputation level, J. Vasc. Sure. 2: 220 (1985).
J. M. Rabkin, T. K. Hunt, Local heat increases blood flow and oxygen tensions in wounds, Arch. Surg. 122: 221 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hofer, S.O.P., van der Kleij, A.J., Bos, K.E. (1992). Tissue Oxygenation Measurement: A Directly Applied Clark-Type Electrode in Muscle Tissue. In: Erdmann, W., Bruley, D.F. (eds) Oxygen Transport to Tissue XIV. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 317. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_95
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_95
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6516-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3428-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive